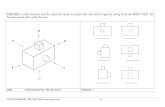
19834221 Orthographic Projection
-
Upload
govundan-guru -
Category
Documents
-
view
266 -
download
32
Transcript of 19834221 Orthographic Projection

ENGINEERING GRAPHICS IENGINEERING GRAPHICS I
Prof. N. P. Jadhav Prof. S. A. Ladkat
Presented by
Department of Mechanical EngineeringSinhgad Academy of Engineering, Pune
FIRST YEAR ENGINEERINGFIRST YEAR ENGINEERINGFIRST YEAR ENGINEERINGFIRST YEAR ENGINEERING

Unit 1 Curves used in Engineering Practice
SYLLABUS
Unit 2 Orthographic Projections
Unit 3 Auxillary Projections
Unit 4 Isometric Projections
Unit 5 Interpretation of Given Views/Missing
ViewsUnit 6 Freehand Sketching

Weightage for each Unit
SECTION I
Unit 1) Engineering Curves 15
Unit 2) Orthographic Projections 20
Unit 3) Auxillary Projections 15
SECTION II
Unit 4) Isometric Projections 20
Unit 5) Missing Views 20
Unit 6) Freehand Sketching 10

NATURE OF QUESTION PAPER
SECTION I
Q 1) Engineering Curves 15OR
Q 2) Engineering Curves 15
Q 3) Orthographic Projections 20
Q 4) Orthographic Projections 20OR
Q 5) Auxillary Projections 15
Q 5) Auxillary Projections 15OR

NATURE OF QUESTION PAPER
SECTION II
Q 7) Isometric Projections 20OR
Q 8) Isometric Projections 20
Q 9) Missing Views 20
Q 10) Missing Views 20OR
Q 11) Freehand Sketching 10
Q 12) Freehand Sketching 10OR

TERM WORK
Sheet No. 1 Engineering CurvesTo draw any four curves.
Sheet No. 2 Orthographic Views To draw two principal views, one sectional
views for two objects
Sheet No. 3 Auxillary ViewsTo draw auxillary views from the given views for any two objects.
Sheet No. 4 Isometric ViewsTwo problems
Sheet No. 5 Missing ViewsTwo problems

BOOKS
1 N.D. Bhatt, Elementary Engineering Drawing
2 P.S. Gill, Engineering Graphics
3 D. N. Johle, Engineering Drawing
4 Engineering Graphics by M. L. Dabhade.

ORTHOGRAPHICS PROJECTIONSORTHOGRAPHICS PROJECTIONSORTHOGRAPHICS PROJECTIONSORTHOGRAPHICS PROJECTIONS

Contents :
* Types of Drawing* Theory of projections* Types of projections* Perceptive projections* Oblique projections* Isometric projections* Orthographic projections* Quadrant systems* Principal planes* Glass box concept* First angle projection method

Contents :
* Principal projections* Conversion of pictorial view in to orthographic views
* Problems

Types of Drawings
Nature Drawings ( landscape, scenery etc.)
Geographical Drawings ( maps etc.)
Botanical Drawings ( plants, flowers etc.)
Zoological Drawings (creatures, animals etc.)
Portraits ( human faces,
expressions etc.)
Engineering Drawings
Machine component DrawingsBuilding Related Drawings
Orthographic Projections(FV,TV & SV.-Mech.Engg. terms)(Plan, Elevation- Civil Engg.terms)
(Working Drawings 2-D type)
Isometric ( Mech.Engg.Term.)or Perspective(Civil Engg.Term)
(Actual Object Drawing 3-D)

TorchLight Rays Ball
(Observer)(Projectors)
(Object)
(Plane of Projection)
Theory of Projection
Shadow
(Projection)
Wall

Projection means “To throw Forward”.
In this Object are being thrown (projected) forward in the form of Projection.
Torch Ball Shadow Wall
Torch Observer
Ball Object
Shadow Projection
Wall Plane of Projection

Types of Projection
Orthographic ProjectionOrthographic Projection
Oblique Projection
Perspective Projection
Isometric Projection

Perspective Projection
* Observer is at finite distance.
* Rays or Projectors are converging at observer’s eye.
* It does not provides exact size and shape of object.
ObjectPlane of p
rojection
Projection
Station point

Orthographic Projection
* Assume that observer is at infinite distance and rays or Projection lines are Parallel to each other and Perpendicular to the Plane of Projection.
* ORTHO means Perpendicular.
* Since the projectors are perpendicular to the plane of projection, the view is called Orthographic View and the projection method is called Orthographic projection.
Latin Origin

Orthographic Projection
* Orthographic projection is a two dimensional projection method.
* FV : Length and height of Object
* As projectors are Parallel to each other, the size of Orthographic View of an object is equal to the actual size of an object.
FOR F.V.
90 o90 o

Oblique Projection
* Observer is at infinite distance.* Rays or Projectors are Parallel to each other.
* Rays or Projectors are not Perpendicular to the Plane of projection. (i.e. projectors are inclined to the plane of projection i.e. oblique)
Φ ≠ 90o
Object
Projectors
Plane of projection
shadow

Isometric Projection
* Observer is at infinite distance.
* Rays or Projectors are parallel to each other & perpendicular to the plane of projection.
* All faces of the object are equally inclined to the planes of projection.
* All faces of the object are visible in a single view.

Quadrant system
1ST Quad.2nd Quad.
3rd Quad. 4th Quad.
VP
HPObserver
X
Y

Quadrant system
QuadrantQuadrant Observer; Object; Plane Observer; Object; Plane positionspositions
Position of object w.r.t. planes Position of object w.r.t. planes of projectionof projection
First Observer – Object – Plane Above HP, In Front of VP
Second Observer – Plane – Object Above HP, Behind VP
Third Observer – Plane – Object Below HP, Behind VP
Fourth Observer – Object – Plane Below HP, In Front of VP

TYPES
HORIZONTAL PLANE (H P)
PROFILE PLANE (PP)
VERTICAL PLANE (VP)
PRINCIPAL PLANES

Glass box concept

V. P.P. P.
H. P.
1st angle projection method

Projectors are perpendicular to respective Reference Plane and are also Parallel to each others
NOTE
F.V.
T.V.
L.H.S.V.
1st angle projection method

F.V.
T.V.
L.H.S.V.
NOTENOTE
Horizontal plane is rotated clockwise from the left and profile plane is rotated anticlockwise from the top so that all the three principal planes lies in a single plane .

V.P.
H.P.
P.P.
F V
T V
L H S V

V.P.
H.P.
P.P.
F V
T V
L H S V

F V
T V
L H S VX Y
X1
Y1

Important points for first angle projection methodImportant points for first angle projection method
* Object is situated in the First Quadrant.
* Object lies between the observer & Principal Planes.
* Orthographic projection of an object obtained on the VP is FV & always lies above the X-Y line.
* Orthographic projection of an object obtained on the HP is TV & always lies below the X-Y line.
* Orthographic projection of an object obtained on the PP is SV & always lies on the side of FV & above the X-Y line.
* RHSV is drawn on the left side of FV.* LHSV is drawn on the right side of FV.

PRINCIPAL PROJECTIONS
Direction of Direction of SightSight
Plane of ProjectionPlane of Projection Name of ProjectionName of Projection
Front Vertical Plane (VP) FV or ElevationTop Horizontal Plane
(HP)TV or Plan
Right Hand
Profile Plane (PP) RHSV
Left Hand Profile Plane (PP) LHSV

Conversion of Pictorial view into Orthographic Views
Study of the object.
Find the overall size of object i.e. Length, Width & Height.
Draw blocks for F.V. (L x H), T.V. (L x W) & S.V. (W x H) in their respective position according
to the method of projection.
Take suitable distance of above blocks from reference lines (X-Y & X1-Y1).

In respective block, first draw the contour of the view followed by visible edges & at the end draw the hidden details.
After drawing all views give all necessary dimensions (specify major dimension).
Draw the view first which gives maximum visibility & which is simple to draw.

IMPORANT POINTS
If line is parallel to both Vertical Plane & Horizontal Plane then Front View & Top View of the line always gives True Length on respective plane.
TL TL
CASE 1 :
TL
If line is perpendicular to one of the reference plane (say ┴ to H.P.) then the view obtained is always Point view.

IMPORANT POINTS
If Plane is Parallel to V.P. then in F.V. we get True Shape of Plane while in T.V. only Line View is observed.
TS
CASE 2 :
If Plane is Parallel to H.P. then in T.V. we get True Shape of Plane while in F.V. only Line View is observed.
TS

X Y
L.H.S.V.FOR L H S V
FOR T V
ORTHOGRAPHIC PROJECTIONS
FOR F V
F V
T V
X1
Y1
PROBLEM 1

X Y
FOR L H S V
FOR T V
FOR F V
X1
Y1
F V
T V
L.H.S.V.
PROBLEM 2
ORTHOGRAPHIC PROJECTIONS

PROBLEM 3
X
Length = 63 mm
Height = 37 + 10 = 47 mm
Width = 40 mm
F.V. = L x H = 63 x 47
T.V. = L x W = 63 x 40
S.V. = W x H = 40 x 47

X Y
X1
Y1X

PROBLEM 4
X
Length = 27+20+27 = 74 mmHeight = 8+8+25 = 41 mmWidth = 41 mm
F.V. = L x H = 74 x 41
T.V. = L x W = 74 x 41
S.V. = W x H = 41 x 41

X Y
X1
Y1X

Problem5 - Pictorial view of the object is as shown in fig. draw 1) Front View in direction of Arrow X
2) Top View 3) Right hand side view.
XX

H =
44
H =
44
L = 86W = 44
W =
44
T.V
F.VR.H.S.V.
L = 86
X
X1
Y
Y1


X Y
X1
Y1