An Introduction to the Geography of Health: Exercises€¦ · Web view* Countries are grouped...
Transcript of An Introduction to the Geography of Health: Exercises€¦ · Web view* Countries are grouped...

Chapter 8: HealthcareGlobal Patterns in Healthcare
With a partner or in a small group, consider what we can learn from the figures and data tables below.
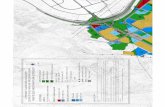
Figure 1: Per capita expenditure on healthcare by country, 2007
Data from: WHO. (2010f) WHO Global Health Observatory [Online]. Available: <http://apps.who.int/ghodata/>
1. What geographic patterns are apparent when we map healthcare spending?
From this map, we could hypothesize that healthcare spending is positively correlated with the affluence of a country. Use the table of healthcare expenditure by country below to investigate this hypothesis.
Anthamatten and Hazen (2011), An Introduction to the Geography of Health

Table 1: Healthcare Expenditure by Country
Total expenditure on health as % of GDP
(2003)
Government expenditure on health,
as % of total health expenditure (2003)
Private expenditure on health, as % of
total health expenditure (2003)
Low Income*Afghanistan 6.5 39.5 60.5Angola 2.8 84.2 15.8Bangladesh 3.4 31.3 68.7Colombia 7.6 84.1 15.9Haiti 7.5 38.1 61.9Solomon Islands 4.8 93.4 6.6Tajikistan 4.4 20.8 79.2Zambia 5.4 51.4 48.6
Middle Income*Armenia 6.0 20.2 79.8Brazil 7.6 45.3 54.7Costa Rica 7.3 78.8 21.2India 4.8 24.8 75.2Iraq 2.7 51.8 48.2Malaysia 3.8 58.2 41.8Mexico 6.2 46.4 53.6Thailand 3.3 61.6 38.4
High Income*Australia 9.5 67.5 32.5Canada 9.9 69.9 30.1France 10.1 76.3 23.7Japan 7.9 81.0 19.0New Zealand 8.1 78.3 21.7Portugal 9.6 69.7 30.3UK 8.0 85.7 14.3USA 15.2 44.6 55.4
* Countries are grouped according to the World Bank’s low- (under $995) middle- ($996 to $12,195) and high-income ($12,196 or more) classifications.
Source: WHO. 2006. Working Together for Health. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization, Annex Table 2. Available at: http://www.who.int/whr/2006/en/. Date Accessed: August 7, 2010.
Anthamatten and Hazen (2011), An Introduction to the Geography of Health

2. Does healthcare spending seem to correlate well with a country’s affluence?
3. What patterns appear in terms of the proportion of healthcare funded by the government compared with private sources?
4. Which countries do not fit the patterns that you noted? What might explain these anomalies?
Anthamatten and Hazen (2011), An Introduction to the Geography of Health

Table 2: Global Health Workforce
Total health workforce (per
1000 population)
Health service providers (% of total
health workforce)
Health management and support workers
(% of total health workforce)
Africa 2.3 83 17Eastern Mediterranean 4.0 75 25Southeast Asia 4.3 67 33Western Pacific 5.8 78 23Europe 18.9 69 31Americas 24.8 57 43World 9.3 67 33
Data extracted from: World Health Organization. Global Atlas of the Health Workforce. (http://www.who.int/globalatlas/default.asp).
5. Where might we hypothesize that there are health worker shortages from the data presented in Table 2?
6. Does the fact that the Americas has more health workers imply that we would find superior healthcare in this region compared with Europe? Why or why not?
7. How does the ratio of health service providers to health management and support workers differ between the Americas and Europe? How might this be significant?
Anthamatten and Hazen (2011), An Introduction to the Geography of Health

Figure 2: Per capita expenditure on health and under-five mortality
Data from: WHO. (2010) WHO Global Health Observatory [Online]. Available: http://apps.who.int/ghodata/
8. Examine this scatterplot graph. How would you describe the relationship between expenditure on health and under-five mortality? What factors might intervene in the relationship between health spending and child mortality to weaken it?
Anthamatten and Hazen (2011), An Introduction to the Geography of Health