12.01Q Which is the smallest blood vessel? 1.arteriole 2.artery 3.capillary 4.vein © Copyright 2008...
-
Upload
denise-pascal -
Category
Documents
-
view
218 -
download
1
Transcript of 12.01Q Which is the smallest blood vessel? 1.arteriole 2.artery 3.capillary 4.vein © Copyright 2008...

12.01Q Which is the smallest blood vessel?
1. arteriole
2. artery
3. capillary
4. vein
© Copyright 2008 Pearson Prentice Hall

12.01A Which is the smallest blood vessel?
Answer:capillary
Explanation:Capillaries are microscopic blood vessels that connect arterioles and venules. They are only one cell layer thick.
© Copyright 2008 Pearson Prentice Hall

12.02Q Which of the following contains blood with the highest oxygen content?
1. Capillaries in the tissues
2. Pulmonary artery
3. Pulmonary vein
4. Superior vena cava
© Copyright 2008 Pearson Prentice Hall

12.02A Which of the following contains blood with the highest oxygen content?
Answer:pulmonary vein
Explanation:The pulmonary vein carries blood from the lungs to the heart. Blood receives oxygen in the lungs and will contain the most oxygen at that time.
© Copyright 2008 Pearson Prentice Hall

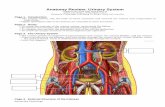
12.03Q Which of these most correctly traces the path of blood from the heart to a kidney and back to the heart again?
1. Left ventricle, vena cava, renal vein, kidney, renal artery, aorta, right atrium
2. Right atrium, aorta, renal artery, kidney, renal vein, vena cava, left atrium
3. Left ventricle, renal artery, kidney, renal vein, vena cava, right atrium
4. Left ventricle, aorta, renal artery, kidney, renal vein, vena cava, right atrium
© Copyright 2008 Pearson Prentice Hall

12.03A Which of these most correctly traces the path of blood from the heart to a kidney and back to the heart again?
Answer:Left ventricle, aorta, renal artery, kidney, renal vein, vena cava, right atrium
Explanation:Since blood is going to the body, begin with the left ventricle. According to Figure 12.1, blood next flows through the aorta to the renal artery, through the kidney and out the renal vein. The renal vein combines with the inferior vena cava and enters the heart through the right atrium.
© Copyright 2008 Pearson Prentice Hall

12.04Q Heart sounds result from ______.
1. closing of the heart valves
2. contraction of the ventricles
3. expansion and elastic recoil of arteries
4. flow of blood as it enters the heart
© Copyright 2008 Pearson Prentice Hall

12.04A Heart sounds result from ______.
Answer:closing of the heart valves
Explanation:The characteristic sounds of the heart are associated with the closing of the valves. The first sound is produced when the AV valves shut and the second heart sound is the closure of the semilunar valves.
© Copyright 2008 Pearson Prentice Hall

12.05Q What provides nutrients and oxygen to the heart muscle?
1. blood flowing through the heart
2. branches from the pulmonary veins
3. capillaries from the mammary arteries
4. cardiac circulation
© Copyright 2008 Pearson Prentice Hall

12.05A What provides nutrients and oxygen to the heart muscle?
Answer:cardiac circulation
Explanation:Coronary circulation services the tissues of the heart. Coronary arteries branch from the aorta, bringing oxygen and nutrients to the coronary tissue. After passing through the capillary beds that nourish the heart, blood enters cardiac veins, which join to form the coronary sinus returning blood to the right atrium.
© Copyright 2008 Pearson Prentice Hall

12.06Q If we had a two-chambered heart (one atrium and one ventricle) with the vena cava entering the atrium and the aorta leaving the ventricle, which of the following would be true?
1. no blood would reach the head and neck
2. no oxygen would reach the cells
3. the blood would be unable to carry food to the cells
4. there would be no bodily circulation
© Copyright 2008 Pearson Prentice Hall

12.06A If we had a two-chambered heart (one atrium and one ventricle) with the vena cava entering the atrium and the aorta leaving the ventricle, which of the following would be true?
Answer:no oxygen would reach the cells
Explanation:A two-chambered heart with the vena cava entering the auricle and the aorta leaving the ventricle would totally by pass the pulmonary circuit. The blood would never reach the lungs and would never pick up a fresh supply of oxygen to take to the cells.
© Copyright 2008 Pearson Prentice Hall

12.07Q Which of the following statements is correct for a normal heartbeat?
1. At any given time, either the atria or ventricles are contracted.
2. At any given time, the atria, the ventricles, or neither may be contracted.
3. Both right chambers of the heart contract simultaneously in one large surge.
4. Both atria and both ventricles contract simultaneously in one large surge.
© Copyright 2008 Pearson Prentice Hall

12.07A Which of the following statements is correct for a normal heartbeat?
Answer:At any given time, the atria, the ventricles, or neither may be contracted.
Explanation:During atrial systole both atria contract at once. During ventricular systole both ventricles contract at once. Then during diastole the atria and ventricles are both relaxed.
© Copyright 2008 Pearson Prentice Hall

12.08Q Normal blood pressure is considered to be 120/80. What does the “120” represent?
1. The pressure in the veins
2. The maximum pressure that can be sustained by the arteries before bursting
3. The highest ideal arterial pressure for someone at rest
4. The lowest pressure in the arteries that will keep someone from fainting when they stand up
© Copyright 2008 Pearson Prentice Hall

12.08A Normal blood pressure is considered to be 120/80. What does the “120” represent?
Answer:The highest ideal arterial pressure for someone at rest
Explanation:The systolic pressure, the highest pressure in the artery during each heartbeat of a healthy adult is about 120 mm of mercury.
© Copyright 2008 Pearson Prentice Hall

12.09Q Which of the following is a function of the lymphatic system?
1. cause elephantiasis
2. defend against disease
3. provide a mechanism for the spread of cancer cells
4. transport red blood cells and fibrinogen
© Copyright 2008 Pearson Prentice Hall

12.09A Which of the following is a function of the lymphatic system?
Answer:defend against disease
Explanation:The lymphatic system functions to return excess interstitial fluid to the bloodstream, transport products of fat digestion from the small intestine to the bloodstream, and help defend against disease-causing organisms.
© Copyright 2008 Pearson Prentice Hall

Stop & Think In a coronary bypass operation, why is it important for
the surgeon to suture the vein in place in the correct orientation?
1. The veins won’t attach properly and will leak
2. The heart will pump backward
3. Blood flow will be too turbulent
4. The one-way valves found in veins will prevent blood flow
© Copyright 2008 Pearson Prentice Hall

Stop & Think In a coronary bypass operation, why is it important for
the surgeon to suture the vein in place in the correct orientation?
Answer:The one-way valves found in veins will prevent blood flow
Explanation:Since veins do not have a pumping mechanism to move blood back to the heart, one-way valves prevent pooling in our lower extremities. Blood is prevented from flowing in the opposite direction by a flap-like valve.
© Copyright 2008 Pearson Prentice Hall

Stop & Think Cancer cells often break loose from their original site,
a process called metastasis. The cancer cells have easy access to the highly permeable lymphatic capillaries. Explain why the lymph nodes are often studied to determine whether the cancer has spread.
1. Lymph nodes strain out cells from the lymph. The presence of cancer cells indicates that the nearby organs may be affected.
2. Cancer makes lymph nodes swell like any infection.
3. Lymph nodes are the least likely cells to be cancerous.
4. Lymph nodes are easier to access than the nearby organs.
© Copyright 2008 Pearson Prentice Hall

Stop & Think Cancer cells often break loose from their original site,
a process called metastasis. The cancer cells have easy access to the highly permeable lymphatic capillaries. Explain why the lymph nodes are often studied to determine whether the cancer has spread?
Answer:Lymph nodes strain out cells from the lymph. The presence of cancer cells indicates that the nearby organs may be affected. Explanation:Lymph nodes cleanse the lymph. Since lymphatic vessels reach nearly all parts of our body, cancer may spread from the initial site to other organs.
© Copyright 2008 Pearson Prentice Hall

Stop & Think If an artery is cut, blood is lost in rapid spurts. In
contrast, blood loss through a cut vein has an even flow. What accounts for these differences?
1. Arteries are bigger than veins
2. Arteries have valves that open and close
3. Arterial blood is pumped by the heart, while blood in the veins moves through skeletal muscle pressure
4. Veins carry less blood than arteries
© Copyright 2008 Pearson Prentice Hall

Stop & Think If an artery is cut, blood is lost in rapid spurts. In
contrast, blood loss through a cut vein has an even flow. What accounts for these differences?
Answer:Arterial blood is pumped by the heart, while blood in the veins moves through skeletal muscle pressure
Explanation:Blood from a cut artery will spurt with each heart beat. Blood moves back to the heart through veins. These veins have one-way valves that prevent backflow. The pressure to force blood through the veins comes from muscle contractions when we move and breath.
© Copyright 2008 Pearson Prentice Hall

Stop & Think Why would sitting with your legs crossed favor the
formation of varicose veins?
1. The pooling of blood, expands the walls of the vein placing extra pressure on the valves
2. The lack of oxygen supply causes cell death
3. Constricting the arteries increases the pressure
4. Crossing your legs crushes the capillaries
© Copyright 2008 Pearson Prentice Hall

Stop & Think Why would sitting with your legs crossed favor the
formation of varicose veins?
Answer:The pooling of blood, expands the walls of the vein placing extra pressure on the valves
Explanation:The walls of the veins are very thin. Constriction of blood flow causes the pooling of blood that expands the walls of the vein. This places extra pressure on the valves. Sometimes a valve might weaken and fail placing even more strain on the next valve below.
© Copyright 2008 Pearson Prentice Hall

Stop & Think C-reactive protein (CRP) is an inflammatory chemical
released by injured cells in the artery lining. Why might CRP prove to be a better predictor of atherosclerosis than blood cholesterol level?
1. The added pressure on the heart causes inflammation
2. The accumulation of bad cholesterol in the artery is triggered by a small injury or inflammation
3. The C-reactive protein indicates high levels of stress
4. C- reactive protein is cheaper to measure than cholesterol
© Copyright 2008 Pearson Prentice Hall

Stop & Think C-reactive protein (CRP) is an inflammatory chemical
released by injured cells in the artery lining. Why might CRP prove to be a better predictor of atherosclerosis than blood cholesterol level?
Answer:The accumulation of bad cholesterol in the artery is triggered by a small injury or inflammation
Explanation:Atherosclerosis is thought to begin with an inflammation response to some injury in the artery. The damaged cells begin to accumulated LDL (the bad kind of cholesterol). The LDL stimulates the body’s defense response that thickens the walls. The cells continue to accumulate LDL molecules and a plaque develops.
© Copyright 2008 Pearson Prentice Hall

There are thousands more people in need of a heart transplant than there are available donor hearts. An artificial heart, AbioCor, is now approved by the FDA. To qualify as a recipient, a person must have a 70% chance of dying within the next 30 days. Some of the recipients have died within a day of receiving the artificial heart. Most have lived several months. As of mid-2004, the longest living recipient survived for 17 months. If you were in need of a transplant would you participate in the testing of an artificial heart?
1. No
2. Maybe
3. Yes
© Copyright 2008 Pearson Prentice Hall
What would you do?












![Capillary thermostatting in capillary electrophoresis · Capillary thermostatting in capillary electrophoresis ... 75 µm BF 3 Injection: ... 25-µm id BF 5 capillary. Voltage [kV]](https://static.fdocuments.in/doc/165x107/5c176ff509d3f27a578bf33a/capillary-thermostatting-in-capillary-electrophoresis-capillary-thermostatting.jpg)





