5.4 – Use Medians and Altitudes
description
Transcript of 5.4 – Use Medians and Altitudes

5.4 – Use Medians and Altitudes

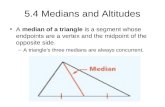
Median
Altitude
Line from the vertex of a triangle to the midpoint of the opposite side
Line from the vertex of a triangle perpendicular to the opposite side

Construct a triangle with the given sides. Then construct the median for each side of the triangle. What do you notice?
A B
A C
B C

A B
C

A B
C

Special Segment
Definition
Median
Line from the vertex to midpoint of opposite side

Concurrency Property Definition
Centroid 2/3 the distance from each vertex and 1/3 distance from the midpoint

Construct a triangle with the given sides. Then construct the perpendicular bisector for each side of the triangle. What do you notice?
A B
A C
B C

A B
C

A B
C



Special Segment Definition
Altitude
Line from vertex to the opposite side

Concurrency Property Definition
orthocenter
If obtuse – outside of triangle
If right – at vertex of right angle
If acute – inside of triangle

Perpendicular Bisector
Circumcenter
Angle Bisector
Incenter
Median Centroid
Altitude Orthocenter
P
A
M
A
C
I
C
O

6

In PQR, S is the centroid, PQ = RQ, UQ = 5, TR = 3, and SU = 2. Find the measure.
Find TP.
3

In PQR, S is the centroid, PQ = RQ, UQ = 5, TR = 3, and SU = 2. Find the measure.
Find SV.3
2

In PQR, S is the centroid, PQ = RQ, UQ = 5, TR = 3, and SU = 2. Find the measure.
Find RU.3
24 + 2 = 6 4

In PQR, S is the centroid, PQ = RQ, UQ = 5, TR = 3, and SU = 2. Find the measure.
Find ST.3
24
3

In PQR, S is the centroid, PQ = RQ, UQ = 5, TR = 3, and SU = 2. Find the measure.
Find VQ.3
24
3
5

In ABC, G is the centroid, AE = 12, DC = 15. Find the measure.
Find GE and AG.
A C
B
F
D E
G12
GE = 4
AG = 8

In ABC, G is the centroid, AE = 12, DC = 15. Find the measure.
Find GC and DG.
A C
B
F
D E
G12
GC = 10
DG = 5
15

Point L is the centroid for NOM. Use the given information to find the value of x.
OL = 5x – 1 and LQ = 4x – 5
5x – 1 = 2(4x – 5)
5x – 1 = 8x – 10
–1 = 3x – 109 = 3x3 = x
5x – 1
4x – 5

Point L is the centroid for NOM. Use the given information to find the value of x.
LP = 2x + 4 and NP = 9x + 6
3(2x + 4) = 9x + 6
6x + 12 = 9x + 6
12 = 3x + 66 = 3x2 = x
2x + 4
9x + 6