Ancient Egypt by Charles & Jetson
-
Upload
ms-wilson -
Category
Technology
-
view
111 -
download
3
description
Transcript of Ancient Egypt by Charles & Jetson


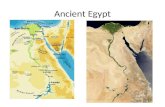
Map Of Ancient EgyptAncient Egypt was considered one of
the longest civilization in Africa. It was located along the middle to lower reaches of the Nile River. The kingdom reached from the Nile Delta in the north, as far as the south of Jebel Barkal at the fourth Cataract.
Ancient Egypt lasted over 3000 years because they were surrounded by many natural barriers that includes the eastern and western deserts. The east and western deserts were very effective because if you try to get to Egypt with a big army you would get dehydrated since it’s a very wide desert. The other two barriers are the Mediterranean Sea and the cataracts on the south.
Egyptian Map w/ Major cities
Cities Egyptian Empire
KEY
Mediterranean Sea
RedSea

Ancient Egyptian Time Frame
Pre 3100 BC Predynastic Period •Area around Nile settled
3200-3000 BC Protodynastic Period •Thinis takes over Naqada and Nekhen•Unified Egypt
2950-2575 BC Early Dynasty Period (1st and 2nd)
•Memphis becomes the capital
2575-2150 BC Old Kingdom (3rd-6th dynasty)
•Art of Embalming started•Pyramid of Djoser is build
2125-1975 BC 1st intermediate period (7th-11th dynasty)
•Unification of Egypt fell apart•Weather changes stopped the flooding of the Nile
1975-1640 BC Middle Kingdom(12th and 13th dynasty)
•2055 BC Mentuhotep|| reunited Egypt•1979 BC Campaign to Nubian began
1630-1520 BC 2nd intermediate period(14th-17th dynasty)
•Egypt was not unified once again at the start of 14 th dynasty•17th dynasty reunite Egypt
1539-1075 BC New kingdom(18th-20th dynasty)
•First female pharaoh, Hatshepsut•Reign of Akhenaten, built new capital “Akhenaten”
1075-715 BC 3rd intermediate period(21st-25th dynasty
•Egypt Split up once again into two areas, upper and lower
715-332 BC Late Period •Egypt Conquered by Persians•404 BC Independent again
332 BC- 395 AD Roman Period •Alexander the Great invades Egypt and eventually declared as pharaoh•Alexandria is built
Present Present •Egypt conquered by Arab forces, becomes Islamic after 300 years of Christianity.

BackgroundThe Egyptians lived for many centuries around the fertile banks along its side its banks.
Flooding in the Nile Enriched the soil and is brought to good harvest and wealth to the land, which is why they lasted for a long time. Since Egypt was a warm place the Egyptian homes were built in mud bricks.
The Egyptians did not have some food they want, so they grew some of their food and trade it in at the market for a different food or some goods. Most of the Ancient Egyptian were
farmers, traders, scribes and craftsmen but a small group of people were nobles. Altogether these different groups of people makes the Egyptian population. The ancient
Egyptian are know for the things they invented such as the pyramids in Giza, they are known for the mummies, the papyrus used for writing and drawings, the
pharaohs such as King Omatep and King Tut, Black ink, Paper and an organized labour. They were also know for their written words which is the hieroglyphic.
Scribe
Egyptian Houses
Egyptian getting water

Social StructureThe very top of Ancient Egyptian social is the Pharaoh since he controls basically everything, the Army, the Politics etc. The second highest lies the nobles since every noble was related to the Pharaoh, there were also the priests and the pharaoh’s trusted man which is the Viziers. The third highest of the Ancient Egyptian population are the traders, shopkeepers, scribes and artisans. The scribes were the only Egyptians who knew how to read and write, standing out from the surrounding illiteracy by their command of the secret skills of
reading and writing. The Fourth least important of the Egyptian social structures were the farmers herders and workers. At the bottom of all the different classes of people in ancient Egypt are the slaves and unskilled workers. They represents a great percent of the Egyptian population.They support all the classes above them which is why they are at the base of the Social structure
Social Pyramid

HousingThe houses in ancient Egypt were made out of Mud bricks from annual floods from the Nile
River. The brick makers would place mud into wooden molds and let them bake and harden in the sun. After that the bricks were stacked to be used for building. The wealthy people made their homes double-thick wall to increase the security of the house, but the poor people are only able to pay only one brick thick.
The average of Egyptian homes had four rooms, a central room with smaller rooms joined to it. A family spent most of their time in the central room and used it for sleeping quarters of the night. In the house from the central room I s a kitchen and another room that is used for storage or as an extra bedroom and off the street was an entry
room, that led into the central room.
A nobleman’s house had a central
room in his house. Inside the
house there were more rooms surrounding the central room,
the furniture was also much more complex. Flooring was made
of mud tiles or was covered with plaster-like material. Wood for
building was rare in Ancient Egypt because the wood had to be
imported since it was so hot in Egypt the trees did not produce
good boards. Wood was used to support doorways, steps and
ceilings. Most of Egyptian kids lives with their father and mother
in a family, but usually they have brothers and sisters. Egyptian
families don’t often have their gramps and grams living with them
since are already dead by the time you have kids.
Egyptian house plan
Nobles house

How the wealthy lived?The wealthy and the nobles lived in large houses, unlike the lower-classes
they often have slaves to take care of their sons and daughters, so
they could attend to their daily needs. Court officials and nobles
helped the pharaoh rule the country and in exchange the pharaoh
would often give them rewards with gift of land or money if they had
done some sort of achievement. If you are wealthy you are send to
school, so some day you can either become a scribe or a priest. The
wealthy people are usually well-known, they live in a lifestyle with good wine, high fashion Egyptians and they often go to a lot of
parties with other rich or nobles . Basically the wealthy people had finer
and attractive things such as furniture, jewellery, houses and clothing. The wealthy people had better tombs for their dead ones, since they have a lot of money the rich often buy stuff from different places in Egypt. Being rich is something you would want in ancient Egypt.
Nobles house
Egyptian Amulet

FoodSince Egypt was very dry and warm, the ancient Egyptians relied on the Nile River to water
their crops. The Egyptians were only able to grow certain kinds of food, they mostly grew wheat and barley. The wheat and barley were turn into
different types of food such as wheat getting turned into bread and into soup and porridge, while they turn barley into beer by adding hops. The beer was put in an Egyptian grave so they would have beer in the afterlife, that is if they pass the test.
The Egyptians also ate meat because they could go to a butcher shop and buy meat, just as we do today. Meats were stored outside in the courtyard because it rarely rains in Ancient Egypt. Although the Egyptians ate meat they would not eat pigs
(bacon, ham, pork, salami) just like the
Jewish people in the Eastern Mediterranean because they thought
pigs carries leprosy. They only ate beef, mutton, duck and goose.
For desserts, Egyptians liked to eat dates. Dates were also put into
a persons grave so they could eat them in the afterlife, the Egyptians also grew water melons, and other kinds of melons
Egyptian Beer Jars
Egyptian Dates
Egyptian Butcher Shop

Family LifeIn ancient Egypt they highly valued family life. They treasured their children and consider
them a blessing. In lower-class families the mother would take care of the kids while the father goes for work, but the wealthy and the nobles had slaves and servants to help them take care of their children. If you’re a father you are responsible for the economic well-being of your family while upper-class man become scribes or priest. The lower-class men were farmers, hunters and craftsmen. Women supervise the household, the servants(if you’re rich or is a noble) and her children while upper-class women
priestesses or musicians.
Children stayed home until they reached their
adulthood. Most of the time Egyptian kids
spent their time preparing for adult hood. If you’re a kid you usually get taken to be an apprentice by your father. Some privilegedkids are able to participate in school to become a scribe or a military official.
Gender Upper-class
Lower-class
Male Scribe or priest
Farmers, hunters,
Female Musician, Priestess
Anyone female can become musician and Priestess

MarriageMarriage in Ancient Egyptian was considered as a sacred bond. Families runs smoothly since
it is broken down into different roles to different people. A father would work all day as a scribe, farmer, a hunter or as a craftsman for his family, while the women would take care the household. Taking care of the household involves Cooking, cleaning and watching the children. A bride could be from 14-15 years old with a husband of 17-20 years old or more if he was divorced or is a widower. In order to get married there must a be a parents permission, especially in the upper-classes.
In Ancient Egypt divorce was allowed only if you hated your wife/husband, your wife betrayed you on some sort or she was unable to
have kids. When these circumstances are met,
the wife could get returned to her
parents. When a divorce is
granted, she gains the custody of
her children along with her
dowries if there was one. Dowries
did not appeared after the
Romans came to Ancient Egypt there, the Egyptians were
influence by the Romans.Egyptian Necklace
Egyptian Man and Wife

ChildbirthChildbirth was important in Ancient civilization and Ancient Egypt. There
were two reasons why having a family was considered so necessary Ancient Egypt. One reason was that Egyptians relied on their children to take care of them in their old. While most people died of injury or sickness long before they had a chance to grow old, many did live long enough to have to rely on their sons or daughters to care for them. Without at least one son to assist them the olds were in serious trouble since they were not able to walk, cook and help themselves if there’re in trouble. The second reason was that all Ancient Civilizations needed to increase their population so that meant more workers. More workers meant greater wealth and a better chance of repelling invaders from different neighbors. In ancient Egypt words such as midwife, obstetrician or gynecologist because these words did not exist, even though the words did not exist it doesn’t mean there isn't one. Most Egyptian Women labored and delivered their babies on the cool roof on their houses or in arbor or in confinement for the nobles. Since delivering a baby is dangerous the midwife would pray to the gods and goddesses for help and protection of the child and the mother.

ChildhoodIn ancient Egypt, Children were the heart of the family. If a couple could not have a child
they would adopt a child. In Ancient Egypt children were thought to be kind and honest, to respect their parents, to help with family business such like watching over their store, they were thought to take care the elder members of their family. In Ancient Egypt it was important for children to be caring because they believe in “ma’at” –order and justice. The children spent a lifetime trying to be fair all the time. The children did this because the Egyptians believed that in order to reach the after their heart must be weight against a feather, and if the heart is lighter they would go to the afterlife but if not they are fed to monsters.
Young boys learned trading or craft from their father while young girls worked and is trained at home with their mother. Young boys had more privilege than girls because women are expected to raise the children and take care of household duties. Young boys were able to go to school while girls are home schooled. If their parents died, the son would inherit the land, while daughters inherit the household goods such as furniture and jewellery. The ancient Egyptians treasured their children and regarded them as a great blessing which is why they treated them like their little pharaohs and little queens and expected them to be kind, caring, truthful, and respectful.
Egyptian Family

Childhood Difference Between Canada and Ancient Egypt
The childhood in Ancient Egypt is similar and different compared to the childhood in Canada. First of all, the children in Ancient Egypt are never given any voice. This means that they didn’t have any right to say. They always had to do what their leader or parents told them to do. In Canada, every children has some rights. Children have a right to say and they can also argue, too. A similarity is that the job of parents were to educate their children like it is in Canada. However, only a small amount is known how girls were treated. In Ancient Egypt, boys were thought to be better than girls. TheAncient Egyptians thought that boys needed a firm hand toguide them. In Canada, boys and girls are treated equally.They are treated equally when they are young and they’retreated equally when they’re old, too. Both boys and girlsreceive education. Another thing is that in Ancient Egypt,children were cherished for their role of protecting their parents. In Canada, children are cherished because they’re eventually going to grow up and become the adults of the future. So, that’s why there are both many differences and similarities between Canada and Ancient Egypt.

Education The children in Ancient Egypt stayed at their homes
with their mothers until they reached the age of four. Before they reached the age 4, they had a great respect for their mothers. After they reached the age 4, only boys’ and some girls’ education were taken over by their fathers. Since trading was the most important skill in Ancient Egypt, the sons followed the same way that their fathers once practiced. At this time some boys were put in just village schools and some others were put in schools just for a specific career. Schools taught writing, reading, math, and also sports. When they reached the age of 14, sons of farmers joined their father’s job. The other boys who were the sonsof fathers who had high level jobs, studied more in templeor government related schools. Although the boys weretreated like that, the girls weren’t treated equally as boys.Most of the girls were trained by their mothers how tobecome a good wife. However, daughters of rich andrespected nobles received education in schools.

ReligionThe Ancient Egyptian religion was passed down for 3,000 years until
Christianity took over. The Ancient Egyptian religion was worshipped with sacrifices and prayers. The god for the Ancient Egyptians changed frequently during different periods in the Egyptian history. Some of the famous gods are Anubis, the God of Death, Ra, the Sun God, and God Osiris. Also, the myths that were related to those gods changed every time. Because of that, the Egyptians don’t have any myths from the olden times. Although they didn’t have a clear mythology, they had many complex beliefs.
One famous complex belief is the one about the afterlife. Ancient Egyptians thought that when people died, they had another life called the afterlife. Because they believed in this “afterlife,” they preserved people’s bodies. They wrapped the dead bodies in linen, then they put them in stone coffins, and finally they put the bodies inside pyramids with other jewelleries in it, so that they can use it in their “afterlives.”
Anubis Ra Osiris

Anubis, The God of Death
Anubis is the God of Death and is also known as the God of Mummification. Anubis means a jackal-headed god in Greek. He is one of the famous gods in Ancient Egypt because he is the God of Mummification. Anubis is known as half human and half jackal. He was believed to protect the journey to the afterlife, and his duty was also to guide the souls of the death to the underworld. Because he was respected so much and was believed to be very powerful, whenever there was a mummification, the head embalmer always wore a jackal mask for good luck. There are lots of myths about who were Anubis’s parents. Some myths say that Nephthys gave birth to him, and some myths say that he was the son of Ra, the Sun God. However, after he took control for a long time, myths say that Osiris took over the job of being the God of Death.

Clothing Since the environment of Ancient
Egypt was very hot, wore thin and very light clothes or sometimes no clothes at all. To make these clothes so light, most of the clothes were made out of linen. Linen was made out of flax, which was a plant that had very tiny leaves, blue flowers, and very long stem. Using linen, workers made longtransparent robes for both men and women. Whether theywere poor or rich, they all wore jewellery. Although, wealthypeople wore gold and expensive jewellery, which showed that they were wealthy. Also, most Ancient Egyptians walked barefooted. They didn’t cover their heads either. An interesting fact is that they had a replacement for sunscreen called kohl, which was to help keep the glare down of the sun. It tells clearly that the Ancient Egyptians made their own clothes from what their environment provided them.

Art and MusicThe art of Ancient Egypt is from 5000 B.C. to 300 A.D. It includes
paintings, sculptures, crafts, and architecture done by the civilization in the lower Nile Valley. The Ancient Egyptians’ art were about the things they were influenced. They also made art for kings, queens, the dead, and gods. Pictures about their religion were frequently drawn. There were also different kinds of art forms. One interesting art form was relief art. Relief art meant pictures that were carved into layers. Its purpose was to give a raised look. They were often made in soft limestone. Another piece of art was their language. It was called hieroglyphics. It was their language in writing. Even though it was their language, they still counted it for their art. It is famousfor its unique styles.
Although there were music in Ancient Egypt, the evidence for it only starts after 3100 B.C.E. Music was an important part of worshipping in Ancient Egypt. There were also gods related with music, such as Hathor and Bes. One instrument that they played was harps.

Festivals There were several festivals in Ancient
Egypt. One of these festivals was called the Beautiful Festival of the Valley. This festival was celebrated once a year in Thebes starting from the Middle Kingdom period. This festival was held originally in remembrance of the dead. Another festival that was famous was the Min Festival. This ceremony was held to celebrate thecontinued rule of a pharaoh. This festival was also celebrated to worship the God Min. The festival was started by the king himself. The queen, royal family, and the court came out with the king. The king, himself, entered the sanctuary of God Min and brought goods and offerings.
Another festival that was held in Ancient Egypt was the Opet Festival. This festival was celebrated in Thebes during the New Kingdomperiod. In this festival, the statues of the Theban Triad, wasescorted to the temple of Luxor to relive their marriage.
Also, a festival called the Sed Festival was celebratedin Ancient Egypt. The Sed Festival is one of the mostimportant celebration because it was celebrated for thecontinued rule of a pharaoh just like the Min Festival.

MilitaryThe Ancient Egyptian army was divided into an
army and a navy. They were divided in these two teamsbecause the West Delta of the Nile was threatened bydesert raiders and the East Delta of the Nile wasthreatened by the invaders from Asia. Because Egyptdidn’t know horses, the Asians were much stronger sincethey had bronze strong weapons and horses. So, theAncient Egyptians always had to keep an eye aroundeverywhere. Eventually, the Ancient Egyptian armiesbuilt fortresses on the most attackable spaces, so thatthey didn’t need to always be frightened of where their enemies will come out from. Also, the Ancient Egypt was unified under one government. The main problem of the military was keeping enemies out. This was a very hard problem because everywhere around Ancient Egypt was the perfect spot to attack. As a solution, the Ancient Egyptian army built fortresses all around, so that it would be easier for them to block their enemies.

LawIn Ancient Egypt, the court systems were very unfair. Noble men and
rich citizens weren’t dealt harshly. Also, judges and tax collectors used their powers to control other people and for their own goods. Also, in Ancient Egypt rulers called pharaohs made the rules. The pharaohs made many strict rules and harsh punishments so that the citizens will stay in control. In Ancient Egypt, it was a huge shame for the familyif a family member was a criminal and was harshly punished. One crime is 100 hits with a stick. If it was a really bad crime 5 more bleeding cuts would be added in the punishment. Also, if it was the worst crime ever, they would have to die in such painful ways like drowning, executing, and burning on fire. The people who catches these criminals are officials who are like police nowadays. They would know if a person is an official because they wear golden Ma.

Ancient Egypt Ancient Egypt was an ancient
civilization that was in North Africa. Egypt is at the exact spot where Ancient Egypt used to be. The civilization started around 3150 B.C. and ended at 31 B.C. when the Romans took over. Ancient Egypt isfamous for varieties of things, such as pyramids, sphinx, mummies, and papyrus. One thing that Ancient Egypt is famous for is the belief about the afterlife. Ancient Egyptians thought that when a person died, they had another life called the afterlife. They thought that Anubis, the God of Death, led dead souls to the underworld. So, they made up the process of preparing for the afterlife called mummification. They would wrap up dead bodies with linen and then put them in pyramids. Ancient Egypt was a very strict civilization. They had harsh rules and also punishments. They really trusted and believed in their gods. A similarity between Canada and Ancient Egypt is that we both have governments. They make up the rules, and there are also courts to argue their cases. Another thing is that they had police officers that were called officials. Ancient Egypt was a very smart civilization.

Text BibliographyBackground Text Class lessons of Ancient Egypt Egyptian Life. N.p., n.d. Web. 4 June 2010.
http://www.ancientegypt.co.uk/life/home.html
Housing Rymer, Eric. Housing In Ancient Egypt. N.p., n.d. Web. 4 June 2010.
<http://historylink101.net/egypt_1/a-housing.htm>.
Child Hood Egypt:Daily Life. N.p., n.d. Web. 4 June 2010.
<http://www2.sptimes.com/Egypt/EgyptCredit.4.2.html>.
Family Life Life in Anicent Egypt. N.p., n.d. Web. 4 June 2010.
<http://www.carnegiemnh.org/exhibitions/egypt/guide.htm>. Egypt:Daily Life. N.p., n.d. Web. 4 June 2010.
<http://www2.sptimes.com/Egypt/EgyptCredit.4.2.html>.

Text Bibliography 2Marriage Eternal Egypt. N.p., n.d. Web. 4 June 2010.
<http://www.eternalegypt.org/EternalEgyptWebsiteWeb/HomeServlet?ee_website_action_key=action.display.module&story_id=&language_id=1&module_id=175&ee_messages=0001.flashrequired.text>.
Marriage in Ancient Egypt. N.p., n.d. Web. 4 June 2010. <http://www.kingtutshop.com/freeinfo/Marrage-in-Ancient-Egypt.htm>.
Map Ancient Egypt: The Ancient Egyptian World. N.p., n.d. Web. 4 June 2010.
<http://www.theancientweb.com/explore/content.aspx?content_id=9>.
How the Wealthy Live Life in Anicent Egypt. N.p., n.d. Web. 4 June 2010.
<http://www.carnegiemnh.org/exhibitions/egypt/guide.htm>. Rymer, Eric. Housing In Ancient Egypt. N.p., n.d. Web. 4 June 2010.
<http://historylink101.net/egypt_1/a-housing.htm>.

Text Bibliography 3 Map Class Knowledge Ancient Egypt Timeline. N.p., n.d. Web. 4 June 2010. <http://www.ancient-egypt-
online.com/ancient-egypt-timeline.html>.
Childbirth PREGNANCY AND CHILDBIRTH . N.p., n.d. Web. 4 June 2010.
<http://www.womenintheancientworld.com/pregnancy%20and%20childbirth.htm>.
Ancient Egyptian Midwifery and Childbirth. N.p., n.d. Web. 4 June 2010. <http://www.mnsu.edu/emuseum/prehistory/egypt/dailylife/midwifery.htm>.
Books Neering, Rosemary, and Peter Grant. Other Places, Other Times. Toronto,
Ontario: A Division of Canada Publishing Corporation, 1986 Toutant, Arnold, and Susan Doyle. Ancient Worlds. Canada: Oxford
University Press, 2000

Information Bibliography 4 Ancient Egyptian Religion . Wikipedia, n.d. Web. 31 May 2010.
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ancient_Egyptian_religion Childhood of Ancient Egypt . Reshafim, n.d. Web. 31 May 2010.
http://www.reshafim.org.il/ad/egypt/people/childhood.htm Ancient Egypt Education . Historylink, n.d. Web. 31 May 2010.
http://historylink101.net/egypt_1/a-education.htm Anubis . Wikipedia, n.d. Web. 31 May 2010.
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Anubis Anubis . Touregypt, n.d. Web. 31 May 2010.
http://www.touregypt.net/anubis.htm Ancient Egyption Clothing. Jesse.: Sara., Courtney. Web. 4 June 2010.
<http://www.islandnet.com/~kpotter/egypt/cloth.htm> Ancient Egyptian Clothing .Kidipede, n.d. Web. 4 June 2010.
http://www.historyforkids.org/learn/egypt/clothing/index.htm Art of Ancient Egypt . Wikipedia, n.d. Web. 31 May 2010.
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Art_of_ancient_Egypt

Information Bibliography 5 The Art of Ancient Egypt. Nesima. Web. 4 June 2010.
http://www.kyrene.org/schools/brisas/sunda/arthistory/egypt.htm Music in Ancient Egypt. Umich, n.d. Web. 4 June 2010.
http://www.umich.edu/~kelseydb/Exhibits/MIRE/Introduction/AncientEgypt/AncientEgypt.html
Festivals in Ancient Egypt . Wikipedia, n.d. Web. 31 May 2010. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Category:Festivals_in_Ancient_Egypt
Ancient Egyptian Military. King-tut, n.d. Web. 4 June 2010. http://www.king-tut.org.uk/ancient-egyptians/ancient-egyptian-military.htm
Law and Order. Reshafim, n.d. Web. 4 June 2010. http://www.reshafim.org.il/ad/egypt/law_and_order/index.html
Laws in Ancient Egypt. Riverschool.: Hannah. Web. 4 June 2010. http://www.riverschool.org/students/work/culture.e.laws.htm
Ancient Egypt . Wikipedia, n.d. Web. 31 May 2010. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ancient_Egypt

Picture Bibliography
Title slide Giza pyramid from www.flickr.com/photos/brunogirin/20151400/ by Bruno Girin
Girin, Bruno. Giza Pyramid. Web. 4 June 2010. <www.flickr.com/photos/brunogirin/20151400/ >. King Tut from thewhizzer.blogspot.com/ by buck1936
buck1963. King Tut. Web. 4 June 2010. <thewhizzer.blogspot.com/>. Egyptian Sphinx from www.gnosislondon.com/index.php?pr=Esoteric_Art
Web. 4 June 2010. <www.gnosislondon.com/index.php?pr=Esoteric_Art >. Egyptian Warriors From womenslens.blogspot.com/2008_03_01_archive.html by Aimee
Kligman
Kilgman, Aimee. Egyptian Warriors. Web. 7 June 2010. <womenslens.blogspot.com/2008_03_01_archive.html>.
Map of Ancient Egypt Map of Egypt from commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Map_Ancient_E...
Background Egyptian Fishing from sallyss6.posterous.com/ by sallyss6
Social Structure Social Structure from sites.google.com/.../Home/egypt by Mr. Crain

Picture Bibliography 2Housing Average Egyptian Housing plan from ancient-egypt-life.blogspot.com/ by Kamis Noble’s house from : unusualhistoricals.blogspot.com/2009_01_01_ar...by
Jean Adams
Food Beer from www.historyforkids.org/.../food/egyptfood.htm by Jane Shuter Butcher shop from www.historyforkids.org/.../food/egyptfood.htm by Jane Shuter Dates from www.historyforkids.org/.../food/egyptfood.htm by Jane Shuter
Child Hood Family and child from egypt.mrdonn.org/homes.html by mr.donn
Family Life Priest from www.teachnet.ie/.../third_task.htm Egyptian hunter from www.bizorigin.com/2007/do-entrepreneurs-have-add Egyptian farmer from www.bizorigin.com/2007/do-entrepreneurs-have-add Egyptian musician from commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:C%2BB-Music-F.. Egyptian priestess from karenswhimsy.com/ancient-egyptian-symbols.shtm by Kerens
Whimsy

Picture Bibliography 3Marriage Man and wife from www.mfa.org/collections/search_art.asp?recvie... Egyptian Necklace from commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Broad_collar_... By
http://www.flickr.com/photos/unforth

Picture Bibliography 4 http://kenoath.files.wordpress.com/2008/05/relief-anubis.jpg http://i246.photobucket.com/albums/gg90/SecretSunBlog/ra3.jpg http://www.pagefarm.net/wiki/images/1/15/Osiris3big.jpg http://www.maat.sofiatopia.org/inianchchnoem.jpg http://www.reshafim.org.il/ad/egypt/people/childhood.htm http://www.iw-
chameleon.co.uk/history/ancient_egypt/images/educate/scribe.jpg http://www.albyanschool.com/image/about_egypt_clip_image001_0004.jpg http://www.ihistory101.net/espanol/images/anubis.jpg http://fontes.lstc.edu/~rklein/Doc5/anubis_files/anubis4.jpg http://3.bp.blogspot.com/_q5KlmdfTujo/SHzZp6p9HTI/AAAAAAAAAY0/w8T
ngWleTCE/s400/Tut%2BAnubis%2BHathor.jpg http://www.cuesd.tehama.k12.ca.us/maywood/staff/hohenstein/images/egyp
t1.jpg

Picture Bibliography 5 http://ancientegyptmoberly.pbworks.com/f/fashion4.jpg http://aishasvisualjourney.files.wordpress.com/2009/10/sennefer-tombart-70
17141.jpg http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Harp_from_the_New_Kingdom.jpg http://www.only4ukids.com/festivals/thanksgiving/graphics/egypt.jpg http://www2.naples.k12.ny.us/6/egypt06/celebrations_files/image004.jpg http://www.dailygalaxy.com/photos/uncategorized/2008/05/28/
soldier5_2.jpg http://www.ancient-egypt.org/glossary/miscellaneous/
punt_tribute_bearers.jpg http://www.duhaime.org/Portals/duhaime/images/hieroglyphics.jpg http://listverse.files.wordpress.com/2007/11/image-3-tm.jpg http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Egypt.Giza.Sphinx.01.jpg http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Ac_papyrus.jpg http://static.howstuffworks.com/gif/willow/ancient-egypt-
history2..imagech004885_lr001785-p2010.gif