Acquiring Immunity
description
Transcript of Acquiring Immunity

Acquiring Immunity
Long Term Protection

Individual Activity (means no talking)
• Read Acquiring Specific Immunity at top of p317 of Biology 2.

• Why is Specific Immunity also called Acquired Immunity??
• Specific immunity is Acquired Immunity (you only develop immunity following exposure.
• What is the difference between active and passive immunity?
• Active – antibodies are made in the body• Passive – antibodies are produced in one person
and transferred to another
Questi ons

Individual Activity (still means no talking)
• Read section Active Immunity on p317-318

• What is natural active immunity?• Antibodies are produced in the body (naturally)
following exposure to a pathogen.
• What is induced active immunity?• Antibodies made after immunisation with toxoid or
with killed or treated organisms (vaccines).
• REVISE IMMUNE RESPONSE - Label diagram and paste into your notes.
Questi ons

Purpose (what they do):
Following exposure its specific ANTIGEN, the cell will reproduce to form:
Maturation: (each cell as a specific ANTIBODY
on its surface
Cell ProductionLymphocytes are produced in the BONE MARROW
B CELLS mature in the bone
marrow.
PLASMA CELLS which produce
antibodies
Antibodies react with specific antigens. An
antigen involved in such a
response is no longer able to damage host
cells.
B MEMORY CELLS
Provide long term immunity to
the specific pathogen. React faster and more
vigorously in subsequent exposures.
T CELLS mature in the thymus
HELPER T CELLS (Th Cells)
Help B Cells recognize
antigens (from engulfed
pathogens) on Phagocytes. Needed for
production of Plasma Cells
CYTOTOXIC T CELLS (Tc Cells)
Kill cells that have been
infected with a virus. Identifies
cell by its antigen (viral protein left on cell surface).
T MEMORY CELLS
Provide long term immunity to the
specific pathogen. React faster and
more vigorously in subsequent exposures
Antibody Mediated Response Cell Mediated Response

Individual Activity (still means no talking)
• Read section Eradicating a Disease by Vaccination on p318-320

Questi ons• Vaccination is the process of introducing the vaccine into the body where as
Immunisation is the immune response to the vaccine that results in immunity. What is a vaccine?
• Vaccines (dead or live but weakened(attenuated) pathogens and synthetic antigens) are used to activate the immune system against that specific disease, without causing the disease. Vaccines have the same antigens as the infective pathogen. Vaccines are usually injected or ingested.
• Copy this graph into your notes. With reference to the Immune System and this graph, what is Immunisation?


Usually involves a series of injections to bring on lasting immunity. This is the immunisation program and involves:
1. A first vaccination, in which the vaccine in introduced into the body for the first time
2. A primary response, during which plasma cells slowly produce small amounts of antibodies, resulting in short term immunity. Some memory cells are produced. This takes about 10 days and the amount of antibodies quickly declines once infection has cleared
3. A second vaccination, in which a second vaccine (or booster) is introduced into the body. Existing memory cells respond.
4. A secondary response, during which plasma cells rapidly produce large amounts of antibodies much more quickly (approximately 3 days) and in much greater amounts. The level of antibodies in the secondary response remain much higher for longer than the primary response resulting in long term immunity.

• What is a Toxoid?• Some pathogens secrete toxins which can be
treated with Toxoids in a similar way to vaccines.
• Give some examples of Vaccine preventable diseases.
• Tetanus, Diphtheria, Pertussis (Whooping Cough), Hepatitis A, Hepatitis B, Varicella Zoster (Chicken Pox), Poliomyelitis, Measles, Mumps, Rubella (German Measles), Influenza, there are many more
Questi ons

Individual Activity (still means no talking)
• Read section Passive Immunity and Rabbits as antibody making machines on p320-321

• What is natural passive immunity?• Antibodies acquired by baby across placenta or in
mother’s milk
• What is induced passive immunity?• Antibodies acquired through injection of
Immunoglobulins (antibodies)
• Copy and Label the following diagram
Questi ons

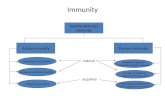
Acquired Immunity
Natural
Passive Immunity
Acquired (Induced)

Acquired Immunity
Active Immunity
Natural
Antibodies made after exposure to infection
Induced
Antibodies made after immunisation with
toxoid or with killed or treated organisms
Passive Immunity
Natural
Antibodies acquired by baby across placenta or in mother’s milk
Induced
Antibodies acquired through injection of
Immunoglobulins (antibodies)
Memory B and T cells No Memory Cells

Individual Activity (still means no talking)
• Read section Adverse Event Associated with Immunity on p322-323

IMMUNE DOCUMENTRY
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0u6z6yFxahg&feature=relatedhttp://www.youtube.com/watch?v=OBMIkfMMTHs&feature=relmfuhttp://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gGemkOYPtmw&feature=relmfu - skiphttp://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ysw_Zs-ydP8&feature=relmfuhttp://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lZWOh3NEsag&feature=relmfuhttp://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_49z0Xf235Q&feature=fvwrelhttp://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ouqVl6CpW-U&feature=relmfuhttp://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ouqVl6CpW-U&feature=fvwrelhttp://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qIH9T-GBjm4&feature=relmfuhttp://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SAsTwG5Mxow&feature=relmfu