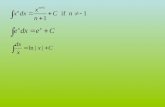A C CURA TE EXTRA C TION OF TISSUE P ARAMETERS FOR MONTEpeople.na.infn.it/~mettivie/MCMA...
Transcript of A C CURA TE EXTRA C TION OF TISSUE P ARAMETERS FOR MONTEpeople.na.infn.it/~mettivie/MCMA...

ACCURATE EXTRACTION OF TISSUE PARAMETERS FOR MONTE
CARLO SIMULATIONS USING MULTI-ENERGY CT
Arthur Lalonde and Hugo Bouchard
Département de physique, Université de Montréal

2
THE IMPORTANCE OF MC IN RT
Monte Carlo (MC) simulations offer many
advantages over conventional algorithms for dose
calculat ion:
• In brachytherapy, dose deposition depends
strongly on Z due to the dominance of
photoelectric effect at low photon energies.
• In particle therapy, accurate beam range
calculation is critical for optimal planning and
patient safety.0 50 100 150 200
Depth [mm]
0
20
40
60
80
100
Re
lative
do
se
[%
Dm
ax
]
183 MeV protons
Muscle
Adipose

3
PATIENT GEOMETRY TO MC INPUTS
• One of the key steps in the preparation of a MC simulation is the
creation of the patient geometry, including the assignment of
material composit ion in each voxel.
• Complete elemental composit ion and mass density is necessary to
calculate the exact cross sect ions for all interactions considered.
• Great at tent ion must be paid to this step as it influences all results
generated by the simulation: « Rubbish in, Rubbish out ».

4
THE SCHNEIDER METHOD
To extract MC inputs from single energy CT (SECT) data, the gold
standard is the method of Schneider et al. (2000). The CT is calibrated to
construct a segmented look-up table (LUT) that links every possible HU
to a certain set of MC inputs.
ALLO ALLOASTRO
ALLO ALLO
Reference
dataset
-1000 -500 0 500 1000 1500 2000 2500 3000
HU
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1
1.2
1.4
1.6
1.8
SP
R
Com
posi
tion 1
Com
posi
tion 2
Com
posi
tion 2
3
Com
posi
tion 3
Com
posi
tion 4
…

THE SCHNEIDER METHOD
To extract MC inputs from single energy CT (SECT) data, the gold
standard is the method of Schneider et al. (2000). The CT is calibrated to
construct a segmented look-up table (LUT) that links every possible HU
to a certain set of MC inputs.
ALLO ALLOASTRO
ALLO ALLO
Reference
dataset
-1000 -500 0 500 1000 1500 2000 2500 3000
HU
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1
1.2
1.4
1.6
1.8
SP
R
-150 -100 -50 0 50 100
HU
0.94
0.96
0.98
1
1.02
1.04
1.06
1.08
1.1
1.12
SP
R
Adiposetissue3
Adiposetissue2
Yellowmarrow
Adiposetissue1
Mammarygland1
Mammarygland2
Adrenalgland
Redmarrow
BrainCerebrospinalfluid
SmallintestinewallGallbladderbile
Pancreas
LymphProstate
Urine
Mammarygland3
Eyelens
Kidney1
Liver2 Spleen
Trachea
Skin1
Liver3
Skin2
Skin3
Thyroid
Connectivetissue
Up to 4.4%
errors
Com
posi
tion 1
Com
posi
tion 2
3
Com
posi
tion 2
Com
posi
tion 3
Com
posi
tion 4
…
5

6
DUAL AND MULTI-ENERGY CT
• With dual- or mult i-energy CT,
empirical LUT are obsolete, as
more information can be extracted
directly from MECT data
HU1
{
HU2
{
http://www.healthcare.siemens.com/.

7
DUAL AND MULTI-ENERGY CT
• With dual- or mult i-energy CT,
empirical LUT are obsolete, as
more information can be extracted
directly from MECT data
• Still not enough information to
derive directly MC inputs
• How can we use opt imally the
added informat ion to improve
the quality of MC inputs?
HU1
{
HU2
{
http://www.healthcare.siemens.com/.

8
CT DATA TO MONTE CARLO INPUTS
• We want to extract full atomic composit ion and mass density, but we have
only limited information (# of energies) per voxel.
• Tissue characterization for Monte Carlo dose calculat ion from CT data is an
underdetermined problem
• We propose to use principal component analysis (PCA) on reference dataset
to extract a new basis of variables that can describe human tissues
composition more efficient ly by reducing the dimensionality of the problem.
• We call these variables Eigent issues (ET)

9
CT DATA TO MONTE CARLO INPUTS
• We want to extract full atomic composit ion and mass density, but we have
only limited information (# of energies) per voxel.
• Tissue characterization for Monte Carlo dose calculat ion from CT data is an
underdetermined problem
• We propose to use principal component analysis (PCA) on reference dataset
to extract a new basis of variables that can describe human tissues
composition more efficient ly by reducing the dimensionality of the problem.
• We call these variables Eigent issues (ET)

10
EIGENTISSUE REPRESENTATION OF HUMAN BODY
• All informat ion relevant for dose calculat ion can be stocked in a
vector of partial electron densities:
• The ET representation consists of a linear t ransformat ion of x:
x = ⇢e [λ1 λ2 ... λM ]
= [x1 x2 ... xM ]
x = y1 ·ET1 + y2 ·ET2 + ... + yM ·ETM
Density of electrons Fraction of electrons of element M in the tissue
Vector of the partial densities in the M th eigentissue




14
APPLYING PCA TO HUMAN TISSUES
• Human tissues are composed of a limited number of elements.
Including trace elements, only 13 different chemical components are
reported in the literature.
• Also, the weight fraction of these elements is often strongly
correlated (ex: P & Ca) or ant icorrelated (ex: C & O).
• The eigentissues allow to characterize human t issues with less than 13
variables without losing much accuracy.
1414

15
ADAPTATION TO CT DATA
• Using a suitable stoichiometric calibrat ion, the photon at tenuat ion of
each ET can be estimated for any spect rum or imaging protocol.
ALLO ALLOASTRO
ALLO ALLO µ(Ei ,x) ⇡ f⇣k
(i )1 ,k
(i )2 , ...
⌘µ(Ei ,ET1)
µ(Ei ,ET2)...
µ(Ei ,ETM )
15

16
ADAPTATION TO CT DATA
• Once their attenuation coefficient is estimated, the ETs are treated as
virtual materials.
• If K information is available (i.e. K energies), decomposit ion is
performed to extract the fract ion of the K more meaningful ETs in
each voxel.
0
B@
y1
...
yk
1
CA ⌘
0
B@
µ(E1,ET1) . . . µ(EK ,ET1)...
......
µ(E1,ETK ) . . . µ(EK ,ETK )
1
CA
− 1 0
B@
µ(E1)...
µ(EK )
1
CA
1616

17
APPLICATION TO DECT: BENCHMARKING WITH OTHER
METHODS
• Comparison with two recently published
methods for the characterization of 43
reference soft tissues using DECT:
• Water-Lipid-Protein (WLP)
decomposition (Malusek et al. 2013)
• Parameterizat ion (Hünemohr et al. 2014)
• Simulated HU for 80 kVp and 140/Sn kVp
spectra of the SOMATOM Definition Flash
DSCT
EAC SPR
0
0.5
1
1.5
2
2.5
3
RM
S e
rro
r [p
.p.]
WLP
Parametrization
PCA
17
RMS error Mean error-0.2
0
0.2
0.4
0.6
Re
lative
err
or
on
SP
R [
%]
Schneider 2000
3 Materials
Parametrization
ETD

18
POTENTIAL EXTENSION TO MECT
• Separating a 140 kVp
spectrum in five
energy bins, the
method shows
improvement in
extracting elemental
weights with more
than two informat ion.
H C N O P Ca
Element
0
5
10
15
20
RM
S e
rro
r [p
.p.]
1 Energy bin
2 Energy bins
3 Energy bins
4 Energy bins
5 Energy bins
1818

19
VALIDATION OF ETD ON PATIENT GEOMETRY
• A virtual pat ient generated from real anatomical
data is used as ground truth for MC dose calculation
• A reference t issue with known composit ion is
assign to each voxel, while the density is allowed to
vary.
• SECT and DECT images are simulated using
Matlab
• Dose calculation is performed using the EGSnrc
user-code BrachyDose for Brachytherapy and
TOPAS for proton therapy
Adipose
Air
Calcifications
Femur spherical head
Femur conical trochanter
Muscle
Prostate
Red marrow
Small intestinewall
Bladder
0.9
1
1.1
1.2
1.3
1.4
3
Mass
den
sity
(g.c
m−
3)
19

20
ETD FOR BRACHYTHERAPY: RESULTS
No
nois
e
SECT DECT
-30 %
-20 %
-10 %
0 %
10 %
20 %
30 %
No
nois
eSECT DECT
-30 %
-20 %
-10 %
0 %
10 %
20 %
30 %
SECT - Schneider DECT - ETD
Relative
error on
dose
20See Poster #144 - Remy et al.

21
GT
ETD
GT
SECT
ETD FOR PROTON THERAPY: RESULTS

GT
ETD
GT
SECT
22
ETD FOR PROTON THERAPY: RESULTS
Range error up to 1.5 mm using SECT

23
CONCLUSION
• Eigent issues representation of human body composit ion minimizes the number of parameters needed for accurate
characterizat ion
• Adapting this representation to material decomposit ion of CT data allows extracting high quality Monte Carlo
inputs from only few measurements
• The method is accurate and versat ile:
• Not limited to only two parameters (EAN and ED)
• Valid through the whole range of X-ray energies (e.g. kV and MV)
• More accurate dose calculation for both low-kV photons and protons than the gold-standard SECT approach
• Associated Publicat ions:
• A. Lalonde and H. Bouchard (2016), A general method to derive tissue parameters for Monte Carlo dose
calculation with dual- and multi-energy CT, Phys. Med. Biol.
• A. Lalonde, E. Bär and H. Bouchard (2017). A Bayesian approach to solve proton stopping powers from noisy
multi-energy CT data, Med. Phys.
23

24
THANK YOU FOR YOUR ATTENTION
24
Acknowledgements:
• Charlotte Remy
• Esther Bär
• Jean-François Carrier
• Dominic Béliveau-
Nadeau
• Mikaël Simard