Anatomy Topography of the Eye
Transcript of Anatomy Topography of the Eye


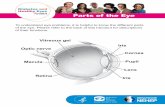
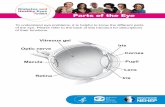
OutlineTopographic Precorneal TearfilmParts of the EYE:
CorneaScleraLimbusAnterior chamberTrabecular
meshworkUveal tract
Iris Ciliary Body ChoroidLensRetinaMaculaOra SerrataVitreous
Orbit and Adnexa

Topographic features of the globe
23-25 mm
3 mm
24 mm
16 mm

250 µL 60 µL
5-6 mL
3 chambers

3 concentric layers

Precorneal tearfilm

Importance: Lubricates the surface of the cornea and
conjunctiva (vital for normal corneal function)
Produce a smooth optical surface
Provide O2 and other nutrients
Contain immunoglobulins, lysozyme and lactoferrin

Cornea
• Main refractive element of the eye


Sclera


Limbus



Surgical Limbus divided into 2 equal zones;
Anterior bluish gray zone overlying clear cornea and extending from Bowman’s layer to Schwalbe’s line
Posterior white zone overlying the trabecular meshwork and extending from Schwalbe’s line to the scleral spur or iris root
*** Essential in cataract surgery/glaucoma-filtering procedure

Anterior Chamber


Trabecular meshwork
Trabeculocytes -have
contractile properties = influence outflow resistance
- have phagocytic properties
3 layers:
• uveal portion•Corneoscleral meshwork•Juxtacanalicular tissue (adjacent to Schlemm’s canal


GonioscopyShows the anatomical structures of a normal anterior chamber angle: ciliary body (A), scleral spur (B), trabecular meshwork (C), and Schwalbe’s line (D).


Uveal tract
Attachment to sclera:
Scleral spurExit points of vortex veinsOptic nerve

Iris



Dilator M. – contracts w/ sympathetic α1 adrenergic stimulation
- inhibited by cholinergic parasympathetic stimulation
- via ophthalmic div. of CN V
Sphincter M. – inhibited by sympathetic innervation, relax in darkness
- parasympathetic via CN III (3%), constrict

Ciliary Body

Epithelium & stroma: 2 parts:
Pars plana – avascular, from ora serrata to ciliary process
- safest surgical approach to the vitreous cavity
Pars plicata – richly vascularized, consists of ciliary processes

Layers:longitudinalRadialCircular
Change with ageInnervation:
parasympathetic CN III (97%), constrict

Choroid

3 layers of vessels:Choriocapillaries
(innermost)Small vessels (middle)Large vessels
(outermost)
From long and short posterior A. and anterior ciliary A.
Drains to vortex system

Stroma – melanocytes
Degree of pigmentation – depends on the No. of pigmented melanocytes
Considered in photocoagulation

Lens
3 mm
6.5 mm
Lacks innervation
Avascular
Nourishment from aqueous and vitreous

Ant. Capsule = thicker than Post capsule
Human lens, cell division continues throughout life

Distant focus zonule is tensed lens flattened
Accommodation ciliary contracts zonule forward & inward lens globular

Retina


INNER
OUTER
FXNS:• Vit A met’m•Maintenance of outer blood-retina barrier•Absorption of light•Heat exchange

Macula

1.5 mm



Ora Serrata
20 mm


Vitreous• route for metabolites
•Vol = 4 mL
•Gel-like , 99% H2O
•More fluid= inc. age