Active Transport
description
Transcript of Active Transport

Active Transport
Requires use of energy because it does not happen naturally through diffusion or facilitated diffusion.
Requires a carrier protein* that uses energy from ATP molecules (Adenosine Tri-Phosphate, a nucleotide that stores energy and can release it when bonds are broken.)
Why? Moving stuff against the concentration gradient requires a “pump”.
ORFusing/rebuilding of cell membranes

Compare Membrane ProteinsActive Transport vs. Facilitated Diffusion :
Both use…. Carrier Proteins
But only active transport carrier proteins require…
ATPBecause they need energy to change their
shape!

ATP
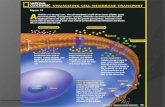
Sodium – Potassium Pump
Phos
phol
ipid
B
ilaye
r
Na+
Phos
phat
es fr
om
ATP
brea
kdow
n
K+

Active Transport - Bulk Transport
One large or many small particles moved in or out of cell using membrane bubbles called vesicles that can fuse with the cell/plasma membrane
Exocytosis – materials moved out of cellEx.: secretion of tears & sweat

Active Transport - Bulk Transport
Endocytosis – materials moved into cell
Phagocytosis – “cell eating” solid particle(s) taken inEx.: phagocytes such as macrophages & other immune cells ingesting bacteria
Pinocytosis – “cell drinking” liquid/many small particle(s) taken inEx.: Cells “gulping up” plasma from blood, leaving RBCs in blood

08-19a-PhagocytosisAnim.mov
08-19b-PinocytosisAnim.mov

Endocytosis?
Exocytosis?
# 2
# 1
#3

Endocytosis
1. Pinocytosis
2. Phagocytosis

Contractile Vacuole‘Sump Pump’ in unicellular aquatic organisms
Environment is 99% Water
Cell is 95% Water
Active or Passive?