Activity 3 axial skeleton
-
Upload
meleebirdsong -
Category
Education
-
view
5.831 -
download
1
Transcript of Activity 3 axial skeleton

The Axial Skeleton
Salt Lake Community CollegeBIO 2325
Compiled by: Kathryn Watson Edited by: Claudia Gonzales (Anatomy Assistant)

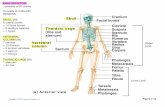
• Axial skeleton - forms long axis of bodyAxial skeleton - forms long axis of body• SkullSkull• Vertebral columnVertebral column• Thoracic cageThoracic cage
• Appendicular skeleton (next week) – Appendicular skeleton (next week) – appendages and what appendages and what they attach tothey attach to• Upper limbs (arms)Upper limbs (arms)• Pectoral girdle (shoulder)Pectoral girdle (shoulder)• Lower limbs (legs)Lower limbs (legs)• Pelvic girdlePelvic girdle

Axial skeletonSkull
Vertebral columnThoracic cage
Axial skeleton is shown in green

SuturesSutures
• Largest 4 skull sutures: where bones articulate Largest 4 skull sutures: where bones articulate with parietal boneswith parietal bones• CoronalCoronal• SagittalSagittal• SquamousSquamous• Lambdoid Lambdoid

Paranasal sinusesParanasal sinuses• Air-filled chambers named for the bone in which they are Air-filled chambers named for the bone in which they are
housedhoused
• ““Paranasal” because they cluster around and connect to the Paranasal” because they cluster around and connect to the nasal cavitynasal cavity

FontanelsFontanels• Unossified remnants of Unossified remnants of
membranesmembranes
• Present at birthPresent at birth
• Anterior fontanel largestAnterior fontanel largest
• Called “soft spots”Called “soft spots”
• Ossify by 1 ½ - 2 yearsOssify by 1 ½ - 2 years
Continue to ossify into adulthood; the sutures can become fused in old age

http://homepage.smc.edu/wissmann_paul/bones/EBbonestutorial.htmlhttp://homepage.smc.edu/wissmann_paul/bones/EBbonestutorial.html
For labeled photographs of the human skeleton go to the webpage below:


Cranial and Facial BonesCranial and Facial Bones• Frontal BoneFrontal Bone• Supraorbital foramen: supraorbital artery and nerve go through Supraorbital foramen: supraorbital artery and nerve go through
it.it.• Frontal sinus: moistens air.Frontal sinus: moistens air.
99
• Parietal Bones• Nasal Bones

Cranial and Facial BonesCranial and Facial Bones
• Sphenoid bone: Sphenoid bone: • Greater WingGreater Wing• Lesser WingLesser Wing• Sella Turcica: Houses pituitary glandSella Turcica: Houses pituitary gland• Optic foramen/canal: contains CNII (Optic Nerve)Optic foramen/canal: contains CNII (Optic Nerve)• Foramen Ovale: contains mandibular branch of CNVForamen Ovale: contains mandibular branch of CNV• Foramen Rotundum: contains maxillary branch on CNVForamen Rotundum: contains maxillary branch on CNV
1010

Cranial and Facial BonesCranial and Facial Bones
• Foramen Spinosum: contains middle meningeal vesselsForamen Spinosum: contains middle meningeal vessels• Foramen LacerumForamen Lacerum• Superior Orbital Fissure: contains CNIII, ophthalmic branch Superior Orbital Fissure: contains CNIII, ophthalmic branch
of CNV, and CNVIof CNV, and CNVI• Inferior Orbital Fissure: contains Maxillary branch of CNVInferior Orbital Fissure: contains Maxillary branch of CNV• Sphenoidal Sinus: moistens airSphenoidal Sinus: moistens air• Lateral and medial platesLateral and medial plates• Pterygoid PlatesPterygoid Plates
1111

SphenoidSphenoid
1212

Cranial and Facial BonesCranial and Facial Bones
• Ethmoid BoneEthmoid Bone• Perpendicular Plate: Superior part of nasal septumPerpendicular Plate: Superior part of nasal septum• Superior and middle nasal concha(e): Increase surface area Superior and middle nasal concha(e): Increase surface area
for warming and filtering air.for warming and filtering air.• Cribriform plate and foramina: passageway for olfactory Cribriform plate and foramina: passageway for olfactory
nerves.nerves.• Crista Galli: attachment site for dura mater to skull.Crista Galli: attachment site for dura mater to skull.
1313

Ethmoid

Cranial and Facial BonesCranial and Facial Bones• Inferior Nasal Conchae BonesInferior Nasal Conchae Bones
• Lacrimal BonesLacrimal Bones• Lacrimal GrooveLacrimal Groove
• Zygomatic BonesZygomatic Bones• Temporal Process: forms anterior portion of zygomatic arch Temporal Process: forms anterior portion of zygomatic arch
(cheekbone)(cheekbone)
• Maxilla BonesMaxilla Bones• Infraorbital Foramen: passageway to infraorbital artery, and Infraorbital Foramen: passageway to infraorbital artery, and
maxillary branch of CNVmaxillary branch of CNV
1515


Cranial and Facial BonesCranial and Facial Bones
– Alveolar Processes: contain upper teeth.Alveolar Processes: contain upper teeth.– Palatine Processes: form anterior portion of hard palate.Palatine Processes: form anterior portion of hard palate.
– Incisive Foramen (Fossa): passageway to branches of Incisive Foramen (Fossa): passageway to branches of nasopalatine nerve from CNVnasopalatine nerve from CNV
• MandibleMandible– BodyBody– RamusRamus
– Alveolar Processes: contain lower teeth.Alveolar Processes: contain lower teeth.
1717

MaxillaMaxilla
1818

Cranial and Facial BonesCranial and Facial Bones
• AngleAngle• Mental Foramen: passageway for mandibular branch of Mental Foramen: passageway for mandibular branch of
CNV and blood vesselsCNV and blood vessels• Coronoid Process: Insertion point of temporalis muscleCoronoid Process: Insertion point of temporalis muscle• Mandibular Condyle or Condylar Process: Forms joint with Mandibular Condyle or Condylar Process: Forms joint with
mandibular fossa of temporal bone.mandibular fossa of temporal bone.• Mandibular NotchMandibular Notch
1919

MandibleMandible
2020

Cranial and Facial BonesCranial and Facial Bones• Temporal BonesTemporal Bones
• Zygomatic process: Forms posterior portion of zygomatic arch Zygomatic process: Forms posterior portion of zygomatic arch (cheekbone)(cheekbone)
• Squamos Region: Squamos means flat, flat part of bone.Squamos Region: Squamos means flat, flat part of bone.• Styloid Process: Attachment for Hyoid and tongue musclesStyloid Process: Attachment for Hyoid and tongue muscles• Mastoid Process: Insertion for sternocleidomastoid muscleMastoid Process: Insertion for sternocleidomastoid muscle• External Acoustic Meatus: Opening of auditory canalExternal Acoustic Meatus: Opening of auditory canal
2121

Cranial and Facial BonesCranial and Facial Bones
• Petrous part: Petrous means rock.Petrous part: Petrous means rock.• Internal Acoustic Meatus: passageway for CNVII, CNVIII and Internal Acoustic Meatus: passageway for CNVII, CNVIII and
blood vessels to inner ear.blood vessels to inner ear.• Jugular Foramen: passageway for internal jugular vein, Jugular Foramen: passageway for internal jugular vein,
CNIX, CNX and CNXICNIX, CNX and CNXI• Carotid Canal: passageway for internal carotid artery.Carotid Canal: passageway for internal carotid artery.• Mandibular Fossa: Forms joint with mandibular condyleMandibular Fossa: Forms joint with mandibular condyle
2222

Temporal BoneTemporal Bone
2323

Cranial and Facial BonesCranial and Facial Bones
• Occipital BoneOccipital Bone• Foramen Magnum: passageway for spinal cord, vertebral Foramen Magnum: passageway for spinal cord, vertebral
arteries and CNXI.arteries and CNXI.• Hypoglossal canal: passageway for CNXII hypoglossal nerve.Hypoglossal canal: passageway for CNXII hypoglossal nerve.• External Occipital Protuberance and crest: attachment site External Occipital Protuberance and crest: attachment site
for neck/back muscles.for neck/back muscles.• Occipital Condyles: Articulates with Atlas.Occipital Condyles: Articulates with Atlas.
2424

2525

2626

2727

2828

Cranial and Facial BonesCranial and Facial Bones
• Palatine BonesPalatine Bones• Horizontal plates: forms posterior portion of hard palate.Horizontal plates: forms posterior portion of hard palate.
• Vomer: Vomer: Forms inferior part of nasal septum. Forms inferior part of nasal septum.
2929

3030

3131

3232

The Skull = cranial bones The Skull = cranial bones and facial bonesand facial bones

Cranial bonesCranial bones
parietal
parietal
frontal
temporalparietal
occipital
_______sphenoid_____ethmoid
occipital

VertebraeVertebrae• Typical Vertebrae (32)Typical Vertebrae (32)• Lamina: connects transverse to spinous process.Lamina: connects transverse to spinous process.• Pedicle: connects body to transverse process.Pedicle: connects body to transverse process.• Transverse Process: Process directed laterallyTransverse Process: Process directed laterally• Spinous Process: Process directed posteriorly.Spinous Process: Process directed posteriorly.• Superior and Inferior Articular Processes: Forms joint Superior and Inferior Articular Processes: Forms joint
between adjacent vertebraebetween adjacent vertebrae• Vertebral Foramen: Contains spinal cord.Vertebral Foramen: Contains spinal cord.• Body: largest part of the vertebra.Body: largest part of the vertebra.• Intervertebral Foramen: Formed when 2 vertebra come Intervertebral Foramen: Formed when 2 vertebra come
together, contains spinal nerves.together, contains spinal nerves.• Intervertebral Disc (not a bone):Fibrocartilage found Intervertebral Disc (not a bone):Fibrocartilage found
between adjacent vertebral bodies.between adjacent vertebral bodies.3535

VertebraeVertebrae
3636

VertebraeVertebrae
• Cervical Vertebrae (7): have bifurcated spinous Cervical Vertebrae (7): have bifurcated spinous processesprocesses• Transverse Foramen: Cervical vertebrae have transverse Transverse Foramen: Cervical vertebrae have transverse
foramen which contain the vertebral arteries.foramen which contain the vertebral arteries.
• Atlas (C1)Atlas (C1)• Arch: contains articulation point for dens of axis.Arch: contains articulation point for dens of axis.
• Body: C1 has no body; body has become the dens of axis.Body: C1 has no body; body has become the dens of axis.
• Axis (C2)Axis (C2)• Body: has odontoid process or densBody: has odontoid process or dens
• Odontoid Process or Dens: fused body of C1; articulated with atlas.Odontoid Process or Dens: fused body of C1; articulated with atlas.
• Vertebra Prominens (C7): Vertebra Prominens (C7): • Spinous Process: very large and easily felt under the skin.Spinous Process: very large and easily felt under the skin.
3737

Cervical VertebraeCervical Vertebrae
3838

C1, C2 and C7C1, C2 and C7
3939

VertebraeVertebrae
– Thoracic Vertebrae (12)Thoracic Vertebrae (12)• Transverse Process: On thoracic vertebrae transverse Transverse Process: On thoracic vertebrae transverse
processes contain costal faucets for articulation with angle processes contain costal faucets for articulation with angle of a rib.of a rib.
– Lumbar Vertebrae (5)Lumbar Vertebrae (5)
– Sacrum ( 5 fused)Sacrum ( 5 fused)• Anterior Sacral Foramina: contain ventral rami of sacral Anterior Sacral Foramina: contain ventral rami of sacral
spinal nerves.spinal nerves.
• Posterior Sacral Foramina: contain dorsal rami of sacral Posterior Sacral Foramina: contain dorsal rami of sacral spinal nerves.spinal nerves.
4040

Thoracic VertebraeThoracic Vertebrae
4141

Lumbar VertebraeLumbar Vertebrae
4242

VertebraeVertebrae
• Median Sacral Crest: represents fused spinous processes of Median Sacral Crest: represents fused spinous processes of sacral vertebrae.sacral vertebrae.
• Auricular Surfaces: ear-like process, articulates with the iliac Auricular Surfaces: ear-like process, articulates with the iliac bones.bones.
• Superior Articular Processes: Articulate with inferior articular Superior Articular Processes: Articulate with inferior articular processes of L5processes of L5
• Coccyx (2-3 fused)Coccyx (2-3 fused)• Cornu or horns: Small horns that point superiorlyCornu or horns: Small horns that point superiorly
4343

Sacrum and CoccyxSacrum and Coccyx
4444

Sternum and RibsSternum and Ribs
• SternumSternum• Manubrium (top)Manubrium (top)
• Sternal or jugular notchSternal or jugular notch
• Sternal angle: division between manubrium and body.Sternal angle: division between manubrium and body.
• Clavicular notch: articulate with clavicles.Clavicular notch: articulate with clavicles.
• Costal notch: articulates with ribsCostal notch: articulates with ribs
• BodyBody• Costal notches: articulates with ribsCostal notches: articulates with ribs
• Xiphoid Process Xiphoid Process
4545

SternumSternum
4646

Sternum and RibsSternum and Ribs
• RibsRibs• True Ribs (1-7)True Ribs (1-7)
• Head (capitulum)Head (capitulum)
• NeckNeck
• TubercleTubercle
• AngleAngle
• Costal GrooveCostal Groove
• Shaft (body)Shaft (body)
• False Ribs (8-12)False Ribs (8-12)• Floating Ribs (11-12)Floating Ribs (11-12)
4747

RibsRibs
4848