10.5Ay Hyperbolas at Origin.notebook · 10.5Ay Hyperbolas at Origin.notebook 1 April 09, 2013 Dec...
Transcript of 10.5Ay Hyperbolas at Origin.notebook · 10.5Ay Hyperbolas at Origin.notebook 1 April 09, 2013 Dec...

10.5Ay Hyperbolas at Origin.notebook
1
April 09, 2013
Dec 78:03 AM Dec 78:03 AM
Dec 810:08 AM Apr 910:08 AM
Dec 810:51 AM Nov 297:37 AM
Algebra 2 10.5A Hyperbolas Centered at the OriginObj: able to write an equation of a hyperbola and sketch its graph
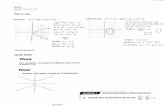
A hyperbola is the set of all points (x, y) such that the difference of the distances between (x, y) and two distinct fixed points, the foci (singular: focus), is a constant. The line through the foci (the two fixed points) intersects the hyperbola at two points, the vertices. The line segment joining the vertices is the transverse axis, and its midpoint is the center of the hyperbola. The graph of a hyperbola has two branches. The two diagonal lines that go through the reference rectangle are asymptotes for the hyperbola.

10.5Ay Hyperbolas at Origin.notebook
2
April 09, 2013
Nov 297:39 AM
Standard Equation of a Hyperbola (Center at Origin)The standard form of the equation of a hyperbola with center at (h, k) = (0, 0) is as follows.
Horizontal transverse axis
Vertical transverse axis
The vertices and foci are, respectively, a and c units from the center, and
Sketch the graphs of the following hyperbolas, including the reference rectangle and the asymptotes.1.
a = ____ b = ____ c = ____
C : ________________ F : _____________
V : ________________
Nov 297:42 AM
Sketch the graphs of the following hyperbolas, including the reference rectangle and the asymptotes.2.
Equation : ______________________________
a = ____ b = ____ c = ____
C : ________________ F : _____________
V : ________________
Nov 297:43 AM
Write an equation of a hyperbola with the given foci and vertices.3. Foci: (5, 0) and (5, 0) Vertices:(3, 0) and (3,0)
Nov 297:44 AM
Identifying the conic from the equation.
Parabola: only one variable was squared, either x2 or y2 .Examples: and
Circle: both x and y are squared, the coefficients on x2 and y2 are the same, and there is addition b/w x2 and y2 .
Example:
Ellipses: both x and y are squared, the coefficients on x2 and y2 are different, and there is addition b/w x2 and y2 .
Example:
Hyperbolas: both x and y are squared, the coefficients on x2 and y2 are different, and there is subtraction b/w x2 and y2 .Example:
Apr 97:55 AM