Crandall ISD - Crandall High School - 2003 Texas School Survey of Drug and Alcohol Use
Altruism 8 June 2004. Evolutionary Perspective Inclusive Fitness/Kin Selection –Carnegie...
-
Upload
barnaby-fisher -
Category
Documents
-
view
212 -
download
0
Transcript of Altruism 8 June 2004. Evolutionary Perspective Inclusive Fitness/Kin Selection –Carnegie...

Altruism
8 June 2004

Evolutionary Perspective
• Inclusive Fitness/Kin Selection– Carnegie Foundation
– Burnstein, Crandall, & Kitayama (1994)
• Does our implicit understanding of helping match the evolutionary psychology model of altruism?

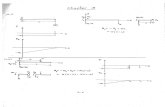
Helping and AltruismBurnstein, Crandall, & Kitayama, 1994
• Helping others is a direct function of recipients’ ability to enhance the inclusive fitness of the helpers
• Study: Imagine individuals asleep in different rooms of a rapidly burning building– You only have time to
rescue one of them• Ss circle the target they’re most
likely to help• Ss cross out the target they’re
least likely to help
Everyday situations
Life or death situations
0
1
2
3
4
0.5 0.25 0.125 0
Kinship
Ten
denc
y to
hel
p

More Burnstein et al., 1994:Tendency to help by Age of Target
1.0
1.5
2.0
2.5
3.0
> 1 yr. 10 yrs. 18 yrs. 45 yrs. 75 yrs.
Age of Target
Everyday situations
Life or death situations

Even More Burnstein et al., 1994:
Tendency to help under famine conditions.
1.0
1.5
2.0
2.5
> 1 yr. 10 yrs. 18 yrs. 45 yrs. 75 yrs.
Age of Target

More Evolution
• Reciprocal Altruism– Evolutionarily stable
strategies, or why “pure” altruism can’t exist
• Helping in big cities vs. small towns

Social Exchange Theory
• Cost-benefit or economic theory of helping: – help only if it will get you
more than you give
• Allen NY subway experiment– 3 Conditions
– DV: % subjects correcting Scary Muscle Guy Control Insult Threat
50
25

Empathy Altruism Theory
Batson• “Pure altruism” exists• Occurs when people help
because they empathize with the sufferer
• If no empathy, then helping = social exchange (not altruistic)

Negative State Relief Model
• No such thing as pure altruism
• We help others to make ourselves feel better– If we can make ourselves feel
better in a way that’s easier than helping, we won’t help
• Evidence?

Negative State Relief, cont’d
• Kids must learn that helping makes them feel good– Perry (1986)
– Cialdini & Kenrick (1976)

More Negative State ReliefSchaller & Cialdini, 1989
• One IV– Post-tape expectation:
news vs comedy vs “easy help”
• One DV – How many hours are
subjects willing to donate to Katie?
• Results?
hour
s
News Comedy Easy Help

Even More Negative State Relief:Effects of Guilt
• McMillen & Austin (1971)
– IV1: confed either gives away answers or not
• DV: % lying
– IV2: expter asks for help or not
• DV: minutes helping
• Regan (1972)– Field experiment
• IV: guilt vs. control
• DV: % helping

Negative States Don’t Always Lead to Helping
• Thompson et al. (1980)
– IV: Self- vs. other-focused grief
– DV: % giving anonymous help
0
20
40
60
80
100
self-focused other-focused

What about Positive States?
• Ibsen et al. (1976) Field study– IV: free stationary vs.
control
– DV: % willing to help
• Why do happy people help?– Prolongs good mood
• Good mood • Positive thoughts • Positive behaviors • Good mood • Etc.

What Kinds of Situations Increase or Decrease Helping?
• Location location location….
• Granet field experiment:– Helping in subway vs.
in airport
• 2 theories tested:– SES?
– Familiarity?

Having the Time to Help
• Darley & Batson (1973): Seminary students in a hurry…– IV’s: hurry vs. control
group; speech topic
– DV: helping
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
jobs good samaritan parable
hurry control

Where We Live• Levine
– Helping in 36 cities of different sizes
• Results:– Geography
– Population vs. population density
– SES

Who do we help?
Gender• Eagly & Crowley (1986)
meta-analysis– Short term help by
males vs. by females– Why?
Similarity Bias• Emswiller (1971) field
experiment

How to Increase Helping?
• Teach moral inclusion
• Model altruism– Sarason et al., 1991– Hearold, 1986
• Attribute helpful behavior to altruistic motives (Batson, 1978; 1979)