Anatomy Abdomen
-
Upload
hassan-nor-boransing-mangorsi -
Category
Documents
-
view
57 -
download
5
description
Transcript of Anatomy Abdomen

Anatomy of the Abdomen, Pelvis & Retroperitoneal
Structures

Outline
AbdomenLayers, muscles and organs
Innervation of abdominal organsRetroperitoneum
Structures and innervationPelvic Organs and innervation

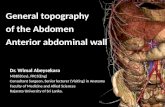
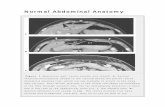
Abdomen

Surface Anatomy of AbdomenUmbilicus Linea alba = white line
Xiphoid process to pubic symphysisTendinous line
Inferior BoundariesIliac crestAnt. Sup. Iliac spineInguinal ligamentPubic crest
Superior BoundaryDiaphragm

Abdominal wall

Layers of abdominal wall
Fatty superficial layer - Camper’s fasciaMembranous deep layer - Scarpa’s fasciaDeep Fascial
External oblique muscleInternal oblique muscleTransverse abdominal muscle
Transversalis fasciaParietal Peritoneum

Muscles of Anterior Abdominal WallExternal Obliques
O: lower 8 ribs I: aponeurosis to linea albaFunction: Flex trunk, compress abd. wall (together)
Rotate trunk (separate sides)Internal Obliques
O: Lumbar fascia, iliac crest, inguinal ligamentI: Linea alba, pubic crest, last 3-4 ribs, costal marginFunction: Same as External obliques
Transversus AbdominisO:same as Internals, plus last 6 ribsI: Xiphoid process, costal cart. 5-7Function: Compress abdomen
Rectus AbdominisO: Pubic crest, pubic symphysis I: Xiphoid, cost cart 5-7Function: Flex, rotate trunk, compress abdomen, fix ribs

Peritoneum Extension of serous membrane in the abdomino-pelvic cavityMesentery: Double layer of peritoneum
Hold organs in placeStore fatRoute for vessels + nerves
Retroperitoneal: some organs behind peritoneum (eg) distal esophagus, duodenum, ascending + descending colon, rectum, pancreasPeritoneal: remain surrounded by peritoneal cavity (eg) liver, stomach, ileum + jejunum, +

DiaphragmTrefoil central tendon5 openings
CavalEsophagealAorticGaps for psoas m
Crus arise from lumar vertebraeInnervation
Phrenic nerve unilaterally plus associated pleura and peritoneumPeripheral - lower intercostal nerves

Inguinal Canal

Inguinal Hernias

Innervation of Abdominal Organs

Overview of Nerves of AbdomenDiaphragm
Parietal peritoneum of under surface of diaphragm supplied by phrenic nerve centrally and intercostal nerves peripherallyStimulation centrally refers to neck and shoulder (C3 - C5)Peripheral irritation refers to lower chest wall
Parietal PeritoneumSomatic nerves from spinal nerves
Visceral PeritoneumNerves from autonomics; sensitivey similar to viscera

Innervation of Viscera
Viscera normally not sensitive to painful stimuli applied to skin
Mid-esophagus to anal vergeBurn and crush not painfulStretch, over distension, traction are normally painfulSpasm, isometric conditions, ischemia and inflammation painful

Visceral Afferents and Efferents

Vagus Nerves
Parasympathetic preganglionic fibers and sensory fibers to viscera of abdomenExcept left half of transverse colon and descending colonSacral parasympatheticsCell bodies
Motor: dorsal motor nucleus of medullaSensory: inferior nodose ganglion

Abdominal Splanchnics
Lower thoracic splanchnics main source of presynaptic sympathetics to abdominal viscera
Greater: T5-T9Lesser: T10-T11Least: T12
Pierce crus of diaphragm to reach prevertebral ganglia

Abdominal Prevertebral GangliaCeliac Plexus
Largest prevertebral plexusComposed of celiac ganglia and fibersAnterior to crura of diaphragm and L1Anterior to abdominal aorta at level of celiac artery and root of superior mesenteric arteryPosterior to stomach, omental bursa, pancreas, portal vein and inferior vena cava
Organs innervated by fibers passing thu celiac plexusStomach, duodenum, jejunum, ileum, spleen, appendix, gallbladder and liver, kidneys, ureters, adrenals, ascending and transverse colon

Secondary Ganglia andPlexusesfrom Celiac Plexus
Subsidiary preverterbral gangliaCeliac gangliaSuperior mesenteric gangliaInferior mesenteric ganglia Aorticorenal gangliaSecondary plexuses
Phrenic, gastric, hepatic, splenic, renal, superior mesenteric, intermesenteric, aortic, etcInferior mesenteric plexus chiefly from aortic but also from lumbar sympathetics

Table of Splanchnic Nerves

Autonomic Fibers and GangliaKey9. Celiac trunk and ganglion10. Superior mesenteric artery and
ganglion13. Superior hypogastric plexus and
ganglion32. Lesser splanchnic nerve33. Lumbar splanchnic nerves34. Sacral splanchnic nerves35. Inferior hypogastric ganglion and
plexus37. Aorticorenal plexus and renal
artery38. Ganglion impar

Abdominal Organs

Esophagus, Stomach and Bowel
Distal esophagus (retroperitoneal)Nociception via greater and lesser splanchnics (T5-9) and vagus
Stomach and duodenumNociception via greater splanchnic nerves (T5-9) for stomach and T8-11 splanchnics for distal duodenum
Jejunum and ileumNociception via sympathetic afferents in splanchnic nerves to superior mesenteric plexus T8-12

Large intestine
Nociception to transverse colon via sympathetic afferents from T8-12 splanchnics to superior and inferior mesenteric plexusesDescending and sigmoid colon via superior hypogastric plexus and parasympathetic afferents to the pelvic plexus at S2-S4
RectumSuperior hypogastric plexus
Note that there are some nociceptive afferents with the vagus

Diagrams of Innervation of Colon

Liver and Biliary TreeLiver
Hepatic Plexus - largest derivative of celiac plexusBiliary Ducts
Nociception via sympathetic fibers and right splanchnic nerves from T6-10
Vagus nerve plays no role in pain transmissionInflammatory biliary disease stimulates afferent fibers of the parietal peritoneum causing somatic pain in the T6-9 distribution (RUQ)

RetroperitoneumRetroperitoneal organs
Duodenum and pancreasAscending and descending colonKidneys and uretersBladder and uterusGreat vesselsRectum

Pancreas
Nociception via splanchnic nerves T5-9 through celiac plexusVagal afferents do not mediate pancreatic pain

Kidneys and UretersKidneys
Lesser and least splanchnic nervesCeliac plexusAorticorenal plexus
AdrenalsGreater, lesser and least slanchnicsCeliac plexus
UretersNociceptive fibers with sympathetics in renal, aortic and superior and inferior hypogastric plexuses

Posterior Abdomen
Fascia removedUreter crosses common iliacVas deferens and inguinal canalLateral femoral cutaneous, ilioinguinaland genitofemoral n.Celiac and mesenteric arteries

Muscles of the Posterior Abdominal Wall
Psoas majorO: Lumbar vertebrae + T12
I: Lesser trochanter of femur via iliopsoas tendonFunction: Thigh flexion, trunk flexion, lateral flexion
Quadratus lumborumO: iliac crest, lumbar fascia I: trans. proc of upper lumbar vertebrae
Function: Flex vertebral column

Posterior Abdominal Wall

Somatic Nerves of Posterior Abdominal WallObturator (L2 - L4)
Medial border psoasFemoral (L2- L4)
Lateral border psoasLumbosacral trunk
L4, L5 over sacral alaS1-S4 sacrum
NervesIlioinguinal (L1)Iliohypogastric (L1)Genitofemoral (L1, L2)Lateral femoral cutaneous (L2, L3)

Pelvic Organs and Innervation

Pelvic Autonomics
Superior hypogastric plexus (presacral nerve)Contains no parasympathetics
Hypogastric nerveInferior hypogastric plexus
Contains parasympathetic fibers from the pelvic splanchnics
Ganglion impar

Pelvic InnervationHypogastric PlexusesPelvic Splanchnics not sympatheticDerive from ventral rami of spinal nerves (S2-S4)Convey presynapticparasymathetic fibers to inferior hypogastric(pelvic) plexus

Pelvic Autonomics

Innervation of the Bladder
SympatheticsT12, L1, L2
ParasympatheticsPelvic splanchnic nervesNervi erigentesS 2, 3, 4
Nociceptive afferentsSacral roots (S 2, 3, 4)Not sympathetics

Innervation of Uterus, Cervix and Ovaries
Uterovaginal plexus from superior and inferior hypogastric plexuses
Sympathetic, parasympathetic and somatic afferentFundus and body (intraperitoneal) - Inferior and superior hypogastric plexusesCervix (subperitoneal)
Inferior hypogastric plexus to pelvic (splanchnic) nerves (S2-S4) (most texts)Bonica: LUS and CX same as fundus
Ovaries - afferents with hypogastric plexuses (T10-11)

Innervation of the Vagina
Superior 3/4thsUterovaginal plexusPelvic plexus (sacral fibers)
Lower 1/4thPudendal nerve via sacral fibers
PerineumPudendal nerve

Innervation of Prostate, Testes and Scrotum
ProstateProstatic plexusInferior hypogastric plexus
Testicle (T10)Vas deferens (T10-L1) Epididymis (T11-12)Prostate (Prostatic plexus; similar to bladder)Scrotum
Ilioinguinal and genitofemoralPerineal nerve (branch of pudendal)

Rectum, Anus and PerineumSympathetics
Superior and inferior hypogastric plexusesParasympathetics
Pelvic splanchnic nervesNociceptive afferents
Pudendal nerve (somatic)Also with pelvic splanchnic nerves
AnusInferior rectal nerve via pudendal
Perineum by pudendal and branches

Pudendal NerveSupplies skin, organs and muscles of perineumDistribution similar in males and femalesPudendal nerve blockade
Medial to ishial tuberosityat sacrospinous ligamentTransvaginal
FunctionsMicturationDefecationErectionEjaculationParturition

Neural Blockade of Perineum

Neural Blockade for Childbirth

ReferencesBonica’s Management of Pain. 3rd Edition, Lippincott Williams and Wilkins, 2001Bonica’s Management of Pain. 2nd Edition, Lippincott Williams and Wilkins, 1990Moore and Dalley. Clinically Oriented Anatomy, 4th Edition. Lippincott Williams and Wilkins, 1999.Cousins and Bridenbaugh. Neural Blockade, 3rd Edition, 1998.Raj and Patt. Pain Medicine: A Comprehensive review, 2nd Edition. Mosby, 2003.