1 Ch. 2-Anatomy and Physiology of Body Systems. 2 2.1 Anatomical Terminology The terms of ption...
-
Upload
felicia-owens -
Category
Documents
-
view
216 -
download
1
Transcript of 1 Ch. 2-Anatomy and Physiology of Body Systems. 2 2.1 Anatomical Terminology The terms of ption...

11
Ch. 2-Anatomy and PhysiologyCh. 2-Anatomy and Physiologyof Body Systemsof Body Systems

22
2.1 Anatomical Terminology2.1 Anatomical Terminology
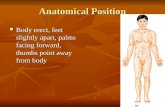
The terms of pThe terms of position includetion include Anatomical positionAnatomical position —The victim is standing erect, arms down —The victim is standing erect, arms down
to the to the sides, palms facing forward. “Right” and “left” refer to the , palms facing forward. “Right” and “left” refer to the victim’s right and left.victim’s right and left.
Supine positionSupine position —The victim is lying face up (on the back) —The victim is lying face up (on the back) Prone positionProne position —The victim is lying face down (on the stomach) —The victim is lying face down (on the stomach) Lateral recumbent positionLateral recumbent position —The victim is lying on the left or —The victim is lying on the left or
right side with the lower arm in front of the body, head dependent right side with the lower arm in front of the body, head dependent with no excess pressure on the chest. This is also known as the with no excess pressure on the chest. This is also known as the recovery, or coma, position.recovery, or coma, position.
Modified HAINES recovery positionModified HAINES recovery position – if the victim has a – if the victim has a suspected injury to the spine, is unresponsive, and has a possible suspected injury to the spine, is unresponsive, and has a possible airway compromise due to a large amount of blood, vomit or airway compromise due to a large amount of blood, vomit or secretions, place the victim in a modified HAINES recovery secretions, place the victim in a modified HAINES recovery position. Extend the victim’s arm above the head, logroll him onto position. Extend the victim’s arm above the head, logroll him onto his side so his head rests on the extended arm. Bend the knees to his side so his head rests on the extended arm. Bend the knees to stabilize his body. stabilize his body.

33
Supine Supine PositionPosition
Left lateral recumbent position Left lateral recumbent position (recovery/coma position)(recovery/coma position)Prone PositionProne Position
Right lateral recumbent Right lateral recumbent position (recovery/coma position (recovery/coma
position)position)
Modified HAINES Modified HAINES positionposition

44
Terms of Direction and Terms of Direction and LocationLocation
SuperiorSuperior—above, or higher —above, or higher than a point of reference than a point of reference (e.g., The knee is superior (e.g., The knee is superior to the ankle.)to the ankle.)
InferiorInferior—below, or lower —below, or lower than a point of reference than a point of reference (e.g., The wrist is inferior to (e.g., The wrist is inferior to the elbow.)the elbow.)
AnteriorAnterior—toward the front—toward the front PosteriorPosterior—toward the —toward the
backback MedialMedial—toward the midline —toward the midline
or center of the bodyor center of the body LateralLateral—to the right or left —to the right or left
of the midline; away from of the midline; away from the midlinethe midline
SuperficialSuperficial—near the —near the surfacesurface
DeepDeep—remote from the —remote from the surfacesurface
InternalInternal—inside—inside ExternalExternal—outside—outside

55

66
PROGRESS CHECKPROGRESS CHECK
1. A victim lying on his or her back is in the 1. A victim lying on his or her back is in the ____________ position. ____________ position. (supine/prone/lateral)(supine/prone/lateral)
2. A victim lying on her or his stomach is in the 2. A victim lying on her or his stomach is in the ____________ position. ____________ position. (supine/prone/lateral)(supine/prone/lateral)
3. ____________ means above a point of reference.3. ____________ means above a point of reference.(Superior/Anterior/Posterior)(Superior/Anterior/Posterior)4. ____________ means below a point of reference.4. ____________ means below a point of reference.(Superior/Inferior/Posterior)(Superior/Inferior/Posterior)5. A wound near the surface is a ____________ wound.5. A wound near the surface is a ____________ wound.(internal/external/superficial)(internal/external/superficial)

77
2.2 The Body’s Framework2.2 The Body’s Framework
SkullSkull Spinal ColumnSpinal Column ThoraxThorax PelvisPelvis Lower ExtremitiesLower Extremities Upper ExtremitiesUpper Extremities Joint MovementsJoint Movements

88
The Muscular SystemThe Muscular System
1.1. Skeletal muscle Skeletal muscle, or , or voluntary musclevoluntary muscle, is , is underunder
a person’s conscious control. a person’s conscious control.
2. 2. Smooth muscleSmooth muscle, or involuntary muscle, is , or involuntary muscle, is musclemuscle
over which a person has little or no conscious over which a person has little or no conscious control.control.
3. 3. Cardiac muscleCardiac muscle forms the walls of the forms the walls of the heart andheart and
is made up of a cellular mesh.is made up of a cellular mesh.

99
VocabularyVocabulary
articulate-articulate- To fit into each other To fit into each other fracture-fracture- A break in the bone A break in the bone skeletal (voluntary) muscle-skeletal (voluntary) muscle- Muscle that is under Muscle that is under
direct voluntary control of the braindirect voluntary control of the brain smooth muscle-smooth muscle- The muscles found in the walls of The muscles found in the walls of
the internal organs and blood vessels, generally not the internal organs and blood vessels, generally not under voluntary controlunder voluntary control
involuntary muscle-involuntary muscle- Smooth muscle over which a Smooth muscle over which a person has no voluntary or conscious controlperson has no voluntary or conscious control
cardiac muscle-cardiac muscle- The muscle that makes up the The muscle that makes up the heartheart

1010
PROGRESS CHECKPROGRESS CHECK
1. The largest bone in the body is the __________. 1. The largest bone in the body is the __________. (tibia/humerus/femur)(tibia/humerus/femur)
2. Dislocation will occur at _________________. 2. Dislocation will occur at _________________. (muscle attachments/joints/tendons)(muscle attachments/joints/tendons)
3. Deliberate acts, such as walking and talking, depend 3. Deliberate acts, such as walking and talking, depend on ____________ muscle. on ____________ muscle. (skeletal/smooth/cardiac)(skeletal/smooth/cardiac)
4. The movement of the intestines depends on 4. The movement of the intestines depends on ____________ muscle. ____________ muscle. (skeletal/smooth/cardiac)(skeletal/smooth/cardiac)

1111
2.3 The Body’s Organ 2.3 The Body’s Organ SystemsSystems
The Circulatory SystemThe Circulatory System HeartHeart Blood VesselsBlood Vessels PulsePulse BloodBlood

1212
The Respiratory SystemThe Respiratory System
ventilationventilation The mechanical process of The mechanical process of moving (breathing) air into and out of moving (breathing) air into and out of the lungsthe lungs
inhalationinhalation The act of breathing in The act of breathing in (inspiration), or the drawing of air or (inspiration), or the drawing of air or other gases into the lungsother gases into the lungs
inspirationinspiration The act of breathing in The act of breathing in (inhalation)(inhalation)

1313
The Digestive SystemThe Digestive System
Purposes:Purposes:
Ingest and carry foodIngest and carry food Digest foodDigest food Absorb nutrientsAbsorb nutrients Eliminate wastesEliminate wastes

1414
The Endocrine SystemThe Endocrine System
endocrine glands endocrine glands The ductless glands The ductless glands that regulate the body by secreting that regulate the body by secreting hormoneshormones

1515
PROGRESS CHECKPROGRESS CHECK
1. 1. The circulatory system has two major fluid The circulatory system has two major fluid transportationtransportation
systems: the cardiovascular and the ____________.systems: the cardiovascular and the ____________.(cardiopulmonary/genitourinary/lymphatic)(cardiopulmonary/genitourinary/lymphatic)2. 2. The mechanical process of moving air into and The mechanical process of moving air into and
out of the lungs is called ____________. out of the lungs is called ____________. (inspiration/ventilation/expiration)(inspiration/ventilation/expiration)
3. 3. The urinary system filters and ____________ body The urinary system filters and ____________ body wastes. wastes. (breaks down/metabolizes/eliminates)(breaks down/metabolizes/eliminates)
4. 4. Endocrine glands, which have no ducts, secrete Endocrine glands, which have no ducts, secrete ____________ directly into the bloodstream.____________ directly into the bloodstream.
(hormones/chemicals/fluids)(hormones/chemicals/fluids)

1616
2.4 The Nerves and Skin2.4 The Nerves and Skin
The nervous systemThe nervous system Enables the person to be aware of the Enables the person to be aware of the
environmentenvironment Enables the person to react to the Enables the person to react to the
environmentenvironment Coordinates responses of the body to Coordinates responses of the body to
stimulistimuli Keeps body systems working togetherKeeps body systems working together

1717
Nervous SystemNervous System
central nervous systemcentral nervous system The part of the nervous system that The part of the nervous system that consists of the brain and the spinal cordconsists of the brain and the spinal cord
peripheral nervous systemperipheral nervous system Structures of the nervous Structures of the nervous system (especially nerve endings) that lie outside the brain and system (especially nerve endings) that lie outside the brain and spinal cordspinal cord
Functional divisions:Functional divisions: voluntary nervous systemvoluntary nervous system is responsible for voluntary is responsible for voluntary
movements throughout the body movements throughout the body autonomic nervous system autonomic nervous system influences the involuntary influences the involuntary
function of muscles, glands and organs.function of muscles, glands and organs. sympathetic nervous systemsympathetic nervous system
parasympathetic nervous systemparasympathetic nervous system

1818
The SkinThe Skin
Protects internal organs from injuryProtects internal organs from injury Prevents dehydrationPrevents dehydration Protects against invasion by microorganismsProtects against invasion by microorganisms Regulates body temperatureRegulates body temperature Aids in elimination of water and various saltsAids in elimination of water and various salts Acts as the receptor organ for touch, pain, Acts as the receptor organ for touch, pain,
heat, and coldheat, and cold
EpidermisEpidermis- the outermost layer- the outermost layerDermisDermis- the inner layer, contains a vast - the inner layer, contains a vast network of blood vesselsnetwork of blood vessels

1919
Body CavitiesBody Cavities
cranial cavitycranial cavity —contains the brain —contains the brain spinal cavityspinal cavity —contains the spinal cord —contains the spinal cord thoracic cavitythoracic cavity —contains the heart, trachea, —contains the heart, trachea,
lungs, large vessels, and esophaguslungs, large vessels, and esophagus pericardial cavitypericardial cavity —the tough fibrous covering that —the tough fibrous covering that
contains the heartcontains the heart abdominal cavityabdominal cavity —contains the liver, spleen, —contains the liver, spleen,
gallbladder, small and large intestine, pancreas, gallbladder, small and large intestine, pancreas, appendix, and stomachappendix, and stomach
pelvic cavitypelvic cavity —contains the reproductive organs, —contains the reproductive organs, urinary bladder, urethra, rectum urinary bladder, urethra, rectum

2020
PROGRESS CHECKPROGRESS CHECK
1. The nervous system has two main functions: communication 1. The nervous system has two main functions: communication and ____________. and ____________. (sensation/control/reaction) (sensation/control/reaction)
2. The brain and spinal cord make up the ____________.2. The brain and spinal cord make up the ____________.(autonomic nervous system/central nervous system/voluntary (autonomic nervous system/central nervous system/voluntary
nervous system)nervous system)3. The peripheral nervous system is nerves located outside the 3. The peripheral nervous system is nerves located outside the
____________. ____________. (brain/spinal cord/brain and spinal cord)(brain/spinal cord/brain and spinal cord)4. The “fight-or-flight” syndrome is regulated by the ____________.4. The “fight-or-flight” syndrome is regulated by the ____________.(parasympathetic nervous system/sympathetic nervous system/ (parasympathetic nervous system/sympathetic nervous system/
central nervous system)central nervous system)5. The outer layer of the skin is called the ____________. 5. The outer layer of the skin is called the ____________.
(epidermis/dermis/subcutaneous)(epidermis/dermis/subcutaneous)6. The cavity that contains the urinary bladder is the ____________. 6. The cavity that contains the urinary bladder is the ____________.
(abdominal/thoracic/pelvic)(abdominal/thoracic/pelvic)








![Anatomical Terms [Zoology]](https://static.fdocuments.in/doc/165x107/54fc200e4a7959d43c8b4bf1/anatomical-terms-zoology.jpg)









