2.7 – Use of Absolute Value Functions and Transformations.
-
Upload
lilian-warner -
Category
Documents
-
view
218 -
download
0
description
Transcript of 2.7 – Use of Absolute Value Functions and Transformations.

2.7 – Use of Absolute Value Functions and Transformations

2.7 – Use of Absolute Value Functions and Transformations
• A transformation changes a graph’s size , shape, position, or orientation.
• A translation is a transformation that shifts a graph horizontally and/or vertically, but
does not change its size, shape, or orientation.

2.7 – Use of Absolute Value Functions and Transformations
• The graph of y = |x – h| + k is the graph of y = |x| translated h units horizontally and k
units vertically.
•The vertex would be (h, k)

2.7 – Use of Absolute Value Functions and Transformations

2.7 – Use of Absolute Value Functions and TransformationsWhen a = -1, the graph of y = a|x| is a
reflection in the x-axis of the graph of y = |x|. When a < 0, but a doesn’t equal -1, the graph of y = a|x| is a vertical stretch or shrink with a reflection in the x-axis of the graph of y = |x|.

2.7 – Use of Absolute Value Functions and Transformations
Example :Graph the function and compare the graph
with the graph of y = |x|:• y = |x -2| + 5
• Y = ¼|x|• f(x) = -3|x + 1| - 2

2.7 – Use of Absolute Value Functions and TransformationsTransformations of General Graphs

2.7 – Use of Absolute Value Functions and Transformations
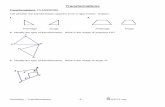
Example: The graph of a function y = f(x) is
shown. Sketch the graph of the given function.
a. y = 2f(x)b. y = -f(x + 2) + 1c. y = .5f(x)d. y = 2f(x – 3) – 1