advances in ic engines-120325133435-phpapp02
description
Transcript of advances in ic engines-120325133435-phpapp02

ADVANCES IN IC ENGINESSANKAR RAM T. , MIDHUN ANTONY JOSEPH
Jyothi engineering college, Cheruthuruthy, Thrissur.

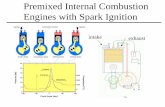
Introduction to IC engines
Invented in early 1680 First attempt by Christian Huygens Converts heat energy produced by
burning of fuel to mechanical output. Basically consists of a piston-cylinder
arrangement. The expansion of air due to the heat
produced moves the piston inside the cylinder.

Classification of IC engines
Two main classifications: Based on combustion
Spark Ignition [SI engines] (Eg: Petrol Engine)
Compression Ignition [CI engines] (Eg: Diesel Engine)
Based on Number of strokes Two stroke Four Stroke Six Stroke

Major areas of advancement The vision behind evolving of IC engine
was to extract maximum power from the fuel while reducing emissions and pollution from the engine.
The main areas of advancement are: Engine Design Material Selection Timing Controls Fuel Injection And Combustion
The advances moves almost parallel and most companies have their own versions of the advances discussed here.

Engine Design
The early designs involved a single cylinder. This caused a large amount of fluctuations in power output.
So more number of cylinders were added to reduce output fluctuations and size of engine
There are four types of engine designs used. Inline V Type Flat Type Radial Engines

Engine Design
Inline Engine
V Type Engine
Flat Engine
Radial Engine

Material selection
When selecting materials for engine, following factors are considered
Weight of material Melting point Coefficient of expansion Heat transmission power Vibration and sound damping
The main metals used in engine manufacture are
Grey Cast Iron Aluminium Magnesium

Use of Sodium in engines
A part of engine is hollowed and is filled with sodium
When temperature of the part becomes 1600C sodium melts
This molten state has better heat transfer that solid metal
Sodium is mainly used in: Sodium Valves (Exhaust Valves) Piston Skirts

Timing controls
The Efficiency of engine is decided by the timing of its sequential operation.
Timing of inlet and exhaust valves Timing of the spark in SI engines Timing of fuel injection in CI engines Sequential operation of each cylinders in multi cylinder
engine
In normal cases these timings are a design parameter set at time of manufacture.
The goal of timing control is to change the timings of engine while its working.

Variable Valve Timing (VVT)
At low rpm, the timing is adjusted for maximum efficiency.
At high rpm, time the valve remains opened is reduced while increasing the opening size.
This helps to pump more charge to cylinder without creating backpressure or scavenching.
An electronic system uses a microcontroller to adjust the solenoid valve.

Variable Valve Timing (VVT)
In a mechanical system, the input from crank is given to a gear which is locked to the cam using a pin.
When adjustment is needed, the pin is removed magnetically and a stepper motor adjusts the cam.
Used in many cars in various namesBMW Valvetronic, VANOSFiat Twin Cam VISGeneral Motors VVT, DCVCPHonda VTEC, i-VTECPorsche VarioCam

Variable Valve Timing (VVT)

Active Valve Train
In active valve train, there will be two cams designed for specific road conditions.
When the microprocessor detects a rough terrain, the cam used will be the one for more power.
But during cruising, the cam is switched to a low power, high efficient cam using a cam tapper.
Introduced first by Lotus Motors and later developed by Nissan Motors.

Cylinder Deactivation
Cylinder deactivation is a derived form of active cam switching.
In this method, while cruising a part of cylinders are switched off by switching to a cam without lobes.
This method is successful because of following Lesser fuel consumption Less heat generation Less power lost in managing other cylinders
This is mostly employed in V Type Engines.

Cylinder Deactivation
The cylinder is deactivated by Keeping the inlet valve closed so that there
is no fuel flow Keeping the exhaust valve open so there is
no work done in compression. Some Companies using cylinder
deactivation are General Motors V8-6-4 (Cadillac) General Motors Active Fuel Management DaimlerChrysler Active Cylinder Control (ACC) (for
Mercedes-Benz) Honda Variable Cylinder Management (VCM)

Fuels and Fuel Injection
The fuels and its input to the engine highly influences the emissions from the engines.
In SI engines a air-fuel mixture called charge is introduced to the cylinder before compression
In CI engines the fuel is injected after the compression stroke to the cylinder. This helps in attaining higher compression ratios.
In SI engines it is not possible because there is a chance that the fuel may burn before hand.

Direct Injection
With direct injection, the advantages of CI engines can be obtained in SI engines also.
In direct injection, first the air is filled in the cylinder. Then half way through the compression stroke, a small amount of fuel is injected to the cylinder to create a lean mixture.
At the end of compression, just before the spark the rest of fuel is injected to the head of spark plug.
The burning of fuel occurs in a stratified pattern near the spark plug.

Direct Injection
Direct injection has many advantages such as No need of carburetor Easy design of manifold Better compression is achievable No case of knocking in engines Lower NOx emissions Due to stratified combustion leaner mixture
can be used which reduces the fuel consumption.

Direct Injection

Superchargers
Consists of a compressor coupled to the engine using a belt.
The output is directly connected to the engine.
As the engine rotates, the air is sucked in and compressed which is then fed to the cylinders.
Increases the amount of oxygen given to engine thus helps in better burning.
Is a must in aircrafts flying at high altitudes were air is less dense.

Turbochargers
Is a derived form of supercharger Consists of a turbine and a compressor
coupled in a shaft. Instead of using the power from engine
to turn the compressor, the exhaust is used to turn the turbine which rotates the compressor.
Turbochargers can only act at high velocity exhaust so they need some time to start up in cold start. This time is called as turbo lag.

Six Stroke Engines
The invention of six stroke engines was for the following reasons:Less weight to power ratioLess scavenchingLess moving partsMore power and fuel economyObtain freedom in designingBetter cooling
Six stroke engines are developed in two different ways

Air/Water injection to Cylinder In this method air or water is injected to
the cylinder at the end of exhaust stroke. The fluid absorbs the heat and expands
providing another power stroke. An exhaust stroke is provided to removed the fluid from cylinder.
Three recognized names in this section are: Bajulaz six stroke engine (Preheating of air) Velozeta six stroke engine (Injection of air) Crower six stroke engine (Injection of
water)

Opposed Piston Engines
This model uses two pistons working in and cylinder.
The pistons are used to open and close ports just like a two stroke engine.
The working of opposed pistons provide better compression.
The pistons have either a change in speed or have a phase shift between them.
Some engines in this section are: Beare Head Engine M4+2 engine

References
en.wikipedia.org www.greencar.com www.mitsubishi-motors.com www.bmw.com/com/en/insights Elements of IC Engines, Rogowsky,
Tata McGraw hill Internal Combustion Engines,
Mathur & Metha, Vol I&II Pergamon Press

Thank You For Your Time !
Questions ?