1 1919 - 1939. Compare the two maps of Europe. What changes do you see in the 1919 map? 1914...
-
Upload
sarah-gray -
Category
Documents
-
view
217 -
download
1
Transcript of 1 1919 - 1939. Compare the two maps of Europe. What changes do you see in the 1919 map? 1914...

11919 - 1939

Compare the two maps of Europe. What changes do you see in the 1919
map?1914 Europe 1919 Europe
2

After WW I things were “GOOD”
3
It was the Roaring 20’s
(5:32)

4
The League of Nations was one of Pres. Wilson’s 14 points.
Why was the League of Nations unsuccessful?
• US didn’t join the league– Senate refused to ratify it
• League members couldn’t agree to use force to stop aggression

5
What option did the League of Nations have to maintain peace?
(think $) • Could only use economic sanctions to
stop aggressionAccording to the League what should
nations reduce in order to prevent future wars?
•Nations should reduce their military

How did the French react when Germany claimed it couldn’t make
its annual payments?• Sent troops to occupy the Ruhr Valley• Would collect payments by running
the mines & factories
6
How did the Germans react?
•Strikes•Printed up more $$$ to pay the workers

7
Hyperinflation
• 1914 • 4.2 marks = 1 US
dollar• 1 Nov 1923• 130 billion marks = 1
US dollar• By the end of Nov
1923• 4.2 trillion marks = 1
US dollar

8
Money in Germany became worthless!

How do they get out of this jam?
• The Dawes Plan– Reduce reparations– matched Germany’s annual payments
with their ability to pay– 200 million loan for Germany recovery– Opened door for American investment
9
•Europe prospered for awhile (1924 – 29)

How did they keep the peace?
• Treaty of Locarno (1925)– Guaranteed Germany’s western borders
• Germany joined the “League” (1926)– Spirit of cooperation
• Kellogg-Briand Pact (1928)– 63 nations pledge – “to renounce war as an
instrument of national policy”
10

11
Then the Depression hit.What was The Great Depression?

12
The Great Depression
was a period of worldwide economic
depression that lasted from 1929 until
approximately 1939.

Credit Expands
• People bought goods they couldn’t afford on credit
• Q: What will happen if people suddenly lose their jobs after paying for things with Credit?
13
What is the Stock Market? (1:58)
What is buying on margin? (2:10)

Reparations
• German industry gone after WWI
• Q: Why would reparations destroy the German economy?
• Q: Where will Europe need to buy products from if they can’t buy from Germany?
• A: America
14

American industry toodominant
• Europe too dependent on US
• Q: What will happen to Europe if the American economy falls apart?
• A: Failed loans. • In the panic US investors withdrew more money
from Germany & Europe.• Thus weakening Europe’s banks.
15

Stock Market Crash,1929 (29 OCT)
• Q: What will happen to Europe now that the US economy is collapsing? Why?
16
$ 30 billion lost in two
days

17
CRASH !
The Great Depression
(1min)

Led to Bank RunsOccurred when a large number of bank customers
withdraw their deposits because they believe the bank is, or might become, insolvent (broke).
18
•Bank deposits were uninsured and thus as banks failed people simply lost their savings. •Surviving banks, unsure of the economic situation and concerned for their own survival, stopped being as willing to create new loans.•This worsened the situation leading to less and less spending.

Led to a Reduction in Purchasing Across the Board
• Which led to: – A reduction in production – A reduction of workers (Loss of
jobs) – Inability to pay for items they had
bought through installment plans – Led to repossession– More and more inventory began to
accumulate– Unemployment rate rose above
25%– which meant, even less spending19
With the stock market crash and the fears of further economic woes, individuals from all classes stopped purchasing items.

High Protective Tariffs
• Tariff = Tax on imported goods
• Hard for countries to trade with each other
• The most protectionist legislation in history, the Smoot-Hawley Tariff Act of 1930 raised tariffs on U.S. imports up to 50%.
20

Effects
21
Effects of the Great Depression (2:30)

Drought Conditions
22

The Dust Bowl
23
Woody Guthrie is perhaps one of the most famous American songwriters and singers of all time. His folk songs include This Land Is Your Land and Bound For Glory. Born in Oklahoma in 1912, Guthrie's song are preserved in the Library of Congress.
Dustbowl disaster (4:46)

The Dust Bowl– The Dirty Thirties -
24

The Dust Bowl– The Dirty Thirties -
25

The Dust Bowl– The Dirty Thirties -
26

Do dust storms still happen here in the
America?
27

28
What was Roosevelt’s plan?
• The New Deal• Public works• Welfare• SS
Didn’t solve the problem.
WW II does!

29
Act or Program Acronym Yr Enacted Significance
Agricultural Adjustment Act
AAA 1933 Protected farmers from price drops by providing crop subsidies to reduce production, educational programs to teach methods of preventing soil erosion.
Civil Works Administration
CWA 1933 Provided public works jobs at $15/week to four million workers in 1934.
Civilian Conservation Corps
CCC 1933 Sent 250,000 young men to work camps to perform reforestation and conservation tasks. Removed surplus of workers from cities, provided healthy conditions for boys, provided money for families.
Federal Emergency Relief Act
FERA 1933 Distributed millions of dollars of direct aid to unemployed workers.
Glass-Steagall Act FDIC 1933 Created federally insured bank deposits ($2500 per investor at first) to prevent bank failures.
National Industrial Recovery Act
NIRA 1933 Created NRA to enforce codes of fair competition, minimum wages, and to permit collective bargaining of workers.
National Youth Administration
NYA 1935 Provided part-time employment to more than two million college and high school students.
Public Works Administration
PWA 1933 Received $3.3 billion appropriation from Congress for public works projects.
Rural Electrification Administration
REA 1935 Encouraged farmers to join cooperatives to bring electricity to farms. Despite its efforts, by 1940 only 40% of American farms were electrified.
Securities and Exchange Commission
SEC 1934 Regulated stock market and restricted margin buying.
Social Security Act 1935 Response to critics (Dr. Townsend and Huey Long), it provided pensions, unemployment insurance, and aid to blind, deaf, disabled, and dependent children.
Tennessee Valley Authority
TVA 1933 Federal government build series of dams to prevent flooding and sell electricity. First public competition with private power industries
Wagner Act NLRB 1935 Allowed workers to join unions and outlawed union-busting tactics by management.
Works Progress Administration
WPA 1935 Employed 8.5 million workers in construction and other jobs, but more importantly provided work in arts, theater, and literary projects.

30
What were some of the effects of the Great Depression?
• People became desperate
• Renewed interest in Marxism
• Little confidence in their government
• Paved the way for extremist political parties

31
The Rise of Dictatorial Regimes
• By 1939 only two major European countries were still democratic
1.France
2.Great Britain

32
Why did Dictatorial Regimes Arise?
• Inflation
Severe economic problems after WW I
Workers strikes
Fear ofSocialist

33
Totalitarian• a form of govt. in which the political
authority exercises absolute and centralized control over all aspects of life
• the individual is subordinated to the state
• opposing political and cultural expressions are suppressed

34
The Rise of Nationalism in Europe...(8:30)

35
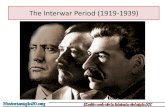
Benito Mussolini – Italy
• 1922• Fascist Party• Secret Police,
Imprisonment, Outlawing other parties, Propaganda, Censorship (press)
“IL DUCE”

36
New Era in the Soviet Union
• Between 1920 – 22 Russia was near an economic disaster (agriculturally & industrially)
• Lenin instituted a new economic policy (NEP) (modified capitalism)
• 1922 Russia became the USSR
• Union of Soviet Socialist Republics
• NEP saved Russia

37
Rise of Stalin
• Lenin died in 1924• Politburo was divided over country’s future
Joseph Stalin – continue NEP, rejected worldwide communism, focus on Russia, rapid industrialization would hurt the living standards of the peasants
Leon Trotsky – end the NEP, rapidly industrialize, spread communism

38
Joseph Stalin – USSR • By 1928• Communist Party• Purges• Prison camps• Secret Police• State-run press• Forced labor camps• Executions• 5 Year Plans –
economic plans
“Man of Steel”

39
Adolf Hitler – Germany
• 1933• NSDAP (Nazi)• SS police force,
propaganda, State-run press, Terror, Repression, Racial laws, Concentration & death camps

40
What is the difference?
• Communism – far Left (ultra Liberal)– Government controlled everything– No private ownership of industry!
• Fascism – far right (ultra conservative)– Racism– Uniforms (military)– Nationalism

41
10 Things You Don't Know About – ''Adolf Hitler'‘
(21:59)