Epithelial,Connective, Muscle and Nervous Tissues Chapter 5 in your textbook.
Animal Anatomy and Physiology Cells specialized for a function = TISSUES 4 types of tissues...
-
Upload
colleen-morrison -
Category
Documents
-
view
212 -
download
0
Transcript of Animal Anatomy and Physiology Cells specialized for a function = TISSUES 4 types of tissues...

Animal Anatomy and Physiology
Cells specialized for a function = TISSUES
4 types of tissues
Epithelial = lining
Connective = connect organs, tissues together
Nervous tissue = conduct nerve impulses from one part of organism to another
Muscular = movement
Animal structures and their functions
Atom molecule cell tissue organ system organism population community ecosystem biosphere

Epithelial Tissues
Epithelial tissue
Covers outside of body, all organs and all cavities
Basement membrane attaches bottom epithelial to ECM
Simple epi = single layer of cellsStratified epi = multiple layers
May be cuboidal (box shaped) or columnar (column shaped) or squamous (flat)
May secrete mucous (for protection), or other chemicalsMay have ciliaMay absorb chemicals

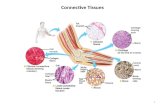
Connective tissue
Population of cells in extracellular matrix
Connect/bind tissues/organs together
Matrix = fibers in ground substanceFibers = proteins = collagen = most abundant protein in animals
elastin = long, resist stretching reticular = thin, branched collagen
Some Cells = fibroblasts = form fibers macrophages = engulf pathogens adipose = store fat osteoblasts = form bone Blood cells = red, white, platelets
Loose connective (adipose) OR dense (tendons, ligaments)

Nervous and Muscle tissueNervous tissue consists of neurons and support cells
Specialized to transmit impulses to communicate fromone portion of body to another
Muscle tissue = skeletal muscle = voluntary movement smooth muscle = involuntary movement
cardiac muscle = heart only
Actin and myosin (proteins) ‘slide’ across each other to cause contraction which causes movement

Bioenergentics = exchange of energy between an organism and its environment
Heterotrophs obtain energy from food
Food broken down by enzymatic hydrolysisEnergy obtained via cellular respiration and glycolysis (ATP) Used to do work = 60%
40% energy lost to environment as heat
Total amount of energy used / time = metabolic rate
Energy measured in Calories (1 C = 1000 c)
Measured by : temp change, O2 consumption
All animals with range of metabolic rate from restingpeak activity
No stress, resting, empty stomach = BMR = endotherm
= SMR = ectotherm

Body plans and energy exchangeLarger use less, smaller use more
Posture effects energy usedAbility to carry load of body requires work
Energy/materials exchange with environment
Small organisms exchange via diffusion directly with environment Larger organisms must
Maintain internal environment with cells bathed in fluidInternal environment bathing cells of vertebrates
= interstitial fluid
Interstitial fluid homeostasis maintained by exchanging nutrients, gases, waste. etc. with blood
Negative feedback Positive feedback