and Miles Cottrell By: Quinn Barret, Joe Delgado, Laura...
Transcript of and Miles Cottrell By: Quinn Barret, Joe Delgado, Laura...

Parts of a SolutionBy: Quinn Barret, Joe Delgado, Laura Langdale, Shivank Shekhar,
and Miles Cottrell

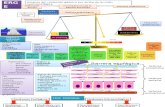
A solution is a homogenous mixture of two or more substances that exist together in a single phase.
Solution

A solute is a component of a solution that is dissolved in the solvent. A solvent is the component into which the solute is dissolved and is usually present in a greater capacity. The solute and solvent are what makes the solution. An example of solvent is water, and an example of solute is sugar.
Solute and Solvent

When the solution is saturated, the solvent has dissolved the maximum amount of solute that it can at the given temperature.
Saturation

Colloids A colloid is a solution microscopically dispersed throughout another substance. Colloids appear like solutions, but the particles are suspended in a solution, unlike a solution which fully dissolve. Colloids are generally considered as heterogeneous mixtures, but can also be a homogenous mixture as well. One example of a colloid is milk.

Another type of solution is is a suspension. Suspensions usually have particles the size of 1000+nm. Suspensions aren’t transparent and the particles can be separated by filters. An example of a suspension is muddy water, paint, and some medicines.
Suspensions

Relevance to the Real WorldWhen it is possible to dissolve solute in a solvent, the solution is said to be unsaturated. If tea is hot, it is easier to introduce sugar to it, but when the temperature is low, sugar will not dissolve as easily. With tea and many other substances, higher temperatures mean that a greater amount of solute can be added before the solution is fully saturated.Not all substances respond to rises in temperature in the manner described, however. As a rule, gases (with the exception of helium) are more soluble at lower temperatures than at higher ones.

Investigative Questions
Is it possible to make a solid solution?
Can any element be mixed into a solution?
Does an metal alloy count as a solution?