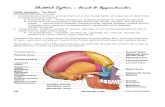
Formed by two sets of bones. ◦ Cranium: encloses and protects the fragile brain tissue ◦ Facial...
-
Upload
christina-barber -
Category
Documents
-
view
212 -
download
0
Transcript of Formed by two sets of bones. ◦ Cranium: encloses and protects the fragile brain tissue ◦ Facial...

The Axial Skeleton

Formed by two sets of bones. ◦ Cranium: encloses and protects the fragile brain
tissue◦ Facial bones: hold the eyes in an anterior position
and allow the facial muscles to show our feelings
Skull

Sutures are interlocking, immovable joints. All but the mandible (jawbone) are joined
together by sutures.
Sutures

Cranial “cavity” – houses brain Smaller cavities
◦ Housing middle and inner ear◦ Nasal cavity◦ Orbits◦ Sinuses
Openings (foramina, canals, fissures) for:◦ Spinal cord◦ Blood vessels◦ Twelve cranial nerves: I-XII

Composed of eight large, flat bones Except for two paired bones ( the parietal
and temporal), they are all single bones 1. Frontal bone – forms the forehead, the
bony projections under the eyebrows, and the superior part of each eye’s orbit
2 &3. Parietal bones – paired bones that form the superior and lateral walls of the cranium, meeting at the midline of the skull
Cranium

4 & 5. Temporal bones – lie inferior to parietal bones and have several important bone markings◦ External acoustic meatus – canal that leads to the
eardrum◦ Styloid process- attachment point for neck muscles◦ Zygomatic process- thin bridge of bone that joins with
the cheekbone (zygomatic bone)◦ Mastoid process – behind ear, contains mastoid
sinuses and point of attachment for neck muscles◦ Jugular foramen, Internal acoustic meatus, and carotid
canal – passageways for blood vessels and nerves
Cranium Continued

6. Occipital bone – most posterior bone of the cranium, forms the floor and back wall of the skull◦ In the base of there is a large hole, foramen
magnum, that surrounds the lower part of the brain and allows the spinal cord to connect with the brain
Cranium continued

7. Sphenoid bone – butterfly- shaped bone that spans the width of the skull and forms part of the floor of the cranial cavity. ◦ Contains Turk’s saddle, which holds the pituitary
gland in place ◦ Contains foramen ovale so the cranial nerves can
pass through
Cranium continued

8. Ethmoid bone- irregular and lies anterior to the sphenoid, forms the roof of the nasal cavity and part of the medial walls of the orbits.
Cranium Continued


Facial bones (anterior aspect of skull)◦ Form framework of face◦ Form cavities for sense organs of sight, taste
and smell◦ Provides openings for passage of air and food◦ Hold the teeth◦ Anchor the muscles of the face
Facial Bones

Fourteen bones Following are all paired:
◦ Maxillae, zygomatics, palatines, nasals, lacrimals, and inferior nasal conchae
Unpaired:◦ Vomer and mandible
Hyoid: not really a skull bone, supported in the neck only by ligaments
Facial Bones

Only bone which does not articulate with any other bone
Moveable base for the tongue
Points of attachment for neck muscles that raise and lower the larynx during swallowing
Hyoid bone

Maxillae : upper jaw Palatine: posterior part of hard palate Zygomatic: Cheekbones, form part of
lateral orbital walls Lacrimal: medial walls of orbits, groove
serves as tear passage Nasal bones: nose bridge
Facial Bones

Of bone and cartilage Roof is ethmoid Floor formed by
palatine processes of the 2 maxillae and horizontal plates of palatine bones◦ These nasal-floor
structures form roof of the mouth, called the hard palate
Nasal cavity nasal bone
ethmoid
vomer
inf nasal concha
(part of slide 18)
maxilla___________

Vomer bone: forms nasal septum Inferior conchae: lateral walls of the nasal
cavity Mandible: lower jaw
Facial bones





Remember that the Axial skeleton includes:
SkullVertebral columnThoracic cage
Axial skeleton is shown in green

Fetus and infant: 33 separate bones, or vertebrae
Adult: 24 vertebrae◦ Inferior 9 have fused forming
The sacrum (5) and The coccyx (4)
The Vertebral Column

Cervical – 7 Thoracic - 12 Lumbar - 5 Sacrum (5 fused) Coccyx (4 fused)
Vertebrae

Cervical and lumbar are concave posteriorly* (lordosis)
Thoracic and sacral are convex posteriorly* (kyphosis)
Abnormal◦ Too much of either◦ Scoliosis (more than 10
degrees of lateral curvature)
*when viewed from the side
Spinal curvatures

Abnormal curvatures


Structure of a typical vertebra

Cervical vertebrae (C1-C7)C1 (atlas)
C2 (axis)

Smallest Lightest Most flexible Triangular
vertebral foramen
Transverse processes have foramina (transverse foramen)
Spinous process bifid (forked) except for C7
Cervical Vertebrae

Heart shaped body
Additional small costal facets (costal=ribs)
Round or oval vertebral foramen
Form posterior part of rib cage
Thoracic Vertebrae T1-T12

Massive blocklike bodies
Short, thick hatchet-shaped spinous processes
Limited mobility
Lumbar Vertebrae L1-L5

The SacrumShapes posterior wall of pelvis
Composite bone of 5 fused vertebrae
Sacral foramina allow passage of vessels & nerves
Coccyx(the tailbone)

Remember that the Axial skeleton includes:
SkullVertebral columnThoracic cage
Axial skeleton is shown in green

The Thoracic Cage

Manubrium
Body
Xiphoid process
True ribs 1-7
False ribs 8-12
Floating ribs 11,12
Sternum Ribs

Vertebral and Sternal Articulations

Typical rib


Skulls of newborns contain fontanels (membranous areas), which allow brain growth.
The infant’s facial bones are very small compared to the size of the cranium
Fetal skull ossifies after 22-24 months
Fetal vs. Adult Skull

Fontanels Unossified remnants
of membranes Present at birth Anterior fontanel
largest Called “soft spots” Ossify by 1 ½ - 2
years
Continue to ossify into adulthood; the sutures can become fused in old age