1 Seminar Overview of IPTV systems October 2009 Ernst Nordström [email protected].
-
Upload
nathaniel-holt -
Category
Documents
-
view
213 -
download
0
Transcript of 1 Seminar Overview of IPTV systems October 2009 Ernst Nordström [email protected].

2
Switch from analog TV to digital TV
• Countries in europe will switch from analog TV to digital TV by 2012
• Competition between traditional DTV operators (cable, satellite, terrestrial) and IPTV operators
• From a customer point of view, the meaningful differences between alternative DTV offerings are functionality, quality and price

3
History of IPTV
• Packet-oriented communication first proposed by Paul Baran, Rand Corporation, US in 1962
• Statistical multiplexing of video proposed by Haskell at Bell Laborarories, US in 1972 for a picturephone application
• First IPTV service in Europe introduced in Italy by FastWeb in 2001
• France Telecom and Telefonica introduced IPTV services in 2003

4
IPTV in parallel with Internet TV
• IPTV is called managed TV since capacity is reserved for video transmissions
• Internet TV is called unmanaged TV since capacity is not reserved for video transmissions
• Today telcos tend to offer IPTV and Internet TV in parallel

5
Worldwide IPTV subscribers
• Today (2009), there are almost 600 commercial IPTV launces worldwide
• Worldwide IPTV subscriber base will reach 19.6 M in 2008• Western Europe will reach 8.2 M subscribers in 2008 and
grow to 18.8 M in 2012• Asia-Pacific will reach 6.5 M subscribers in 2008 and grow
to 8.7 M in 2012• 1.1% of households worldwide will be IPTV subscribers in
2008• 2.8% of households worldwide will be IPTV subscribers in
2012• Some analysts believe it will take several years before the
customer base for IPTV will become significant (2013: 90 million; 2016: 300 million).
Source: Gartner

6
Market share of IPTV in the Swedish DTV market
• The Swedish DTV market is divided between different operator segments: cable operators (23%), satellite operators (35%), terrestrial operators (33%), and IPTV operators (9%).
• The company IDC predicts the market share of IPTV in Sweden will increase to 26% by 2011.
• Dominant digital IPTV operators in Sweden: TeliaSonera, Bredbandbolaget/Viasat, CanalDigital, and FastTV.

7
Top 10 IPTV operators in 2008
• Iliad (Free) - France• France Telecom (Orange) - France• PCCW - Hong Kong• Nuef Cegetel - France• Telefonica - Spain• Chunghwa Telecom - Taiwan• China Telecom - China• Belgacom - Belgium• TeliaSonera - Sweden• Fastweb - Italy

8
IPTV players
• Equipment providers
• Solution integrators
• Network providers
• Service providers
• Content providers

9
IPTV operators
• Incumbent telecoms (telco) operator– Incumbent owns network infrastructure
• Alternative network operator (ANO)– Fiber-to-the-home (FTTH), or – Local loop unbundling (LLU) rented from
incumbent operator

10
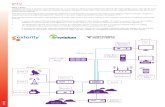
Sections of an IPTV system
• Head end is central or regional site that transmits video information stored on VoD and broadcast servers.
• Home end comprises the modem and reception equipment including PCs and set top boxes (STBs) where content is displayed.
• Aggregation and transport network consists of all the communication equipment to link the home and head ends.

11
IPTV architecture

12
Software components of an IPTV system
• Application and content platform
• Middleware
• Resource and admission control function

13
Hardware components of an IPTV system
• Home network– residential gateway– set top box
• IPTV service network– security and monitoring– IPTV HW platform– IPTV SW platform
• Access network– optical network– access network– IP & Ethernet aggregation– data centre network

14
IPTV video encoding and transmission
• Date centers in existing IPTV networks encode video information by MPEG-2 or MPEG-4 AVC
• Encoded video is transmitted using a CBR or capped VBR model
• CBR model gives constant bit rate at the price of variable quality
• VBR model gives constant quality at the price of variable bit rate

15
Categories of IPTV video transfers
• Stored video– Often requested video contents for BTV and VoD can
be transferred in advance from VHE to VHOs based on channel and program popularity scores
– Rarely requested video contents for BTV and VoD should not be prefetched and must be transferred on an on-demand basis
• Live video– Live video for BTV must be transmitted in real time
can not be prefetched and must be transferred on an on-demand basis

16
IP router
• Packet routers in IPTV networks consist of a switch core and multiple input and output controllers
• Queueing of packets is possible at the input/output controllers
• Input controllers have queues to store packets waiting for switching to an output link
• Output controllers have queues to store packets waiting to be scheduled for transmission

17
Performance measures
• Quality of Service (QoS)– Information transport performance– Packet loss, delay, delay variability
• Grade of Service (GoS)– Network availability– Call blocking probability, call set-up delay
• Quality of Experience (QoE)– Describes users satisfaction of all imperfections
affecting the service– Video quality, channel change time, blocking
probability for VoD requests

18
Traffic engineering in IPTV networks
1. IPTV networks are most likely to operate under packet scale congestion
2. Markov traffic models are sufficient for IPTV networks
3. Traffic smoothing or shaping is recommended and will improve the statistical multiplexing gain
4. Simple metods like Chernoff bound could be used by CAC in IPTV networks