Abdomen - ruc.edu.iq
Transcript of Abdomen - ruc.edu.iq

Abdomen
By
Dr. Safa Ahmed
Rheumatologist (MSc.)

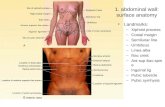
Abdominal region
• Lies between the thorax and the pelvis.
• The cavity outlines are the diaphragm (above) and pelvis below, the abdominal wall (infront) and peritoneum (behind).
• It is divided into 4 quadrants to facilitate the study of this region.

Quadrants of the abdominal region
• Right upper quadrant
• Left upper quadrant
• Left lower quadrant
• Right lower quadrant

9 regions of the abdomen
1. Right hypcochondrium
2. Left hypochondrium
3. Epigastrium
4. Right lumbar region
5. Left lumbar region
6. Umbilical region
7. Right iliac fossa
8. left iliac fossa
9. Hypogastrium


Abdominal wall
• Is a boundary of the abdominal cavity and consist of:
1. skin
2. Subcutanous fat
3. Fascia
4. Muscles
5. Transversalis fascia
6. Extraperitoneal fat peritoneum

Liver
• Is an accessory digestive gland located in the right upper quadrant of abdomen (right hypochondrialregion) just below the diaphragm.
• It lies lateral to the stomach and overlies the gallbladder.
• It is the largest gland in the body.
• It has right and left lobes and is wedge- shaped.
• It secretes the bile that helps in metabolism f fat and stored in the gallbladder.
• Supplied by the portal vein and hepatic arteries.


Stomach• It is a muscular hollow organ and is a part of
the gastro-intestinal tract (GIT).
• It lies between the esophagus(above) and small intestine (below) in the left upper quadrant of the abdomen (epigastric region).
• It is divided into 4 sections: cardia, fundus, body and pylorus.
• Has a greater and lesser curvatures.
• Has 2 sphincters: lower esophageal sphincter and pyloric sphincter.

• Function:
1. Digestion: by secreting digestive juices to metabolize food.
2. Absorption: of water, amino acids and medications….

Spleen • It is an organ that lies below the diaphragm
underneath the 9th, 10th and 11th ribs in the left upper quadrant of the abdomen (left hypochondrial region).
• It is oval in shape and has 4 borders: anterior, superior, posteromedial and inferior.
• Function: filter blood by removing old RBCs and play a role in the immune system.
• Supplied by the splenic artery and drained by the splenic vein.
• It consists of 2 types of tissues:1. White pulp: lymphatic tissue2. Red pulp: venous sinuses and splenic cords


Pancreas
• Is a mixed gland that lies in the abdominal cavity behind the stomach in the left upper quadrant.
• It is divided into: head, neck, body and tail
• Function:
1. Exocrine gland: secretes pancreatic juices and digestive enzymes into the duodenum.
2. Endocrine gland: secrets hormones into blood (insulin, glucagon, somatostatin and pancreatic polypeptide).


Kidneys • Are 2 bean shaped organs that lies in the retro-
peritoneal space on each side of the spine.• The right kidney is slightly lower than the left
kidney.• It is divided into an outer renal cortex and inner
renal medulla.• In the medulla are the renal pyramids that are
conical in shape with the base facing the cortex and apex towards the pelvis.
• The nephron is the structural and functional unit of the kidney which processes the blood that reaches it through filtration, reabsorption, secretion and excretion and the consequence is the production of urine.

• The kidneys are supplied by the renal arteries and drained by the renal veins.
• There is a hilum in both kidneys where the renal artery enters and renal vein and ureter exit.

Small intestine
• Is a part of the GIT that lies between the stomach and the large intestine.
• It has 3 main regions: duodenum, jejunum and ileum.
• Function:
1. mainly is the absorption of nutrients and minerals.
2. Digestion of proteins, lipids and carbohydrates.
3. Support the immune system.

• Supplied by the celiac trunk and superior mesenteric artery and drained by the hepatic portal vein.
• Nerve supply by the celiac ganglia and vagusnerve.

Large intestine
• It is the last part of the GIT.
• It consists of the ceacum, colon, rectum and anal canal.
• It begins in the right iliac fossa where the end of small intestine (ileum) joins the first part of the large intestine (ceacum) at the ilioceacalvalve.
• The water is absorbed here in addition to the waste product that are stored as feces to be removed in defecation.

• Teania coli: are 3 bands of longitudinal smooth muscles that run through the length of the colon and form the haustra (bulges in the colon)

• Sections of the colon:
1. Ascending colon
2. Transverse colon
3. Descending colon
• Of the above parts, the ascending and descending colon are retroperitoneal.
• Supplied by the superior and inferior mesenteric arteries (SMA & IMA) and drained by the superior and inferior mesenteric veins.
• Nerve supply: has a sympathetic and parasympethetic nerve supply.