1 SURVEY OF BIOCHEMISTRY Glycogen. 2 What is Glycogen? Branched polymer of glucose Storage form of...
-
Upload
annabelle-fox -
Category
Documents
-
view
218 -
download
0
Transcript of 1 SURVEY OF BIOCHEMISTRY Glycogen. 2 What is Glycogen? Branched polymer of glucose Storage form of...
2
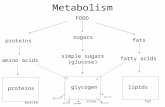
What is Glycogen?
• Branched polymer of glucose
• Storage form of glucose– Liver
• Maintenance of blood glucose levels, especially during fasting
– Skeletal Muscle• Fuel reserve for synthesis of ATP for muscle
contractionDraw Structure
3
Types of Polysaccharide Linkages
• What is an alpha 1->4 linkage?
• What is a beta 1->4 linkage?
• How are monosaccharides branched at C6?
Illustrate
5
Reducing v. Nonreducing Sugars
• A reducing sugar has an anomeric C that has NOT formed a glycosidic bond, such that it can reduce oxidizing agents.
Recall what ananomeric C is!
7
A Closer Look at Glycogen
• Today: Glycogen Breakdown
• Monday: Glycogen Synthesis
• Wednesday: Control of Glycogen Synthesis
8
Three Enzymes Involved in Glycogen Breakdown
• Glycogen Phosphorylase– Produces Glucose 1-Phosphate– Uses Pyridoxal 5’-Phosphate (cofactor)
• Glycogen Debranching Enzyme– 2 Enzymatic functions
• Produces glucose • Transfers branches onto main polymer chain
• Phosphoglucomutase
9
Glycogen Phosphorylase
Glycogen phosphorylase uses the cofactor pyridoxal 5’-phosphate to catalyze production of
glucose 1-phosphate from a terminal end of glycogen.
12
Glycogen Phosphorylase Mechanism
3. Formation of glucose 1-phosphate
+ Glycogenn-1
Glucose1-Phosphate
13
Three Enzymes Involved in Glycogen Breakdown
• Glycogen Phosphorylase– Produces Glucose 1-Phosphate– Uses Pyridoxal 5’-Phosphate (cofactor)
• Glycogen Debranching Enzyme– 2 Enzymatic functions
• Produces glucose • Transfers branches onto main polymer chain
• Phosphoglucomutase
17
How To Study
• Learn all 10 steps of Glycolysis– Substrates– Products– Enzymes– Know general process by which
mechanisms occur
• Learn 3 enzyme activities used to break down glycogen
18
PRS
• What is the maximum number of O2 molecules that hemoglobin can bind?
1. One2. Two3. Three4. Four
19
PRS
• What is the product formed by the activity of triose phosphate isomerase in glycolysis?
1. Glucose 1-phosphate2. Glucose 6-phosphate3. Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate4. Pyruvate
20
PRS
• How many ATP’s are produced after the first stage (Steps 1-5) of glycolysis?
1. None2. One3. Two4. Four
21
PRS
• Which of the following vitamins are fat soluble?
1. Vitamin C2. Vitamin A3. Riboflavin4. Folate
23
PRS
• Oxygen binding to myoglobin results in what shaped curve?
1. Sigmoidal2. Hyperbolic3. Linear4. Sinusoidal
24
PRS
• Which of the following amino acids is not in the catalytic triad of serine proteases?
1. Ser2. Thr3. His4. Asp