1 Urinary System Organs Kidney – Filters blood, allowing toxins, metabolic wastes, and excess...
-
Upload
lionel-griffin -
Category
Documents
-
view
213 -
download
0
Transcript of 1 Urinary System Organs Kidney – Filters blood, allowing toxins, metabolic wastes, and excess...
1
Urinary System Organs
Kidney – Filters blood, allowing toxins, metabolic wastes, and excess ions to leave the body in urine
Urinary bladder – provides a temporary storage reservoir for urine
Paired ureters – transport urine from the kidneys to the bladder
Urethra – transports urine from the bladder out of the body
3
Kidneys -Overview
Blood passes through kidney – filtration occurs at capillaries – 20% of plasma becomes filtrate
Filtrate passes through nephrons – water and electrolytes are reabsorbed
Some electrolytes, drugs and toxins may be secreted into filtrate by tubular secretion
= Urine
4
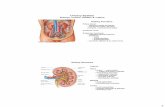
Nephron
Tubular structures that produce filtrate from plasma
Water, electrolytes, drugs and toxins are removed or added to filtrate as filtrate flows through tubules
5
The Nephron
Nephrons are the structural and functional units that form urine, consisting of:
Renal corpuscle
Glomerulus – a tuft of capillaries associated with a renal tubule
Glomerular (Bowman’s) capsule – blind, cup-shaped end of a renal tubule that completely surrounds the Glomerulus
Glomerular endothelium – fenestrated epithelium that allows solute-rich, virtually protein-free filtrate to pass from the blood into the glomerular capsule
8
Renal Tubule
Proximal convoluted tubule (PCT) – composed of cuboidal cells with numerous microvilli and mitochondria
Reabsorbs water and solutes from filtrate and secretes substances into it
Reabsorbs 100% of glucose, amino acids, escaped proteins, some vitamins, 60-70% of Na+, K+, Cl-, Ca++ and water
Secretes H+, NH3 (ammonia), drugs, toxins, uric acid and histamine
9
Renal Tubule
Loop of Henle – a hairpin-shaped loop of the renal tubule
Descending Limb
Impermeable to electrolytes, permeable to water
80% Water is absorbed, filtrate becomes hypertonic
Ascending Limb
Permeable to Na+ and Cl- but not water
Filtrate becomes hypotonic
10
Renal Tubule
Distal convoluted tubule (DCT)
Reabsorbs:
Na+ directed by aldosterone
Water directed by ADH
Ca++ directed by PTH
Some HCO3-, depending on pH of blood
Secretes:
NH3, K+, drugs, toxins, and creatinine
Some H+, depending on pH of blood
11
Collecting Tubule
Reabsorbs
Na+ directed by aldosterone
HCO3- depending on blood pH
Urea to maintain hypertonic interstitial fluid around nephron tubules
Water directed by ADH
12
Afferent and Efferent Arterioles
Larger diameter vessel is incoming – afferent
Smaller diameter vessel is outgoing – efferent and it becomes the peritubular capillaries
13
Capillary Beds of the Nephron
Every nephron has two capillary beds
Glomerulus
Peritubular capillaries
Each glomerulus is:
Fed by an afferent arteriole
Drained by an efferent arteriole