2) Nucleus, plasma membrane, cell wall, mitochondria ......monomers) Function Examples Tests...
Transcript of 2) Nucleus, plasma membrane, cell wall, mitochondria ......monomers) Function Examples Tests...

1
1) Complete the chart below:
Organic Molecule
Building Blocks (subunits,
monomers)
Function Examples Tests
Carbohydrates
Lipids
Proteins
Nucleic Acids
2.02 Structure and function of cell parts.
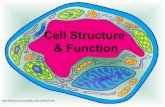
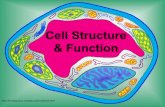
2) Label the following organelles and color them appropriately (use colors from chart below): Nucleus, plasma membrane, cell wall, mitochondria, vacuoles, chloroplast, ribosome.
3) Complete the following organelle chart including their function and an analogy for each organelle.
Organelle Function Analogy (Cell part is like a . .) Found in Animal Cell, Plant Cell, or
Both Nucleus (purple)
Plasma membrane (yellow)
Cell wall (green)
Mitochondria (red)
Vacuoles (brown)
Chloroplast (green)
Ribosome (blue)
4) Which cells would have more mitochondria – fat cells or muscle cells? Why?
5) Which cells would have more chloroplasts – stem, leaf, or root cells? Why?

2
6) Fill in the Venn diagram comparing Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic cells in terms of size, chromosome structure, organelles,
and types of organisms.
Prokaryotic Eukaryotic Both 7) Problem: cell is unable to make proteins. A scientist wants to study the effect of a certain chemical (Proteinex) on cell
function. They add Proteinex to a culture of skin cells. To another culture of skin cells, they add distilled water. The skin cells with Proteinex were unable to synthesize proteins, but the skin cells with distilled water continued to function normally.
Questions: What is your hypothesis on which cell organelle was damaged by Proteinex? What is the independent variable? What is the dependent variable? What is the control group? What is the experimental group?
8) From smallest to largest, fill in levels of cellular hierarchy: ________ à Tissues à_______________ à ________________ _______________ à ____________________ 2.03 Investigate and analyze the cell as a living system. 9) Name an organ in the human body that helps maintain homeostasis and explain how. 10) Define:
a. Active Transport b. Passive Transport c. Diffusion d. Osmosis e. Semi-permeable membrane
11) Using the figure to the right of a beaker filled with water, draw an arrow showing the direction the water would move across the membrane.
2.04 Investigate and describe the structure and function of enzymes. Explain their importance. 12) Explain what is meant by “they are re-usable and specific.”

3
13) Explain lock and key analogy. 14) What affects enzyme activity? 15) Label the diagram using the following terms: 2.05 Investigate and analyze bioenergetic reactions.
16) What are the main differences between aerobic and anaerobic respiration? (which one uses oxygen, which one makes more ATP?)
b. Aerobic – c. Anaerobic –
17) What is alcoholic fermentation? What are the products? What types of cells do this?
18) What type of fermentation might be used in your own muscle cells when they do not get enough oxygen? What might
this cause?
19) Equation for Cellular Respiration: _____ + _______________ à _________ + ___________ + ________ d. Reactants: e. Products:
20) Equation for Photosynthesis: _________ + ___________ + _______ à ______ + _______________
a. Reactants: b. Products:
21) Describe how carbon is cycled in an ecosystem. a. What is the role of photosynthesis in the environment.
b. What is the role of cellular respiration in the environment.
Goal 3: Learner will develop an understanding of the continuity of life and the changes of organisms over time. 3.01 Analyze the molecular basis of heredity. 22) Label the DNA diagram at the right with the following terms: deoxyribose sugar, phosphate group, pair the bases correctly(adenine, thymine, cytosine, guanine), and indicate where hydrogen bonds would be. Circle a nucleotide and draw a rectangle around a codon.
23) Using the Venn diagram below compare/contrast DNA and RNA.
DNA Both RNA

4
b. What is the role of mRNA? c. What is the role of tRNA?
24) Why is DNA Replication considered semi-conservative?
25) When in the cell cycle does DNA replication occur? Where in the cell does it happen? What bond must be broken for replication to occur?
26) What is Transcription and where does it happen?
27) What is Translation and where does it happen?
28) What is a codon?
29) Use this original DNA strand to make a complementary DNA strand. 30) TAC CGA CCT GGG TAT ATG ACT
a. Use the original DNA above to make an mRNA strand: b. Use the mRNA strand to make a polypeptide chain. p.292
31) What is cancer? 3.02 Compare and contrast the characteristics of asexual and sexual reproduction.
32) Complete the Venn diagram and compare and contrast mitosis and meiosis using the list of italicized terms: asexual, crossing over, diploid, clone, DNA replication, gametes, genetic variation, haploid, one nuclear division, two nuclear divisions, somatic (body cells), sexual.
Mitosis Both Meiosis
33) Put the stages of mitosis in order.

5
34) What is happening in this picture to the right? How does it increase variation? 35) A somatic cell of a dog has 78 chromosomes. What would be the haploid number of chromosomes in a sperm cell? What would be the diploid number of chromosomes in a skin cell? 36) What is a gene mutation? Define and give an example of each (with before and after mutation). Ch. 11.3 Before After
a. Point mutation b. Frameshift mutation
3.03 Interpret and predict patterns of inheritance. 37) Define and give an example of each:
a. Homozygous a. Heterozygous b. Genotype c. Phenotype
38) Using the diagram at right, what is the: a. Phenotype of the F1 generation? b. Genotypic ratio of the F2 generation?
39) Two heterozygous tall pea plants are crossed. If tall is dominant to short, what are the expected phenotypic results?
40) Blood Type question (Multiple Alleles): Mr. Jones has blood type A and Mrs. Jones has blood type AB. What is the chance that they will have a child with blood type A if both of Mr. Jones’s parents were AB?
41) Is it possible to have a child with type O blood if one parent is type A and the other is type B? Use a punnett square to prove your answer.
Key:
Key:

6
Key:
Key:
Key:
Key:
42) Color blindness is a sex-linked recessive trait. A mother with normal color vision and a colorblind father have a colorblind daughter. What does this conclude about the mother?
43) Two healthy parents have a child with cystic fibrosis. Use a punnett square to explain how this happened. What are the chances they will have another child with cystic fibrosis?
44) A woman is diagnosed to be heterozygous for Huntington’s. Her husband is healthy. What are the chances their children have the disorder? 45) A man is resistant to malaria. His wife has sickle cell anemia. What are the chances their children could be resistant to malaria? 46) In chickens, feather color is co-dominant. One allele codes for black and another allele codes for white. The heterozygous bird is checkered. Cross two checkered birds. What is the phenotypic ratio that results?
47) In snapdragons, flower color is inherited by incomplete dominance. There is a red allele, a white allele, and the heterozygous is pink. What is the phenotypic ratio if you cross a white flower with a red flower?
48) Use the pedigree showing inheritance of hemophilia to answer the following questions: *Remember: you may have to complete a Punnett square to answer the question correctly.
Key:
Key:

7
A
B
a. What is the genotype of individual I-1? b. What is the genotype of individual I-2? c. What is the phenotype of individual III-1? What is their genotype?
49) Black is dominant in rabbit fur color. Show a test cross you would use to determine a black rabbit’s genotype if mated with a white rabbit, it has 14 offspring: 7 black and 7 white.
50) What is a polygenic trait? Give three examples.
51) Why are males more likely to express a sex-linked disorder?
3.04 Assess the impacts of genomics on individuals and society. 52) What is the figure at the right called? 53) What can you tell about the person in the karyotype? 54) What is nondisjunction? What causes it? 55) A person that has cystic fibrosis receives a breathing treatment with a healthy form of the gene. What is this an example of? 56) How can genetic engineering allow us to produce human insulin using bacteria? Because the bacteria have a human gene inserted into them, they are considered a __________________ organism. 57) What is this image?
b. What process is used to prepare the image? c. Based on the evidence (Evs), who is guilty – suspect 1 or 2?
3.05 Examine the theory of evolution by natural selection. 58) Contrast abiogenesis (spontaneous generation) and biogenesis.
59) What did Louis Pasteur contribute to our understanding of biogenesis? 60) Explain Miller and Urey’s hypothesis and study diagram on page 382. 61) How did early Earth’s conditions contribute to the development of life? 62) What process made aerobic respiration possible? Why? 63) Explain the evolution of eukaryotic cells and aerobic organisms by filling in the boxes using the word phrases given. 64) Where do you find the oldest fossils in this picture?
-Evolution of Nucleus -Evolution of chloroplast from cyanobacteria. -Ancestral Prokaryotes -Evolution of mitochondria from aerobic bacteria.

8
C
D
E
65) Explain homologous structures.
66) Define Natural Selection 67) How are variation and natural selection related? What is the role of mutations in evolution? 68) About 10,000 years ago, a small population of squirrels became isolated on the north rim of the Grand Canyon. Separate gene pools formed and genetic changes appearing in one group were not passed to the other. This led to the formation of a distinct subspecies, the Kaibab squirrel. The native Abert’s squirrel and the Kaibab squirrel are very similar, but have distinctly different fur coloring. What caused the development of the subspecies? 69) Define the following and explain how they are related to natural selection:
Pesticide Resistance
Antibiotic Resistance 4.01 Analyze the classification of organisms according to their evolutionary relationships. Classification of Representative Mammals Kingdom Animalia Animalia Animalia Phylum Chordata Chordata Chordata Class Mammalia Mammalia Mammalia Order Cetacea Carnivora Carnivora Family Mysticeti Mustelidae Felidae Genus Balenopora Mustela Felis Species B. physalus M. furo F. catus Common name Blue whale Ferret Domestic cat 70) According to the chart above, which animal is least related to the others? the whale, ferret, or cat?
At which level does the ferret diverge from the blue whale? At which level does the ferret diverge from the cat?
71) Based on the cladogram, which are more closely related – bacteria and marsupials or birds and marsupials?

9
72) Originally there were only two kingdoms ( and animals), now there are 6 kingdoms. Use the chart to name and describe them all. Prokaryotic (no nucleus)
or Eukaryotic (has nucleus)?
Unicellular or multicellular? Method of obtaining nutrients
Special characteristics
Eubacteria
Archaebacteria
Protista
Fungi
Plantae
Animalia
73) Who came up with the two word naming system? What is this naming system called? 74) Name the eight levels of our current classification system starting from largest (most similarities) to smallest (most specific). 75) What is used to currently classify organisms that Darwin did not have access to? 4.02 Analyze the processes by which organisms accomplish the essential life functions. 76) Describe how each of the following move: a. Amoeba – b. Paramecium - c. Euglena -
77) Plants:
a. Compare and contrast vascular and nonvascular plants. Mosses are vascular or nonvascular? Why?
b. Fill in the chart: Location of seeds Method of seed dispersal
Gymnosperms Angiosperms
78) Why are the highly folded structures of mitochondria, intestines, and mammal brains significant? 4.03 Assess, describe and explain adaptations affecting survival and reproductive success. 79) List the main functions of these plant parts and name adaptations for survival:
a. Roots i. How do mycorrhizae aid in root function (relate your answer to #115)?
b. Stems
i. What are xylem and phloem? What do they do? c. Leaves
i. Label the picture of the leaf epidermis at the right include stomata and guard cells. 80) Discuss the relationship between angiosperms and their pollinators. 4.05 Analyze the broad pattern of animal behavior as adaptations to the environment 81) In the picture the dots in the beaker are single cellular organisms called euglena. What can you infer about these organisms based on the picture below?

10
82) Match the behavior with the definition ____ Innate ____ Social ____ Learned
a. populations of organisms communicates to insure survival of species.
b. inherited behavior in animals. c. behaviors gained from experience
83) Match the behavior with the example given ___ Habituation ___ Courtship ___ Trial and error ___ Imprinting ___ Pheromones ___ Classical conditioning
a. chemical signals b. dog drools at sound of bell after repeated association
of bell with food c. mouse and maze d. ducklings follow mother at birth e. prancing male peacock f. infant sleeps through 3rd week of neighbor’s
construction project Goal 5 Learner will develop an understanding of the ecological relationships among organisms. 5.01 Investigate and analyze the interrelationships among organisms, populations, communities and ecosystems. 84) List the levels of ecological organization from smallest to largest: 85) What is a symbiotic relationship? Define and give an example of the following symbiotic relationships. a. Mutualism-
b. Parasitism- c. What type of symbiosis could Nitrogen Fixation represent? Explain. 86) What is a limiting factor? What are some examples? 87) Using the population graph below label the carrying capacity, & portion of exponential growth. What are abiotic and biotic factors? 5.02 Analyze the flow of energy and the cycling of matter in the ecosystem. 88) What is a food chain? Draw a food chain including the following organisms: heron, minnow, plankton, bass.
a. Using the food chain above, draw and fill in a trophic pyramid. b. How much energy is typically passed from one trophic level to the next? What happens to the rest?

11
89) Label the food web with these terms: producer, primary consumer, secondary consumer, tertiary consumer, herbivore, and carnivore. 90) a. Using the food web, give an example of a predator/prey relationship and identify the predator & the prey.
b. What would happen if the grasshoppers were removed from the food chain by insecticides?
c. Where would you find bacteria in the food web and what is its primary role?
d. The berry tree is the base of this food web. What process does it use to provide energy?
e. What process would an organism use at the bottom of the ocean, where there’s no light?
f. Where would you find fungi in the food web and what is its primary role?
5.03 Assess human population and its impact on local ecosystems and global environments. 91) What does this graph depict about historical human population growth? 92) What does it indicate about possible future growth? 93) How have humans impacted ecosystems through: a. Acid rain
f. Habitat destruction (deforestation/habitat fragmentation)
g. Introduced non-native species

12
94) Climate change factors: a. Define greenhouse effect. i. How does the carbon cycle impact the greenhouse effect? ii. How have humans impacted the carbon cycle?
h. What is global warming and what causes it?
95) Explain ozone depletion. What causes it and why is it a problem? 96) Explain Biomagnification