3 Rock Types
-
Upload
naser-khan -
Category
Documents
-
view
8 -
download
1
description
Transcript of 3 Rock Types

Types of RocksSedimentary, Igneous, Metamorphic

Sedimentary Rocks• Made up of smaller rocks cemented together• Sometimes have fossils• Usually have layers

Sedimentary Rocks• Form when loose sediment (rocks, sand) is
deposited by water, compacted, and cemented together. • Form as a chemical reaction in the water that
leaves a chemical deposit, usually on an ocean bottom. • Form along beaches, by rivers, or under the water
in lake or oceans.

Sedimentary Rocks

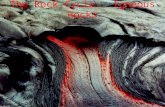
Igneous Rocks• Some were once liquid magma that erupted from
volcanoes. They cooled very quickly. (Extrusive)• Others were once liquid magma, but they did not
erupt from volcanoes. Instead, they cooled slowly underground. (Intrusive)

Igneous Rocks• Extrusive:• Rocks that are from cooled lava (above ground.• They cooled very quickly, therefore formed small
crystals• Intrusive• Rocks that are from cooled magma (below ground)• They cooled very slowly, therefore formed large
crystals

Igneous Rocks• Which is extrusive and which is intrusive?

Igneous Rocks

Metamorphic• Form when igneous, sedimentary, or other
metamorphic rocks are heated and/or squished, forming a new rock type. • Usually has interlocking crystals and layers (called
foliation)

Metamorphic• This can either happen underground or above
ground.• Underground: high pressure and heat• Above ground: volcano erupting• When classifying metamorphic rocks, they always
come from a parent rock

Metamorphic rock

Examples of Metamorphic Rocks