Aim: How to distinguish electrons in the excited state DO NOW: PREPARE FOR QUIZ. 10 MIN.
-
Upload
cynthia-henderson -
Category
Documents
-
view
217 -
download
0
Transcript of Aim: How to distinguish electrons in the excited state DO NOW: PREPARE FOR QUIZ. 10 MIN.
What gives gas-filled lights their colors?
An electric current passing through the gas in each glass tube makes the gas glow with its own characteristic color.
The Nature of LightLight is a part of the electromagnetic spectrum-radiant
energy composed of gamma rays, X-rays, ultraviolet light, visible light, etc.
The energy of the electromagnetic spectrum moves through space as waves
Nature of Light
Sunlight consists of light with a continuous range of wavelengths and frequencies. When sunlight passes through a prism,
the different frequencies separate into a spectrum of colors.
In the visible spectrum, red light has the longest wavelength and the lowest frequency.
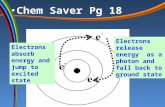
Atomic Spectra When atoms absorb energy, their electrons move to higher
energy levels. These electrons lose energy by emitting light when they return to lower energy levels.
The excitation fallback theory explains the visible emission (bright line) spectrum of element
A ground state for the electrons in an atom is an energy state of lowest energy
An excited state is an energy state of higher energy
In order for an electron to go from its ground state to an excited state, it must absorb a certain amount of energy. If the electron dropped back from that excited state to its ground state, that same amount of energy is emitted.
Emission Spectrum
A prism separates light into the colors it contains. White light produces a rainbow of colors.
Emission Spectrum
Light from a helium lamp produces discrete lines.Excited hydrogen atoms emit a pinkish glow. When the visible portion of the emitted light is passed through a prism, it is separated into specific wavelengths that are part of the hydrogen’s line emission spectrum.
Emission Spectrum
The wavelengths of the spectral lines are characteristic of the element, and they make up the atomic emission spectrum of the element.
No two elements have the same emission spectrum.
The fingerprints of an element.
Energy of Light
Light can be described as a quanta, or packet, of energy that behaves as if they were particles. Light quanta are called photons. The energy associated with a certain frequency of light is related by the equation:
h = 6.63 X 10-34 Js
U DO IT NOW!
For the following configuration: 2-8-18-6
a) Identify the element.
b) Propose an excited state.
Simply add the electrons, which equal protons in a neutral atom, the atomic number.
2-8-18-6: 2+8+18+6 = 34 electrons indicates an atomic number of 34, which is Se
Write a configuration with the same number of electrons as the ground state , but with a different configuration.
2-8-18-6(ground): 2-8-17-7 (excited)♫NOTE – electrons furthest from the nucleus are most likely to be excited (promoted).