ACTIVE TRANSPORT
description
Transcript of ACTIVE TRANSPORT

ACTIVE TRANSPORT
Mr. Cistaro 11/11/12

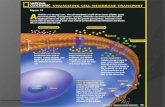
MOLECULAR MEMBRANE

ACTIVE TRANSPORT – SWIMMING AGAINST THE CURRENT Active Transport requires energy.
Molecular TransportEndocytosis
Phagocytosis Pinocytosis
Exocytosis WORD CHECK.
Endo / Exo ??? / ???Cytosis ???

MOLECULAR TRANSPORT Cells use E (ATP) to pump ions/compounds
against the concentration gradient (from low concentration to high concentration).
EXAMPLESodium-Potassium Pump It moves sodium ions
out of cells while moving potassium ions in.Pumps out 3 sodiums for every 2 potassiums it
pumps in. It occurs in animals. It has a particular significance for excitable cells
such as nerve cells, which depend on this pump for responding to stimuli and transmitting impulses.

MOLECULAR TRANSPORT Na+/K+Pump

MOLECULAR TRANSPORT

ENDOCYTOSIS The movement of bulk materials into
cells. Phagocytosis - The movement of solids.Pinocytosis - The movement of liquids.

ENDOCYTOSIS - PHAGOCYTOSIS Phagocytosis (from Ancient Greek
φαγεῖν (phagein) , meaning "to devour", κύτος, (kytos) , meaning "cell", and -osis, meaning "process") is the cellular process of engulfing solid particles by the cell membrane.

ENDOCYTOSIS - PHAGOCYTOSIS Scanning electron micrograph of a
phagocyte (yellow, right) phagocytosing anthrax bacilli (orange, left)

ENDOCYTOSIS - PINOCYTOSIS Pinocytosis is the process in which small
particles are brought into the cell, forming a vesicle, and fuse with lysosomes to break down the particles.

ENDOCYTOSIS - PINOCYTOSIS The difference between Phago and
Pinocytosis?

ENDOCYTOSIS - PINOCYTOSIS The difference between Phago and
Pinocytosis?

EXOCYTOSIS The movement of bulk materials out of
cells.From Greek ἔξω "out" and
κύτος "receptacle“ / "cell"Example: secretion of enzymes

WEIRD WORDS & QUESTIONS ??? Quiz next week.