A and P Mod. #1 Plasma membrane
-
Upload
kelley-crawford -
Category
Documents
-
view
335 -
download
2
Transcript of A and P Mod. #1 Plasma membrane

Notes: Plasma Membrane pages 19 – 24
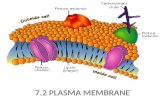
Fluid Mosaic ModelPlasma Membrane Anatomy
(Structure)
Function – regulates what goes in and out of the cell and holds the cell together.

Fluid Mosaic ModelPlasma Membrane Anatomy (Structure)
Structure - cell membrane is a phospholipid bilayer.

Fluid Mosaic ModelPlasma Membrane Anatomy (Structure)
What does that mean?
• it is bilayer – double layered
•the layers are composed primarily of a fat molecule (lipids) with one fatty acid replaced by a phosphate group
•if it dissociates it is easy for it to reform which also allows it to grow

Result of this anatomy of phospholipid bilayer is:
•plasma membrane has polar heads and nonpolar tails
http://www.ccs.k12.in.us/chsteachers/Amayhew/Biology%20Notes/transport%20notes_files/image001.gif

Result of this anatomy of phospholipid bilayer is:
• polar meaning water loving (hydrophilic)
• phosphate heads orient themselves towards the cytoplasm and extracellular fluids(fluids on outside of cell which contain water)

Result of this anatomy of phospholipid bilayer is:
•nonpolar meaning water hating (hydrophobic)
•lipid tails have an attraction for each other and orient themselves towards each other in the middle of the bilayer
Resulting in something like this:


Molecules found in plasma membrane:
1. Phospholipids – make up bilayer

Molecules found in plasma membrane:
2. Proteins float in the middle of the bilayerthere are three types

Molecules found in plasma membrane:2. Proteins
A. Channel proteins • protrude both sides• have channels through them thatlet things in and out
http://kentsimmons.uwinnipeg.ca/cm1504/Image133.gif

Molecules found in plasma membrane:
2. Proteins B. Glycoproteins - exterior
• composed of sugar and protein• used as markers for recognition
http://www.ideacenter.org/stuff/contentmgr/files/e27b080d92450837e43d44bf73780847/misc/glycoprotein.jpg

Molecules found in plasma membrane:
2. Proteins
C. Receptor proteins • receive messages by chemical means
from other cells• example type II diabetes
http://www.scq.ubc.ca/wp-content/uploads/2006/07/transduction.gif

Molecules found in plasma membrane:3. Cholesterol • composes 1/3 of layer• is nonpolar so found in middle• gives firmness to layer
http://www.uic.edu/classes/bios/bios100/lectf03am/cholesterol.jpg http://www.google.com/imgres?imgurl=http://people.csail.mit.edu/seneff/lipid_bilayer.jpg&imgrefurl=http://people.csail.mit.edu/seneff/statins_muscle_damage_heart_failure.html&usg=__tynxmR7yVcergl7D7HFAcPw8JnU=&h=375&w=449&sz=235&hl=en&start=5&sig2=NM3aH4MfKIzJCIJwCedN3A&um=1&itbs=1&tbnid=uMO9ybETB6CyuM:&tbnh=106&tbnw=127&prev=/images%3Fq%3Dcholesterol%2Bin%2Bplasma%2Bmembrane%26um%3D1%26hl%3Den%26rlz%3D1T4GZHY_enUS231US231%26tbs%3Disch:1&ei=s4MsTNb5I5GTkAXVgfWYCw


Membrane Transport

Physiology (functions) of plasma membrane
delimits cell – holds it together
provides receptors -sense the environment receiving messages
controls what moves in and out of the cell or selective permeability

Selective permeability – ability to let certain materials in or out while restricting others.

Membrane Transport
Membrane Transport – movement of substance into and out of the cell

Membrane Transport
There are two basic types of transport in the cells:
1. Passive transport and 2. Active transport

Membrane Transport
1. Passive transport
No energy is required includes diffusion, osmosis, and
facilitated or mediated transport

Passive Transport Processes
DiffusionParticles tend to distribute themselves evenly
Movement is from high concentration to low concentration,
or down a concentration gradient

Passive Transport Processes


Types of diffusion in the plasma membrane
A. Simple diffusion
unassisted process
solutes are lipid-soluble materials or small enough to pass through membrane pores

Types of diffusion in the plasma membrane
1. Simple diffusion
Remember most of membrane is lipid (nonpolar) and nonpolars dissolve nonpolars so fat molecules move easily through membrane

Types of diffusion in the plasma membrane
A. Simple diffusion
B. Osmosis simple diffusion of water Highly polar water easily
crosses the plasma membrane

Types of diffusion in the plasma membrane
A. Simple diffusionB. Osmosis
C. Facilitated/Mediated diffusion/transport
Substances require a carrier protein for passive transport
Carrier protein accepts a certain shaped molecule

Diffusion through the Plasma Membrane



Types of diffusion in the plasma membrane
A. Simple diffusionB. Osmosis C. Facilitated/Mediated diffusion/transport
3 conditions for regulating mediated transport:
i. Specificity – made for specific molecule
ii. Competition – similar shapes compete for same carrier, greater concentration wins
iii. Saturation – all carriers are full

Membrane TransportThere are two basic types of transport in the cells:
1. Passive transport
2. Active transport
The cell must provide metabolic energy
includes large non-lipid soluble molecules and the use of the sodium-potassium pump

Membrane TransportThere are two basic types of transport in the cells:
1. Passive transport2. Active transport
Metabolic energy comes from the molecule abbreviated ATP
ATP = Adenosine Triphosphate
Energy released when ATP looses a phosphate group and becomes ADP

Types of Active Transport
A. Pump – carrier protein will grab molecule and pump it against the concentration gradient (low to high)

Example: Sodium Potassium Pump


Types of Active Transport
B. Endocytosis – the process by which large molecules are taken into the cell

Types of Active Transport
Types of Endocytosis
i. Pinocytosis Means “water drinking” A mechanism by which cells
ingest extracellular fluid and its contents (proteins)
Membrane pinches to form vesicle containing protein

Pinocytosis
i

Types of Active Transport
Types of Endocytosis
ii. Phagocytosis Means “cell eating” The engulfing of microorganisms
or other cells and foreign particles
Not all cells can do this Most common in body are
white blood cells – defense

Phagocytosis

Types of Active Transport
C. Exocytosis the transportation of material from inside the cell to outside the cellGolgi apparatus plays a part

Exocytosis