3-(Winai Wananukul) Pharmacovigilance of vaccines and ...
Transcript of 3-(Winai Wananukul) Pharmacovigilance of vaccines and ...

Pharmacovigilance ofPharmacovigilance of
vaccines and snake antivenomvaccines and snake antivenom
Winai Wananukul, MDWinai Wananukul, MDDepartment of Medicine Department of Medicine
Faculty of Medicine Ramathibodi HospitalFaculty of Medicine Ramathibodi Hospital
Mahidol UniversityMahidol University
Bangkok, ThailandBangkok, Thailand
2nd Annual Symposium on Pharmacovigilance: Pharmacovigilance Strategy to Maximize Drug Safety. Hong Kong 4th March 2011
Faculty of Medicine Ramathibodi Hospital Mahidol UniversityFaculty of Medicine Ramathibodi Hospital Mahidol University

Adverse drug events (AEs) Adverse drug events (AEs)
Adverse drug reactions (ADRs)Adverse drug reactions (ADRs)
Methods of AEs (or ADRs) pharmacovigilance studySpontaneous report
Intensive monitoring

Spontaneous report vs. Intensive monitoringSpontaneous report vs. Intensive monitoring
SpontaneousSpontaneous
Observed population Larger
Feasibility √ √
Confounding +++
IntensiveIntensive
Smaller
√
+

Adverse events following vaccinationAdverse events following vaccinationin USAin USA
Vaccine adverse events reporting system (VAERS) reported incidences of AEs (per 1000,000 population)
H1N1 influenza vaccines 8.2
Seasonal influenza vaccines 4.7
Safety of influenza A (H1N1) 2009 Monovalent vaccines.
MMWR 2009;58:1351‐6.

Adverse events following vaccinationAdverse events following vaccinationin Australiain Australia
Adverse events following immunization (AEFI) reported the number of 46% increase of AEs in 2009.
Rate of AEs (per 100,000 population):H1N1 influenza vaccines in adults 34.2
H1N1 influenza vaccines in elderly 28.0
Seasonal influenza vaccines in adult 2.8
Seasonal influenza vaccines in elderly 1.6
Polysaccharide pneumococcal vaccine in elderly 13.3
Annual report: surveillance of adverse events following immunization in Australia 2009. Commun Dis Intell 2010;34:259‐76.

Pharmacovigilance of vaccinesPharmacovigilance of vaccinesin 2009in 2009--20102010
Mainly attributed to Influenza H1N1vaccine
Mass media and rumors are partially response for
the increased number of reports.

AEs following Influenza A (H1N1) vaccinationAEs following Influenza A (H1N1) vaccination
N=89.6 million dosesN=89.6 million doses
Adverse events Per 100,000
All 9.00
Verified as associated with vaccine 7.31
Safety of influenza A (H1N1) vaccine in postmarketing surveillance in China. N Engl J Med. 2011;364(7):638-47
Sources of data: National Immunization Information System's National Adverse Event Following Immunization Surveillance System

Adverse events following H1N1 Adverse events following H1N1 influenza vaccinationinfluenza vaccination
in Beijing, Chinain Beijing, ChinaTotal Adverse events:
612/2,113,280612/2,113,280 OROR 29.0/100,00029.0/100,000
In 612 cases:201 were coincidental illness
82 were psychogenic reactions
6 were inconclusive
Suspects Adverse events:
321/2,113,280321/2,113,280 OROR 15.2/100,00015.2/100,000
Analysis of adverse events following 2009 influenza A (H1N1) vaccinoprophylaxis in Beijing.
Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi Xue Za Zhi 2010;44:884‐7.

Type of reactions followingType of reactions followingH1N1 influenza vaccinationH1N1 influenza vaccination
in Beijing, Chinain Beijing, China
AEsVaccine reactions
(per 100,000 population)
Common reactions 9.65
Rare reactions 5.54
Serious reactions 0.19
Analysis of adverse events following 2009 influenza A (H1N1) vaccinoprophylaxis in Beijing.Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi Xue Za Zhi 2010;44:884-7

Adverse events followingAdverse events followingH1N1 influenza vaccinationH1N1 influenza vaccination
in Beijing, Chinain Beijing, China
PopulationsVaccine reactions
(per 100,000 population)
Total 15.20
Urban 16.87
Suburban 17.81
Rural 11.53
Analysis of adverse events following 2009 influenza A (H1N1) vaccinoprophylaxis in Beijing.Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi Xue Za Zhi 2010;44:884-7

Adverse events following vaccinationAdverse events following vaccinationin USAin USA
AEs H1N1 Seasonal
All AEs 8.2 4.7
Serious reactions 0.44 0.29
Safety of influenza A (H1N1) 2009 Monovalent vaccines. MMWR 2009;58:1351-6

Adverse events followingAdverse events followingH1N1 influenza vaccinationH1N1 influenza vaccination
in Thailandin Thailand
PopulationsVaccine reactions
(per 100,000 population)
Health personnel 1.71
Pregnancy 58.60
Chronic diseases 2.18
Over all 4.30
The Influenza Vaccine Adverse Event Surveillance SystemMinistry of Public Health, Thailand

Adverse events followingAdverse events followingH1N1 influenza vaccinationH1N1 influenza vaccination
in Ramathibodi Hospital, Thailandin Ramathibodi Hospital, Thailand
PopulationsVaccine reactions
(per 100,000 population)
Thai population 4.30
Health care workers in Ramathibodi Hospital
515(Probable 80.5%, Possible 19.5%)
High Coverage and Safety of Influenza A (H1N1) 2009 Monovalent Vaccination among Health-care Personnel in Thailand .
Am J Infect Control (in press)

82 Adverse events among 32 HCPsCharacteristics Probable Possible N (%)
Fatigue/uncomfortable feeling 18 2 20 (24.4)
Fever 10 1 11 (13.4)
Headache 8 2 10 (12.2)
Myalgia 6 2 8 (9.8)
Local response at injection site 5 0 5 (6.1)
Rashes 4 1 5 (6.1)
Nausea/vomiting 3 1 4 (4.9)
Drowsiness 2 1 3 (3.7)
Sore throat 1 2 3 (3.7)
High Coverage and Safety of Influenza A (H1N1) 2009 Monovalent Vaccination among Health-care Personnel in Thailand .Am J Infect Control (in press

82 Adverse events among 32 HCPsCharacteristics Probable Possible N (%)
Rhinorrhea 1 1 2 (2.4)
Chill 2 0 2 (2.4)
Conjunctivitis 1 0 1 (1.2)
Flushing face 1 0 1 (1.2)
Cough 1 0 1 (1.2)
Palpitation 1 0 1 (1.2)
Fainting 1 0 1 (1.2)
Itchy body 0 1 1 (1.2)
Muscle cramps 0 1 1 (1.2)
Total 66 16 82 (100)
Some health-care personnel might have more than one adverse drug events.
High Coverage and Safety of Influenza A (H1N1) 2009 Monovalent Vaccination among Health-care Personnel in Thailand .Am J Infect Control (in press)

Common Adverse events following vaccination
Over all H1N1 Influenza vaccines
Allergic reaction Allergic reaction
Injection site reaction Headache
Fever Fever
Headache Pain
Malaise Nausea
Nausea Injection site reaction
Annual report: surveillance of adverse events following immunization in Australia 2009. Commun Dis Intell 2010;34:259-76.

Serious reactions following vaccination
Death
Anaphylaxis
Guillian‐Barre′ syndrome

GuillianGuillian--BarreBarre′′ syndrome syndrome following vaccinationfollowing vaccination
Rate (per 100,000)
Swine Influenza vaccine (1976) 1
Seasonal influenza vaccine 0.1‐0.2

AEs following Influenza A (H1N1) vaccinationAEs following Influenza A (H1N1) vaccination
N=89.6 million dosesN=89.6 million dosesAdverse events Per 100,000
All 9.00
Verified as associated with vaccine 7.31
Rare and more serious reactions 1.21
Guillian‐Barre′ syndrome 0.01
Death 0.01
Safety of influenza A (H1N1) vaccine in postmarketing surveillance in China. N Engl J Med. 2011;364(7):638-47
Sources of data: National Immunization Information System's National Adverse Event Following Immunization Surveillance System

Serious adverse events following Serious adverse events following Influenza H1N1 vaccinationInfluenza H1N1 vaccination
in USAin USA
Incidence of serious reactions:Guillian‐Barre′ syndromeAnaphylaxis
Death
Each was less than 0.2/100,000 doses administered
Adverse events following influenza A (H1N1) 2009 monovalent vaccines reported to the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System, United States, October 1, 2009‐January 31, 2010.
Vaccine. 2010;28(45):7248‐55..

AEs following measles vaccineAEs following measles vaccine
Number of vaccination 14.3 millions
Incident of reactions (per 100,000 population)Serious reactions 0.214
Anaphylaxis 0.650
Acute disseminated encephalomyelitis
1 in 14.3 million
Idiopathic thrombocytopenia 1 in 14.3 million
Measles vaccine adverse events reported in the mass vaccination campaign of Sichuan province, China from 2007 to 2008.
Vaccine. 2009 Nov 10

AEs following papillomavirus vaccineAEs following papillomavirus vaccine
Incident of reactions (per 100,000 population)All AEs 53.9
Serious reactions 3.3
Anaphylaxis 0.1
Death 0.1
Transverse myelitis 0.04
Pancreatitis 0.04
Post licensure safety surveillance for quadrivalent human papillomavirus recombinant vaccine. JAMA. 2009 Aug 19;302(7):750‐7.

Safety of vaccines

Pharmacovigilance of Antivenom Pharmacovigilance of Antivenom

AntivenomAntivenom
Immunoglobulin, most common are from Horse (equine)
Sheep (ovine)
Antivenom exists asWhole molecule of IgG
F(ab)2Fab

Immunoglobulin, F(ab)2 and Fab Structures
Adapted from: Microbiology and immunology online, University of South Carolina School of Medicine

AntivenomAntivenom
Monovalent (monospecific):Antivenom neutralizes the venom of only one species of snake.
Polyvalent (polyspecific):Antivenom neutralizes the venoms of several different species of snakes.○ Hematotoxin: green pit viper, Malayan pit viper and
Russell's viper○ Neurotoxin: cobra, king cobra, banded krait and
Malayan krait

Antivenom reactionsAntivenom reactions
All reactions ≈10%
The reactions are both
Dose-related reactions
Hypersensitivity (IgE-mediated Type I hypersensitivity)

Early anaphylactic reactionsEarly anaphylactic reactions
Onset: within 10‐180 minutes of starting antivenom
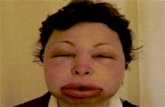
Clinical Manifestation:The patient begins to itch (often over the scalp) and develops urticaria, dry cough, fever, nausea,vomiting, abdominal colic, diarrhoea and tachycardia.
Only a minor proportion of these patients may develop severe life-threatening anaphylaxis.

Mechanism of the reaction
In most cases, these reactions are not truly “allergic”
Likely mechanismsComplement activation by IgG aggregates or residual Fc fragments
Direct stimulation of mast cells or basophils by antivenom protein

Late Late reaction reaction ((serum sickness typeserum sickness type))
Onset: 7 (1-12) days after treatmentClinical features:
Fever, nausea, vomiting, diarrhoeaItching, recurrent urticaria, arthralgia, myalgiaLymphadenopathy, periarticular swellings Mononeuritis multiplexProteinuria with immune complexEncephalopathy (rare)

Frequency of immediateFrequency of immediate--type hypersensitivity type hypersensitivity and anaphylaxis for each antivenomand anaphylaxis for each antivenom
Current use of Australian snake antivenoms and frequency oh immediate-type hypersensitivity reactions and anaphylaxis
MJA 2008;188(8): 473-6.
Study Year No of cases Antivenom reaction (%)
Severe anaphylaxis (%)
Trinca 1963 100 8 3
Campbell 1964 39 54 3
Campbell 1967 28 39 4
Sutherland & Lovering 1979 181 10 3
Jamieson & Pearn 1989 14 21 7
Sutherland 1992 86 5 0
Barret & Little 2003 20 15 NA
Williams et al 2007 136 10 5

Frequency of immediateFrequency of immediate--type hypersensitivity type hypersensitivity and anaphylaxis for each antivenomand anaphylaxis for each antivenom
Antivenom No Patient% of
reaction
Anaphylaxis (%)
Mild Moderate Severe
Brown snake 89 10 3 3 3
Tiger snake 59 41 22 8.5 10.2
Black snake 10 10 ‐ 10 ‐
Death adder 9 44 44 ‐ ‐
Taipan 5 20 20 ‐ ‐
Polyvalent 22 41 27.3 9.1 4.6
Current use of Australian snake antivenoms and frequency oh immediate-type hypersensitivity reactions and anaphylaxis
MJA 2008;188(8): 473-6.

Incidence of early reactions to Incidence of early reactions to horsehorse--derived F(ab)derived F(ab)22 antivenomantivenom
Number patients 254
ReactionsAll reactions 9 (3.5%)
Severe reactions 4 (1.6%)
Type of snake antivenomCobra antivenom caused more reactions than viper antivenom (odd ratio 9.2, 95 CI 1.6‐24.5)
Low incidence of early reactions to horse‐derived F(ab)2 antivenom for snake bite in Thailand.
Acta Tropica 2008;105: 203‐5.


High risk populationsHigh risk populations
Patients who have history of reactions to horse (equine) or sheep (ovine) serum Patients who have a strong history of atopic diseases (especially severe asthma)Antivenom therapy is not an absolute contraindication to antivenom treatment, but it should be given only if there are signs of systemic envenoming.

Prophylaxis regimenProphylaxis regimen
No prophylactic regimen that has been proved by clinical trial for its effectiveness.
The high risk patients may be pre-treatedempirically with subcutaneous adrenaline, (and intravenous antihistamines and corticosteroids)
In asthmatic patients, prophylactic use of an inhaled adrenergic β2 agonist may prevent bronchospasm.


Therapeutic drug Therapeutic drug for anaphyfor anaphylactic lactic reactionsreactions
Adrenaline is the most effective treatment foranaphylactic reactions, by reducing bronchospasm and capillary permeability
Interventions for preventing reactions to snake antivenom.
Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2000;(2):CD002153.

Early anaphylactic Early anaphylactic ReactionReaction
Adrenaline is given intramuscularly (into upper lateral thigh) in an initial dose of
0.5 mg for adults
0.01 mg/kg body weight for childrenThe dose can be repeated every 5‐10 minutes if the patient’s condition is deteriorating.

Additional treatmentAdditional treatment
Antihistamine H1 blocker: such as chlorphenamine intravenously, followed by hydrocortisone intravenously.
The corticosteroid is unlikely to act before several hours, but may prevent recurrent anaphylaxis

Treatment of late reactions Treatment of late reactions ((serum sicknessserum sickness))
Reactions may respond to a 5‐day course of oral antihistamine.Patients who fail to respond in 24‐48 hours should be given a 5 day course of prednisolone.

SummarySummary
Vaccine and antivenom should be considered as safe therapeutic agents.Adverse reactions following vaccination are mostly mild reactions. The serious and fatal reactions are not common. Antivenom adverse reactions are declining. Most reactions are mild.

Thank you for your attention.