11.1 Area of Parallelograms
-
Upload
kristina-roko-evcevska -
Category
Documents
-
view
224 -
download
0
Transcript of 11.1 Area of Parallelograms
-
7/22/2019 11.1 Area of Parallelograms
1/13
-
7/22/2019 11.1 Area of Parallelograms
2/13
Find perimeters and areas ofparallelograms.
Determine whether points on acoordinate plane define aparallelogram and then find its area.
-
7/22/2019 11.1 Area of Parallelograms
3/13
Recall, a parallelogram is a quadrilateralwith both pairs of opposite sides ||.
Any side of a parallelogram can be called
the base. Each base has a corresponding altitude, a
segment which is to the base, called the
height..
height
base
-
7/22/2019 11.1 Area of Parallelograms
4/13
If a parallelogram has an area ofAsquare units, a base of bunits, and a
height ofhunits, thenA = bh.Example 1
Base = 15 units
Height = 12 unitsArea = 15 units x 12 units
Area = 180 sq. units
-
7/22/2019 11.1 Area of Parallelograms
5/13
Find the perimeter and area of theparallelogram.
-
7/22/2019 11.1 Area of Parallelograms
6/13
Since opposite sides are equal, theperimeter would be equal to thefollowing:
10 + 10 + 15 + 15 = 50 units
-
7/22/2019 11.1 Area of Parallelograms
7/13
To find the area you must first findthe height of the parallelogram.
The triangle in the parallelogram isa 30- 60- 90 triangle. With thisinformation we know that theshorter leg is equal to 1/2 of thehypotenuse or 1/2 (10) = 5.
The longer leg, which is the height,is equal to the 3 times the lengthof the shorter leg. Therefore, theheight is 53 or 8.7 units.
The area is then = to the base,15, times the height, 53.
A= 15 53A=129.9 units2
-
7/22/2019 11.1 Area of Parallelograms
8/13
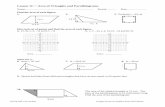
A water park is having a new pool built.Find the total surface area of the pool.
15 m
20 m
45 m
10 m
25 m
-
7/22/2019 11.1 Area of Parallelograms
9/13
15 m
20 m
45 m
10 m
25 m
First, divide the pool into three separate rectangles.
1
2
3
Then, find the lengths and widths (bases and heights) of each rectangle.
Rectangle 1 Rectangle 2 Rectangle 3
L = 20 m, W = 15 m L = 25 m,W = 4520 - 10 or 15 m
L= 25 -15 or 10 mW= 10 m
A = 20 x 15A = 300 m
A = 25 x 15A = 375 m
A= 10 x 10A= 100 m
Total Area= 300 + 375 + 100 or 775 m
-
7/22/2019 11.1 Area of Parallelograms
10/13
COORDINATE GEOMETRY The vertices of a quadrilateral are Q(-1, 4),R(2, 1), S(-1, -2), and T(-4, 1).
a. Determine whether the quadrilateral is asquare, arectangle, ora parallelogram.
b. Find the area of quadrilateral QRST.
Q
S
T R
-
7/22/2019 11.1 Area of Parallelograms
11/13
Slope of QR= =
Slope of RS= =
Slope of ST= =
Slope of QT= =
4-1
-1-2
1-(-2)
2-(-1)
-2-1
-1-(-4)
1-4
-4(-1)
3
-3or -1
3
3or 1
-3
3or -1
-3
- 3or 1
Q
S
T R
Opposite sides have the sameslope, so they are parallel. Also,the slopes of the consecutivesides are negative reciprocals ofeach other, so the sides areperpendicular. The quadrilateralis either a square or a rectangle.
Determine whether quadrilateral QRSTis asquare,rectangle, orparallelogram.
-
7/22/2019 11.1 Area of Parallelograms
12/13
Next, find the distance of the sides.
QR= (-1-2) + (4-1)
= 18 or 32
ST= [-4-(-1)] + [1-(-2)]
RS= [-2-(-1)] + [1-(-2)]= 18 or 32
QT= [-4-(-1)] + (1-4)
= 18 or 32
= 18 or 32
Since all sides have the same length,they are congruent and QRSTis asquare.
Q
S
T R
Let the base be RSand the height be ST. Since QRSTis a square, allsides measure 18 units.
A = bh
A= 18 18
A= 18 units2
-
7/22/2019 11.1 Area of Parallelograms
13/13
Pg. 598
#919, 2028 evens