Anatomy and Physiology of Dogs and Cats Bones, Joints, Synovial Fluid.
-
Upload
amos-mcdowell -
Category
Documents
-
view
219 -
download
1
Transcript of Anatomy and Physiology of Dogs and Cats Bones, Joints, Synovial Fluid.

Anatomy and Physiology of Dogs and
CatsBones, Joints, Synovial
Fluid

Bones
• Cellular structures where the extracellular fluid environment of the cell is surrounded by a rigid, calcified frame

Function of the Skeleton
• Gives identifiable form to body
• Provides protection • Location of blood
formation• Mineral source• Movement• Accommodates loads
and stresses

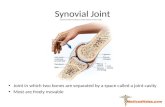
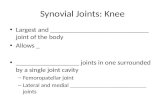
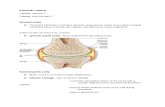
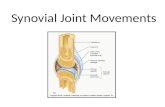
Joint
• Moveable union between two bones
• Enclosed by a joint capsule filled with synovial fluid
• Why SF?

Axial Skeleton
• Lie on long axis (midline) of body• Includes:– Skull– Vertebrae– Ribs– Sternum

Appendicular Skeleton
• Made up of bones of the front (pectoral) and hind (pelvic) limbs and their respective pectoral girdle (shoulder) and pelvic girdle (pelvis)

A & P of Long Bones
• Contains spongy (cancellous) and compact bone
• Spongy bone have trabeculae which are mineralized tissue
• Regions between trabeculae are filled with marrow

A & P of Long Bones
• Rigidity and strength of long bones is caused by the hardness of compact bone and the scaffolding arrangement of the trabeculae (parallel to the lines of maximum stress)

A & P of Long Bones
• The epiphysis refers to either extremity of a long bone and the diaphysis is the cylindrical shaft between the two epiphyses
• The metaphysis is the flared part of the bone at the ends of the diaphysis

A & P of Long Bones
• The diaphysis contains the marrow (medullary) cavity that is surrounded by compact bone– Bone marrow is the site
of blood production

A & P of Long Bones
• The epiphyses have spongy bone surrounded by compact bone
• The epiphyseal plate is composed of hyaline cartilage and represents the point of growth in a longitudinal direction
– In mature bones the cartilage has been replaced by bone

A & P of Long Bones
• The contact area of the bone that articulates with its neighboring bone at a moveable joint is covered with articular cartilage
• All other outer surfaces are covered with periosteum