3g. describe the addition polymerization of alkenes and identify the repeat unit given the monomer,...
-
Upload
kelly-strickland -
Category
Documents
-
view
216 -
download
0
description
Transcript of 3g. describe the addition polymerization of alkenes and identify the repeat unit given the monomer,...

3g. describe the addition polymerization of alkenes and identify the repeat unit given the monomer, and vice versa
Crowe2008
Addition polymerization of alkenes
Connector - Draw the major addition products for the reactions between i) Br2 & ii) HBr with:
propene, but-1-ene, but-2-ene, and 2-methylpropene

C – C CH
H H H
H
H
Br Br
C – C CH
H H H
H
H
H Br
C C C CH
H H H
H
H
H
HBr Br
C C C CH
H H H
H
H
H
HBrH
Markovnikov addition
Markovnikov addition

C C C CH
H H H
H
H
HBrBrH
C C C CH
H H H
H
H
H
HBr H
C C
H CH3
H CH3
Br Br
C C
H CH3
H CH3
H Br
Markovnikov addition

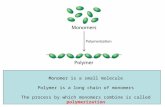
Monomers and Polymers
Ethene
Ethene is called a MONOMER because it is just one small molecule. We can use ethene to make plastics…
Step 1: Break the double bond
Step 2: Add lots of the molecules together:
This molecule is called POLYETHENE, and the process that made it is called POLYMERISATION

Manufacture of addition polymers.• An addition reaction is one in which two or more molecules join
together to give a single product. During the polymerisation of ethene, thousands of ethene molecules join together to make poly(ethene) - commonly called polythene.
• The number of molecules joining up is very variable, but is in the region of 2000 to 20000.
Conditions• Temperature: about 200°C • Pressure: about 2000 atmospheres • Initiator: a small amount of oxygen as an impurity

C CH
H
H
H HHC CHH H
H HC CH H
HHC CH H
HHC CH H
HHC CH H
Andlotsmore..
This is called addition polymerisationaddition polymerisation and is written as:
Pressure
high temperaturecatalyst
C CH
H
H
HC C
HH
H H
nn
ethene
poly(e)thene
1 2 3 4 5 thousands
Another way of drawing it…
n = a large number

Draw the equations for the polymerisation of the following alkenes and name the polymer:
C CnH CH3
HHn
tetrafluoroethene Poly(tetrafluoroethane)or PTFE
C CF F
F FC C
FF
FF
propene

n
tetrafluoroethene Poly(tetrafluoroethene)or PTFE
n
C CF F
F FC C
FF
FF
Poly(propene)C CHH
H CH3n
npropene
C CCH
H H
HHH
CH3

You may be asked to show polymerisation using three or more monomer units. e.g.
Draw a similar process for propene and chloroethene


Thermosoftening polymersor thermoplastics:
weak intermolecular forces –these let the chains slide past each other
These soften when heated and can be remoulded into new shapes

Plastics made of these polymers cannot be stretched, are rigid and have a high melting point. They are called thermosetting plastics (or ‘thermosets’).
strong intermolecular forces(cross-links) –these hold the chains firmly in place
Some polymer chains cannot slide past each other.What are thermosetting plastics?

Homework - Research the problems and solutions wrst the use of polymers.
You should include the following key areas:
• Energy
• costs
• sources
• Resources used
• Disposal problems
• biodegradable polymers
• Carbon footprint
• Recycling/reusing

Use the above data to compare the properties of PLA with polystyrene and PVC.Produce graphs to show the tensile strength, elastic modulus and tear strength as both hard sheets and soft films.How does PLA compare with conventional polymers?

Tensile strength
0102030405060708090
elastic modulus
0
0.5
1
1.5
2
2.5
3
Hard PLA polystyrene PVC Soft PLA polystyrene PVC
tear strength
0
100
200
300
400
500
600
700
800
900
Hard PLA polystyrene PVC Soft PLA polystyrene PVC
How does PLA compare with conventional polymers?
hard sheets soft films

Life cycle analysis

Life cycle analyses of three different materials for gas pipes cast iron polythene PVC
POCP 216 216 215ECA 26 6.4 3.9GWP 31 22 21AP 13 2.5 1.1ADP 9.7 1 0.45HT 14 1.9 0.76NP 2.5 0.61 0.33OTL 11 0.39 0.48ODP 1.25 0.17 0.07EC 748 303 139
•Present the information in the form of a bar chart so that the environmental features may be compared.•Suggest why the scientists may have been surprised by their findings.

Life cycle analyses of three different materials for gas pipes
•Suggest why the scientists may have been surprised by their findings.
cast iron polythene PVC




![ISTANBUL TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY INSTITUTE OF SCIENCE …yusuf/theses/gokhan_acik_MSc.pdf · polymerization with anionic insertion [14], activated monomer [14, 15], cationic [16- 20],](https://static.fdocuments.in/doc/165x107/5cada45b88c993ab638b52cb/istanbul-technical-university-institute-of-science-yusufthesesgokhanacikmscpdf.jpg)