Acidbase#1
Transcript of Acidbase#1

LEWIS ACID BASE THEORY
Nadia and Vito

acidA substance which produces hydrogen ions,
H+, when it is dissolved in water.
Properties: • Acids have a sour taste.• Acids dissolve in water to form solutions which conduct
electricity. • Acids turn blue litmus paper red. • Acids react with reactive metals to form hydrogen and a
salt.• Acids react with carbonates to form a salt, carbon dioxide
and water. • Acids react with bases to produce a salt and water only.

base - alkaliBase is any metal oxide or hydroxide – it
contains either oxide ions, O2-, or hydroxide ions, OH-.
Alkali is a base that is soluble in water.
Properties:• Alkalis have a bitter taste and soapy feel. • Alkalis turn red litmus paper blue. • Alkalis produce hydroxide ions when dissolved in water. • All alkalis can react with acids to form a salt and water only

the lewis acid base theory• The Lewis Acid Base Theory suggests
an acid as the reactant that receives an electron pair from another reactant in a chemical reaction, and a base as the reactant that that donates an electron pair to another reactant.
• In a Lewis Acid-Base reaction, the base donates an electron pair, forming a coordinate covalent bond joining the two species together into the reaction product.

lewis acids and bases• A Lewis acid is a any substance that can
accept a pair of nonbonding electrons. Lewis acids are electron-pair acceptors.– All cations.– All molecules possessing an atom with incomplete octet.
• A Lewis base is any substance that can donate a pair of nonbonding electrons. Lewis bases are electron-pair donors. – All anions.– All molecules having lone-pairs of electrons.

lewis acid base reaction• From the definition of acid and base suggested by Lewis,
we can write acid-base reactions like this:
• Characteristics of these reactions:– They are charge balanced – the total charge of all species is the same on both sides.– The product is sometimes described as a Lewis “complex”.– Red arrows are used to show the how the bond between the acid and base is formed.
• The tail sits on a pair of electrons.• The head sits on points to where these electrons will be in the product.

homo-lumo• In modern theoretical language:– the Lewis base’s filled orbital is the highest
occupied molecular orbit – or HOMO.– The Lewis acid’s empty orbital is the lowest
unoccupied molecular orbit – or LUMO.
• We refer to the interaction as the “filled-empty” interaction or the “HOMO-LUMO” interaction.

example of reactionBF3 + NH3 ?
Consider the molecules BF3 and NH3. If we determine the Lewis structure of BF3 and NH3, we find that B is octet
deficient and can accept a lone pair. While N is capable of donating a lone pair. N donates a pair of electrons to B,
creating a coordinate covalent bond between them.
Acid BaseLewis Complex

• Predict whether the following ions or molecules can act as either a Lewis acid or a Lewis base.– Ag+
–NH3

references
• http://www.nyu.edu/classes/tuckerman/honors.chem/lectures/lecture_21/node4.html
• http://chemistry.umeche.maine.edu/CHY251/Lewis.html
• http://facultyfp.salisbury.edu/dfrieck/htdocs/212/rev/acidbase/lewis.htm
• http://www.wou.edu/las/physci/ch412/ligand.htm• https://chemistry.twu.edu/tutorial/
AcidBaseConceptsSum.html










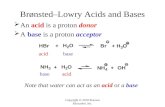



![[XLS] · Web view1 1 1 2 3 1 1 2 2 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 1 1 1 1 2 2 3 5 1 1 1 1 34 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 240 2 1 1 1 1 1 2 1 3 1 1 2 1 2 5 1 1 1 1 8 1 1 2 1 1 1 1 2 2 1 1 1 1](https://static.fdocuments.in/doc/165x107/5ad1d2817f8b9a05208bfb6d/xls-view1-1-1-2-3-1-1-2-2-1-1-1-1-1-1-2-1-1-1-1-1-1-2-1-1-1-1-2-2-3-5-1-1-1-1.jpg)




![1 1 1 1 1 1 1 ¢ 1 1 1 - pdfs.semanticscholar.org€¦ · 1 1 1 [ v . ] v 1 1 ¢ 1 1 1 1 ý y þ ï 1 1 1 ð 1 1 1 1 1 x ...](https://static.fdocuments.in/doc/165x107/5f7bc722cb31ab243d422a20/1-1-1-1-1-1-1-1-1-1-pdfs-1-1-1-v-v-1-1-1-1-1-1-y-1-1-1-.jpg)