8 measles
-
Upload
sumit-prajapati -
Category
Education
-
view
5.639 -
download
1
description
Transcript of 8 measles

MEASLESMEASLES
Fen Hua Chen, M.D.,PhD.Fen Hua Chen, M.D.,PhD.Department of Pediatrics, The Third Affiliated Hospital SuDepartment of Pediatrics, The Third Affiliated Hospital Su
n Yat-sen Universityn Yat-sen University

Measles is…Measles is…
an acute an acute viral infectionviral infection characterized by a characterized by a
maculopapular rashmaculopapular rash erupting successively erupting successively
over the neck, face, body, and extremitis aover the neck, face, body, and extremitis a
nd accompanied by a nd accompanied by a high fever.high fever.
DEFINITIONDEFINITION

ETIOLOGYETIOLOGY
Measles virusMeasles virusAn RNA virus of the genus Morbillivirus in the family of An RNA virus of the genus Morbillivirus in the family of ParamyxoviridaeParamyxoviridaeOne serotype, human’s only hostOne serotype, human’s only hostStable antigenicityStable antigenicityRapidly inactivated by heat and lightRapidly inactivated by heat and lightSurvival in low temperature.Survival in low temperature.

EEPIDEMPIDEMIOLOGYIOLOGYInfection sourcesInfection sources Patients of acute stage and viral carriers of atypical measlPatients of acute stage and viral carriers of atypical measl
esesTransmissionTransmission Highly contagious, approximately 90% of susceptible contHighly contagious, approximately 90% of susceptible cont
acts acquire the disease.acts acquire the disease. Respiratory secretionsRespiratory secretions: : maximal dissemination of virus ocmaximal dissemination of virus oc
curs by droplet spray during the prodromal period (catarrhcurs by droplet spray during the prodromal period (catarrhal stage).al stage).
Contagious from 5 days Contagious from 5 days before symptomsbefore symptoms, 5 days , 5 days after onsafter onset of rashet of rash
Seasons: in the spring, peak in Feb-MaySeasons: in the spring, peak in Feb-May

PATHOGENESIS AND PATHOGENESIS AND PATHOLOGY PATHOLOGY
Portal of entryPortal of entry Respiratory tract and regional lymph nodesRespiratory tract and regional lymph nodes Enters bloodstream (primary viraemia) Enters bloodstream (primary viraemia) monocyte – phagocyte monocyte – phagocyte syste syste
m m target organs (secondary viraemia) target organs (secondary viraemia)Target organsTarget organs The skin; the mucous membranes of the nasopharynx, The skin; the mucous membranes of the nasopharynx,
bronchi, and intestinal tract; and in the conjunctivaebronchi, and intestinal tract; and in the conjunctivae, , ectectResulting In-----Resulting In-----
1) Koplik spots and skin rash: 1) Koplik spots and skin rash: serous exudation and proliferationserous exudation and proliferation of of endotendothelial cells around the capillarieshelial cells around the capillaries
2) Conjunctivis2) Conjunctivis

PATHOGENESIS AND PATHOGENESIS AND PATHOLOGYPATHOLOGY
3)3) Laryngitis, croup, bronchitisLaryngitis, croup, bronchitis :general inflammatory reaction :general inflammatory reaction 4) Hyperplasia of lymphoid tissue:4) Hyperplasia of lymphoid tissue: multinucleated giant cells multinucleated giant cells
(Warthin-Finkeldey giant cells) may be found(Warthin-Finkeldey giant cells) may be found5) Interstitial pneumonitis:5) Interstitial pneumonitis: Hecht giant cell pneumoniaHecht giant cell pneumonia. . 6) Bronchopneumonia:6) Bronchopneumonia: due to secondary bacterial infectionsdue to secondary bacterial infections7) Encephalomyelitis:7) Encephalomyelitis: perivascular demyelinization occurs in arperivascular demyelinization occurs in ar
eas of the brain and spinal cord. eas of the brain and spinal cord. 8) Subacute sclerosing panencephalitis(SSPE):8) Subacute sclerosing panencephalitis(SSPE): degeneration of the cortex and white matter with intranuclear degeneration of the cortex and white matter with intranuclear
and intracytoplasmic inclusion bodiesand intracytoplasmic inclusion bodies

CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONCLINICAL MANIFESTATIONTypical Manifestation: Typical Manifestation:
patients havn’t had measles immunization, or vaccine failure with normal patients havn’t had measles immunization, or vaccine failure with normal immunity or those havn’t used immune globulinimmunity or those havn’t used immune globulin
1. Incubation period1. Incubation period (infection to symptoms) : (infection to symptoms) : 6-18days (average 10 days)6-18days (average 10 days)
2. Prodromal period:2. Prodromal period: 3-4 days3-4 days Non-specific symptoms: fever, malaise, anorexia, headacheNon-specific symptoms: fever, malaise, anorexia, headache Classical triad:Classical triad: cough, coryza, conjunctivitis cough, coryza, conjunctivitis (with(with photophobia, lacrimation)photophobia, lacrimation)

CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONCLINICAL MANIFESTATION Enanthem (Koplik spots):Enanthem (Koplik spots):
Pathognomonic for measlesPathognomonic for measles 24-48 hr before rash appears24-48 hr before rash appears 1mm, grayish white dots with1mm, grayish white dots with slight, reddish areolaeslight, reddish areolae Buccal mucosa, opposite theBuccal mucosa, opposite the lower 2lower 2ndnd molars molars increase within 1day and spreadincrease within 1day and spread fade soon after rash onsetfade soon after rash onset

CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONCLINICAL MANIFESTATION
Koplik spotsKoplik spots

CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONCLINICAL MANIFESTATION 3. Rash period3. Rash period 3-4days3-4days Exanthem:Exanthem: Erythematous, non-pruritic, maculopapularErythematous, non-pruritic, maculopapular
Upper lateral of the neck, behind ears, hairline,Upper lateral of the neck, behind ears, hairline, face face trunk trunk arms and legs arms and legs feetfeet
The severity of the disease is directly related to The severity of the disease is directly related to the extent and confluence of the rashthe extent and confluence of the rash, ,

CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONCLINICAL MANIFESTATION

CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONCLINICAL MANIFESTATION

CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONCLINICAL MANIFESTATION

CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONCLINICAL MANIFESTATION Temperature:Temperature: Rises abruptly as the rash appears Rises abruptly as the rash appears Reaches 40 or higher ℃Reaches 40 or higher ℃ Settles after 4-5 days – if persists, suspect secondarySettles after 4-5 days – if persists, suspect secondary infectioninfection Coryza, fever, and coughCoryza, fever, and cough:: Increasingly severe up to the time the rash has covered the Increasingly severe up to the time the rash has covered the bodybody Lymphadenopathy (posterior cervical region, mesenteric) Lymphadenopathy (posterior cervical region, mesenteric)
splenomegaly, diarrhoea, vomitingsplenomegaly, diarrhoea, vomiting Chest X ray:Chest X ray:
May be abnormal, even in uncomplicated casesMay be abnormal, even in uncomplicated cases

CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONCLINICAL MANIFESTATION 4. Recovery period4. Recovery period 3-4days3-4days Exanthem:Exanthem: Fades in order of appearanceFades in order of appearance Branny desquamation and brownish discoloration Branny desquamation and brownish discoloration
Entire illness – 10 daysEntire illness – 10 days

CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONCLINICAL MANIFESTATION

CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONCLINICAL MANIFESTATIONAtypical Manifestation:Atypical Manifestation:
1. Mild measles1. Mild measles In patients: administered immune globulin products durinIn patients: administered immune globulin products durin
g the incubation period and immunized against measles; ig the incubation period and immunized against measles; in infants <8mon infants <8mo
Long incubation period and short prodromal phaseLong incubation period and short prodromal phase Mild symptomMild symptom No Koplik spotNo Koplik spot The rash tends to be faint, less macular, pinpointThe rash tends to be faint, less macular, pinpoint No branny desquamation and brownish discoloration occNo branny desquamation and brownish discoloration occ
ur as the rash fadesur as the rash fades No complications and short courseNo complications and short course

CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONCLINICAL MANIFESTATION2. Severe measles:2. Severe measles: In cases with malnutrition, hypoimmunity and secondary In cases with malnutrition, hypoimmunity and secondary infectioninfection Persistent hyperpyrexia, sometimes with convulsions and evenPersistent hyperpyrexia, sometimes with convulsions and even coma coma Exanthem:Exanthem: Completely covered the skinCompletely covered the skin Confluent, petechiae, ecchymosesConfluent, petechiae, ecchymoses The hemorrhagic type of measles (black measles), bleedingThe hemorrhagic type of measles (black measles), bleeding may occur from the mouth, nose, or bowel. disseminated may occur from the mouth, nose, or bowel. disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) intravascular coagulation (DIC)

CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONCLINICAL MANIFESTATION

CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONCLINICAL MANIFESTATION3. Atypical measles syndroma:3. Atypical measles syndroma: Recipients of killed measles virus vaccine, who later come inRecipients of killed measles virus vaccine, who later come in contact with wild-type measles virus.contact with wild-type measles virus. Distinguished by high fever, severe headache, severe abdominalDistinguished by high fever, severe headache, severe abdominal pain, often with vomiting, myalgias, respiratory symptoms,pain, often with vomiting, myalgias, respiratory symptoms, pneumonia with pleural effusionpneumonia with pleural effusion Exanthem:Exanthem: First appears on the palms, wrists, soles, and ankles, andFirst appears on the palms, wrists, soles, and ankles, and progresses in a centripetal direction.progresses in a centripetal direction. Maculopapular Maculopapular vesicular vesicular purpuric or hemorrhagic. purpuric or hemorrhagic. Koplik spots rarely appear Koplik spots rarely appear

CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONCLINICAL MANIFESTATION
Atypical measles syndromaAtypical measles syndroma

CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONCLINICAL MANIFESTATION
4. Measles absent of rush4. Measles absent of rush Immunodepressed, or passive immunized recently cases andImmunodepressed, or passive immunized recently cases and occasionally in infants <9mo who have appreciable levels occasionally in infants <9mo who have appreciable levels of maternal antibodyof maternal antibody Non-specificityNon-specificity Difficult to diagnosisDifficult to diagnosis

COMPLICATIONSCOMPLICATIONS1. Respiratory Tract1. Respiratory Tract
Laryngitis, tracheitis, bronchitisLaryngitis, tracheitis, bronchitis – due to measles itse – due to measles itselflfLaryngotrachobronchitis (croup)Laryngotrachobronchitis (croup) –cause airway obstr –cause airway obstruction to require tracheostomyuction to require tracheostomySecondary pneumoniaSecondary pneumonia – immunocompromised, maln – immunocompromised, malnourished patients. pneumococcus, group Aourished patients. pneumococcus, group A
Streptococcus, Staphylococcus aureus andStreptococcus, Staphylococcus aureus and Haemophilus influenzae type B. Haemophilus influenzae type B.
Exacerbation of TBExacerbation of TB

COMPLICATIONSCOMPLICATIONS
2. Myocarditis 2. Myocarditis
3. Malnutrition and Vitamin A deficiency3. Malnutrition and Vitamin A deficiency

COMPLICATIONSCOMPLICATIONS 4. CNS4. CNS
The incidence of The incidence of encephalomyelitisencephalomyelitis is 1-2/l,000 cases of measl is 1-2/l,000 cases of measlesesOnset occurs 2-5 days after the appearance of the rashOnset occurs 2-5 days after the appearance of the rashNo correlation between the severity of the rash illness andNo correlation between the severity of the rash illness and
that of the neurologic involvementthat of the neurologic involvement Earlier - direct viral effect in CNSEarlier - direct viral effect in CNS Later – immune response causing demyelinationLater – immune response causing demyelination Significant morbidity, permanent sequelae – mentalSignificant morbidity, permanent sequelae – mental retardation and paralysis retardation and paralysis
Subacute sclerosing panencephalitis (SSPE): Subacute sclerosing panencephalitis (SSPE): extremely rare, extremely rare, 6-10 years after infection. Progressive dementia, fatal. Interact6-10 years after infection. Progressive dementia, fatal. Interaction of host with defective form of virusion of host with defective form of virus

LABORATORY EXAMINATIONLABORATORY EXAMINATIONIsolation of measles virus from a clinical specimen (e.g., nasopIsolation of measles virus from a clinical specimen (e.g., nasopharynx, urine)harynx, urine)Significant rise in measles IgG by any standard serologic assaSignificant rise in measles IgG by any standard serologic assayyPositive serologic test for measles IgM antibodyPositive serologic test for measles IgM antibodyImmunofluorescence detects Measles antigensImmunofluorescence detects Measles antigensMultinucleated giant cells in smears of nasal mucosaMultinucleated giant cells in smears of nasal mucosa
Low white blood cell count and a relative lymphocytosis in PBLow white blood cell count and a relative lymphocytosis in PBMeasles encephalitis – raised protein, lymphocytes in CSFMeasles encephalitis – raised protein, lymphocytes in CSF

DIAGNOSISDIAGNOSIS
characteristic clinical picture:characteristic clinical picture: Measles contactMeasles contact Koplik spotKoplik spot Features of the skin rashFeatures of the skin rash The relation between the eruption and feverThe relation between the eruption and fever
Laboratory confirmation is rarely neededLaboratory confirmation is rarely needed

DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSISDIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
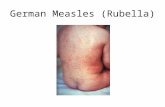
The rash of measles must be differentiated from that of The rash of measles must be differentiated from that of rubella; rubella; roseola intantum; roseola intantum; enteroviral infections; enteroviral infections; scarlet fever; scarlet fever; and drug rashes. and drug rashes.

Pathogen Features Rash fever Vs RashPathogen Features Rash fever Vs RashMeasles Measles Measles virus Cough coryza, conjunctivitis Red maculopapule fever for3-4days Measles virus Cough coryza, conjunctivitis Red maculopapule fever for3-4days Koplik spot after the Face Koplik spot after the Face trunk trunk limbs rises abruptly as limbs rises abruptly as 2nd -3rd fever Desquamation and the rash appears 2nd -3rd fever Desquamation and the rash appears discoloration discoloration Rubella Rubella Rubella virus Disease is mild, postau- Maculopapule Rubella virus Disease is mild, postau- Maculopapule fever fever for1-2daysfor1-2days ricular lymphadenopathy Face ricular lymphadenopathy Face trunk trunk limbs low or absent limbs low or absent No desquamation and during the rashNo desquamation and during the rash discolorationdiscolorationRoseola Roseola Human Generally well, Seizures Rose colored, spreads high fever for3-5 Human Generally well, Seizures Rose colored, spreads high fever for3-5 Infantum Infantum herpesvirus 6 (5-10%) due to high to the neck and theherpesvirus 6 (5-10%) due to high to the neck and the days, ceases withdays, ceases with fever trunk the onset of rash fever trunk the onset of rash Scarlet feverScarlet fever Group A High fever, toxicity, Gooseflesh texture on fever for1-2days Group A High fever, toxicity, Gooseflesh texture on fever for1-2days Streptococcus Angina, strawberry tongue an erythematous base higher as theStreptococcus Angina, strawberry tongue an erythematous base higher as the Circumoral pallor, tonsillitis for 3-5 day, desquam- rash appears Circumoral pallor, tonsillitis for 3-5 day, desquam- rash appears ation after 1 weekation after 1 weekEnteroviral Enteroviral Echovirus, Accompanied by respiratory Scattered maculeEchovirus, Accompanied by respiratory Scattered macule oror Rash appearsRash appearsInfections Infections Coxsackievirus or gastrointestinal maculopapule, few during or afterCoxsackievirus or gastrointestinal maculopapule, few during or after manifestation confluent, 1-3 days, fevermanifestation confluent, 1-3 days, fever no desquamationno desquamationDrug Rash Drug Rash Manifestations of Urticarial, maculopapula Relates to the Manifestations of Urticarial, maculopapula Relates to the primary disease, itchingprimary disease, itching or scarlatiniform rash drugs takenor scarlatiniform rash drugs taken

DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSISDIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Scarlet feverScarlet fever

DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSISDIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Scarlet feverScarlet fever

TREATMENTTREATMENTSupportive, symptom-directedSupportive, symptom-directed
Antipyretics for fever Antipyretics for fever Bed rest Bed rest Adequate fluid intake Adequate fluid intake Be protected from exposure to strong light Be protected from exposure to strong light
Antibiotics for otitis media, pneumoniaAntibiotics for otitis media, pneumoniaHigh doses Vitamin A in severe/ potentially severe High doses Vitamin A in severe/ potentially severe measles/ patients less than 2 yearsmeasles/ patients less than 2 years
100,000IU—200,000IU100,000IU—200,000IU

PREVENTIONPREVENTION1. Quarantine period1. Quarantine period
5 days5 days after rash appears, longer for complicated measles after rash appears, longer for complicated measles
2. Vaccine2. Vaccine The initial measles immunization is recommended at 8mo of The initial measles immunization is recommended at 8mo of ageage A second immunization is recommended routinely at 7yr of A second immunization is recommended routinely at 7yr of age age
3. Postexposure Prophylaxis3. Postexposure Prophylaxis Passive immunization with immune globulin (0.25mL/kg)Passive immunization with immune globulin (0.25mL/kg) is effective for prevention and attenuation of measles withinis effective for prevention and attenuation of measles within 5 days of exposure. 5 days of exposure.

THANK YOUTHANK YOU