Acc 441 Draft
-
Upload
mahinchowdhury -
Category
Documents
-
view
221 -
download
0
Transcript of Acc 441 Draft
-
8/10/2019 Acc 441 Draft
1/13
Materials: Controlling, Costing and Planning
Explanation:- Purchase requisition is the principal form required in purchasing. It is like a
voucher, designed according to its demand.- Purchase department issues purchase order. Purchase order is also a principal
form which gives the vendor a description of the goods and services desired aswell as terms, prices, and shipping instructions. Nowadays, purchase departmentis also named as procurement department
- ccounting department finali!es the amounts that need to "e paid "ut they arenot authori!ed to pay. #reasurer signs for the payment and they are not includedin the accounting department.
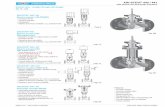
$lowchart for Purchasing, %eceiving, %ecording & Paying for'aterials
Purchase%equisition
ccounting (ept.$or accout no.
account num"erPurchasing (ept.issues purchase order
to:
). *endor+. ccounting (ept.
. %eceiving (ept.-. 'aterials edger /lerk0. $ile /opy
*endor%eturns acknowledge
1 ment copy2hips materials2ends invoice
ccounting (ept.3ses:
). Invoice+. Purchase 4rder
. %eceiving andinspection report5s6 forinvoice approval-. Payment approved forvoucher prepared
%eceiving (ept.Issues receivingreport to:
). Purchasing (ept.+. 4wn $ile. /opies toInspection (ept.
'akes distri"ution to:). 4wn $ile+. ccounting (ept.. 'aterials (ept.
#reasurer$orPayment
'aterials edger/lerk Posts quantityand dollar amounts tomaterials ledger.
materials ledger
'aterials (ept.2torekeeper stores
materials inproper location
)
-
8/10/2019 Acc 441 Draft
2/13
Explanation:
1. Cost of carrying inventory:
- Interest on investment: this is the "asic cost of capital.- Property tax and insurance: this is actually the corporate tax.- 7arehouse 8 storage: this is a significant cost of carrying inventory.- 9andling: loading and unloading cost.- (eterioration and shrinkage cost: normal or a"normal loss it depends on raw
material.- 4"solescence: this is a risk factor it occurs due to technological innovation.
2. Cost of not carrying inventory:
- Extra Purchasing, handling #ransportation /osts: if inventories are not carriedthen goods need to "e purchased frequently. It ultimately increases the cost indiscussed.
- 9igher Prices for 'aterials: when goods are purchased at small lots, "uyers areunlikely to receive discounts that are given on "ulk purchases. #hus they willincur higher prices.
- 2tock outs: occurs when shortage of raw materials stop production process.
- dditional /lerical /osts: incurred due to red tape.- ost sales & "ad will: loss of customers or sales and thus good will when stocks
are not availa"le at the time of sale or on demand.
;uantitative 'odelsPlanning 'aterials
%equirementsPlanning deals with two Fundamental Factors
1. The Quantity 2. The Time to urchase
!nvolves two conflicting "ind of costs
1. Cost of carrying inventory 2. Cost of not carrying inventory
Interest on investmentProperty tax & insurance7arehouse or 2torage9andling(eterioration & 2hrinkage4"solescence
Extra Purchasing, handling#ransportation /osts9igher Prices for 'aterials2tock outsdditional /lerical /ostsost sales &
-
8/10/2019 Acc 441 Draft
3/13
Explanation:Economic order quantity 5E4;6 is the amount of economic inventory ordered at onetime that minimi!es annual inventory cost. If a company "uys materials infrequentlyand in large quantities, the cost of carrying the inventory is high "ecause of thesi!ea"le average investment in inventory. If purchase is made in small quantities infrequent orders correspondingly high ordering cost can result. #hus the optimumquantity to order when carrying cost = ordering costs. 7e must also note thatcarrying cost is inversely related to ordering cost. Economic order quantity is awidely used traditional approach. 'eanwhile, Enterprise %esource Planning 5E%P6 isthe advanced approach.
Economic 4rder ;uantity 5E4;6#he order si!e where cost of material is
minimum/arrying /ost = 4rdering /ost
#um$er of
%rder
Costs
nnual 4rdering /ost
nnual /arrying /ost
#otal /ost
ow Point
Economic 4rder;uantity 5E4;6
-
8/10/2019 Acc 441 Draft
4/13
Mathematical Formulation of &%Q
Economic 4rder ;uantity =CCCU
CORU
+
'here, () * +nnual (euirements
C% * Cost er %rder
C) * Cost er )nit
CC * Carrying Cost Percentage
-
-
8/10/2019 Acc 441 Draft
5/13
(erivation of the Equation
1. #um$er of %rders Placed +nnually:
2. +nnual %rdering Costs:
-. +verage !nventory:
. +nnual Carrying Costs:
/. Total Costs 0+C:
EOQ
RU
EOQ
CORU
+EOQ
+EOQCCCU
+
EOQCCCUEOQ
CORU +
+
EOQCCCU
EOQ
CORUAC
+
=
+) EOQCCCUEOQCORUAC
+=
+
+ CCCUEOQCORU
dEOQ
dAC +=
++
CCCU
EOQ
CORU
dEOQ
dAC +
=
CCCU
CORUEOQ
=++
ssuming, 59ere marginal cost is minimum6.>=dEOQ
dAC
++
CCCU
EOQ
CORU =
CORUCCCUEOQ = ++
CCCU
CORUEOQ
=
+
CCCU
CORUEOQ
=
+
0
-
8/10/2019 Acc 441 Draft
6/13
Explanation: 7hile determining the time to order, the following three factors should"e taken into consideration:
). #ime needed for delivery: ead time is the interval "etween the time an order is
placed and the time when the materials arrive on the factory floor, ready forproduction.
+. %ate of inventory usage: ead time ? daily usage. If lead time or usage is "elowexpectation during an order period, the new materials arrive "efore the existingstock is consumed there"y adding to the cost of carrying inventory. If lead timeor usage is greater than expected, a stock out will occur with its many forms ofcost, including lost customers. If average or normal lead time and usage are usedto determine an order point, a stock out can "e expected on every other order.
. 2afety stock: to minimi!e the possi"le stock out an inventory cushion or safetystock is often the least costly protection. 2tock outs will occur only in times oflead time. #he "asic pro"lem is to determine the safety stock quantity. #ime toorder depends on whether we need safety stocks or not. #he optimum safetystock is that quantity that results in the smallest total cost of stock outs plus safetystock carrying costs.
(etermining the #ime to 4rderFactors:
). #ime Needed for (elivery 5ead #ime6+. %ate of Inventory 3sage 5# ? (aily 3sage6. 2afety 2tock @ to minimi!e the possi"le stock out2afety 2tock will "e maintained where total stock out cost and carryingcost will "e minimum.
Materials Control Method
4rder /ycling 'ethod or /ycle %eview 'ethod'in1'ax 'ethod
#wo1"in 'ethod2elective /ontrol @
-
8/10/2019 Acc 441 Draft
7/13
- Method of Calculation of the (eorder oint when the firm is:
a. 'ithout safety stoc": lead timeusage rate.
$. 'ith safety stoc": safety stoc" 3 0lead timeusage rate4
'here safety stoc" euals:
1. 0ma5imum usage 6 normal usage lead time.
%r
2. 0ma5imum lead time 6 normal lead time )sage rate.
#ormal ma5imum inventory * &%Q 3 safety stoc"
+$solute ma5imum inventory *&%Q 3 safety stoc" 30#ormal usage
7Minimum usage 8ead time
Is holding or maintaining safety stocks rational?
Initially at every level of units we will conduct the trial and error method.#hus, safety stock will "e maintained where total stock out cost and carryingcost will "e at minimum.
B
-
8/10/2019 Acc 441 Draft
8/13
&5lanation:
%rder Cycling Method or Cycle (eview Method: Coodsare examined at the end of each cycle, say, >, A>, D> days./ycle time varies over the types of material. 9igh valuecritical items usually require a short review cycle. $or low1cost, non1critical items a longer review cycle is common"ecause order quantities are large and a stock out is not ascostly. #his is a rough and simple process.
Min7Ma5 method:;uantities of most items are su"ect todefina"le limits. 'aximum quantity is esta"lished for eachitem. 'inimum level provides the margin of safety,necessary to prevent stock outs during a reorder cycle.'inimum level sets the order point and the order quantityusually "rings inventory up to the maximum level "ut notmore than that.
1. %rder Cycling Method or Cycle (eview Method
Coods are examined at the end of each cycle, say, >, A>, D> days/ycle time varies over the products/ostly items have lower cycle time and low1cost items have higher cycle time.
;uantities of most items are su"ect to defina"le limits'aximum quantity is esta"lished for each item'inimum level provides the margin of safety, sets the order point
Each stock item is stored in two "ins, piles, or "undles$irst "in contains enough stock required from receipt of an order to the placingof the next order.2econd "in contains normal lead time usage F safety stock
G
-
8/10/2019 Acc 441 Draft
9/13
Two79in Method:Each stock item is stored in two "ins,piles, or "undles. $irst "in contains enough stock requiredfrom receipt of an order to the placing of the next order.2econd "in contains normal lead time usage plus the safetystock. 7hen the first "in is empty and the second "in is
tapped a purchase requisition for a new supply is prepared.
#ypes of Items /haracteristics @ #ype 9igh value, /ritical items @ #ightest /ontrol
< @ #ype 'iddle value @ 'oderate /ontrol/ 1 #ype Non1critical items @ 2imple Physical /ontrols 5#wo @ "in
&5lanation:
2o far this is the "est method. It is also known as
-
8/10/2019 Acc 441 Draft
10/13
Pro$lems
Page: ;7-2, P;72
2elling price = H+>8packagennual requirement = +>>>?)+=+->>> packages3nit cost= H)> per packageead time = days4rdering cost = H).+> per order/arrying cost =)>
%equirement )
= J 5+ ?+->>>?).+>6 )> ? >.)> = +-> packages
%equirement +
Num"er of 4rders Placed nnually = %3E4;
= +->>> +-> =)>> times
%equirement #otal cost of ordering and carrying "lades, #/ = %3 ?/4 F /3?//?E4; E4; +
=+->>>?).+> F)>?>.)>?+-> +-> + =)+>F)+> =H+-> %equirement -
(aily usage = +->>>A> = AA.AB package %eorder point = lead time?daily usage =?AA.AB =+>> package
)>
CCCU
CORUEOQ
=
+
-
8/10/2019 Acc 441 Draft
11/13
Extra inventory = ->>1+>> = +>> packages(ays can "e used = +>> AA.AB * days
fter days, the next order should "e placed.
%equirement 0#he assumption that E4; formula holds are always wrong, it is not fixed. 2o every timethe manufacturers will face pro"lems. E4; formula ust gives a guideline for themanufacturer.
Page: ;7--, P;7-
%equirement )4rder point = 5ead #ime?(aily usage6 F 5maximum usage 1 normal usage6? ead
#ime = 5)>?+>>6 F 5+>1+>>6?)> =+>>>F>> =+>> units
%equirement + Normal maximum inventory = E4; F safety stock = ->>>F>>
= ->> units %equirement
"solute maximum inventory =E4; F safety stock F 5Normal usage 1'inimum usage6 ?ead time
= ->>>F>>F 5+>>1)0>6?)> = ->>>F>>F0>> = -G>> units
%equirement -
et, /3?// = K E4; = J 5+ ?%3?/46 K 4r, ->>> = J 5+ ?5+>>?+0>6?G>6 K 4r, 5->>>6L = 5J + ?5+>>?+0>6?G>6L K
))
CCCU
CORUEOQ
=
+
-
8/10/2019 Acc 441 Draft
12/13
4r, +?5+>>?+0>6?G> = 5->>>6L K
4r, 5->>>6L ?K = G,>>>,>>>4r, )A,>>>,>>>K = G,>>>,>>>
4r, K = G,>>>,>>> )A,>>>,>>>nswer: K = H >.0
Page: ;7--, P;7
#!T %F
F&T +.0 +>> > +>
-> +.> )A> A> ++>
> ).0 )+> D> +)>
+> ).> G> )+> +>>
)> >.0 -> )0> )D>
-? @.1/ 12 1A/ 1BB
)+
-
8/10/2019 Acc 441 Draft
13/13
)