SBIRT: Screening, Brief Intervention and Referral to Treatment
A test of a new intervention or treatment on people.
-
Upload
frederick-perkins -
Category
Documents
-
view
215 -
download
0
Transcript of A test of a new intervention or treatment on people.


A test of a new intervention or treatment on people

To allow medical professionals and patients gain information about the benefits, side effects and possible uses of new drugs as well as new ways to use existing drugs
To translate results of basic scientific research into better ways to prevent, diagnose, or treat cancer

We need to know that any treatments we recommend are both safe and effective in humans
Cell culture and animal work can only take us so far!
Especially in Oncology, people are always looking for the miracle cure-and it is easy to get dragged into the idea
Scientific, medical, evidence-based paradigm

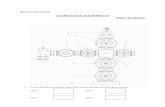
Treatment trials Prevention trials Early-detection trials/screening trials Diagnostic trials Quality-of-life studies/supportive care studies
Genetic trials

It can be a phase I, II or III trial It can be randomized or not It can be blinded or not It can involve a placebo or not It can be a pilot study or not

◦ 15-30 people◦ Determines
what dose is safe How the treatment should given How the treatment affects the body Safety (the safest dose)

◦ Less than 100 people◦ Determines
Whether the treatment does what it is supposed to
How the treatment affects the body If the drug or intervention has an effect
on the cancer Does not compare with other treatments

◦ From 100 to thousands of people◦ Equal chance to be assigned to one of two or
more groups (randomization)◦ Determines
How the new treatment compares with the current standard
Or how it compares with placebo

◦ From hundreds to thousands of people◦ Usually takes place after drug is approved to
provide additional information on the drug’s risks, benefits and optimal use
◦ Post marketing surveillance.

Equal chance to be assigned to one of two Equal chance to be assigned to one of two or more groupsor more groups One gets the most widely accepted One gets the most widely accepted
treatment (standard treatment)treatment (standard treatment) The other gets the new treatment being The other gets the new treatment being
tested, which researchers hope and tested, which researchers hope and have reason to believe will be better have reason to believe will be better than standard treatment than standard treatment
All groups are as alike as possible All groups are as alike as possible Provides the best way to prove the Provides the best way to prove the
effectiveness of a new agent or effectiveness of a new agent or interventionintervention

1
3
79
10
8
2 4
5
6
24
5 6
13
7
9 10
8 Control Group
Investigational group

Open Label clinical trials◦ The doctor and patient know which drug or
vaccine is being administered
Blinded clinical trial◦ Single Blind: the patient doesn’t know which
treatment he/she is getting
◦ Double Blind: neither doctor nor patient knows

The new treatment is tested against an inactive (or dummy) treatment that looks the same

A small study that helps develop a bigger study
A first foray (look) into a particular area Used to iron out possible difficulties, and
help with design of the bigger, more pivotal study.

◦Involve people who are sick ◦Test new treatments, new combinations
of drugs or new approaches to surgery or radiotherapy
◦Determine the most effective treatment for people who have cancer
◦Test safety and effectiveness of new agents or interventions in people with cancer

◦Evaluate the effectiveness of ways to reduce the risk of disease or prevent the recurrence of disease
◦Enroll healthy people at high risk for developing disease
◦Assess new means of detecting disease earlier in healthy people

Early-detection trials/screening trials◦ Test the best way to detect early disease ,
Pap smears, Mammograms Blood tests, X-rays
◦ Detect disease at an earlier stage, resulting in improved outcomes
Diagnostic trials◦ Develop better tools for classifying types and
phases of disease and managing patient care◦ Usually include people who have signs or
symptoms

Quality-of-life/supportive care studies ◦ Aim to improve comfort and quality of life for
patients and their families
Genetic trials◦ Determine how one’s genetic makeup can
influence detection, diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment
◦ Broaden understanding of causes of disease ◦ Develop targeted treatments based on the
genetics of a disease

Clinical research team check the health of the participant at the beginning of the trial, give specific instructions for participating in the trial, monitor the participant carefully during the trial, and stay in touch after the trial is completed.◦ Tests◦ Doctors visits◦ Frequent follow up

All clinical trials have guidelines about who All clinical trials have guidelines about who can participate. Exclusion / inclusion can participate. Exclusion / inclusion criteria help produce reliable results criteria help produce reliable results
Criteria based on factors such asCriteria based on factors such as Age / GenderAge / Gender Type and stage of diseaseType and stage of disease Previous treatmentPrevious treatment Medical conditionsMedical conditions

Physicians and other health professionals may:◦ Be unaware of appropriate trials◦ Be unwilling to lose control of patient’s care◦ Believe that standard therapy is best◦ Believe that clinical trials are more work◦ Have concerns about the patient’s care or how
the person will react to suggestion of clinical trial participation

Patients may:◦ Be unaware of clinical trials◦ Lack access to trials◦ Fear, distrust, or be suspicious of research◦ Have practical or personal obstacles◦ Be unwilling to go against their physicians’
wishes

At a minimum, the best standard treatment Early access to new treatments. If the new
treatment or intervention is proven to work, patients may be among the first to benefit
Participation in advancing medical knowledge. Patients have a chance to help others and improve cancer care
Active role in own health care The medical team conducting the trial will carefully
and regularly monitor the patient’s progress

◦ New treatments or interventions under study are not always better than, or even as good as, standard care
◦ Even if a new treatment has benefits, it may not work for every patient
◦ Unpleasant, serious or even life threatening side effects
◦ May require more time and attention than a non-protocol treatment

Ethical and legal codes that govern medical practice also apply to clinical trials
Informed consent Review boards
◦ Scientific review◦ Institutional review boards (IRBs)◦ Data safety and monitoring boards

Informed consent is a document designed to inform the patient of the purpose and design of a clinical study, possible side effects and benefits and if there are any other options. It should also include information on ◦ voluntary participation◦ Duration of trial ◦ Insurance and compensation◦ Name and phone number of contact person◦ Procedures◦ Individual rights and confidentiality

Scientific review◦ Panel of experts
Institutional review boards (IRBs) ◦ Qualified people to evaluate new and ongoing trials ◦ All institutions that conduct clinical trials must, by law, have a IRB
that approves the protocol Data and safety monitoring boards:
Ensure that risks are minimized Ensure data integrity Stop a trial if safety concerns arise or objectives
have been met

Yes, in general they are. We (the scientific community) strive to make
them so. There are unscrupulous people (and
companies) in any area Guidelines make it easier for us to check up on
ourselves!

Yes (usually) There are stringent guidelines in place Safety and toxicity are closely monitored Trials have built-in stopping rules Subjects are indemnified

The Declaration of Helsinki GCP guidelines Transparency and good communication Use of Institutional Ethics committees

Consider the question I want to answer Write a draft protocol Decide if it is a phase I, II, III or pilot study Write the Ethics Committee application Submit that Work out where funding will come from

Thank you