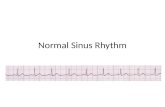
60-100 bpm Normal sinus rhythm : p-waves followed by a QRS complex, then a T-wave. In a normal HR,...
Transcript of 60-100 bpm Normal sinus rhythm : p-waves followed by a QRS complex, then a T-wave. In a normal HR,...

Heart RhythmsWikinursing2012

Normal sinus rhythm
60-100 bpm

characteristics
Normal sinus rhythm: p-waves followed by a QRS complex, then a T-wave.In a normal HR, sinus node creates an electrical impulse to right and left atrial muscles creating electrical impulses on the electrocardiogram (ECG) shown as the p-wave. An impulse travels through the atrioventicular node causing a slower rate. A pause (PR interval) is created before the ventricles are stimulated. Blood from the atria and into the ventricles and into the body. Ventricular contraction are represented as QRS waves. T-wave follows representing ventricles relaxing. Normal sinus rhythm indicates the rhythm of the heart, which can be up to 110-160 bpm for a newborn, 70-110 bpm for a child and 60-100 bpm for an adult.

Manifestations/treatment
o no problems typically associated with rhythm
o no treatment generally associated with this rhythm

Sinus bradycardia
Less than 60 bpm

characteristics
Rate: 60bpm, P-P interval, regular, R-R interval regular. P wave-positive (upright) in Lead II one P wave precedes each QRS complex. P waves look alike. PR interval 0.12 to 0.20 seconds and constant from beat to beat. QRS duration 0.10 seconds or less unless an intraventricular conduction delay exists

causes
•Heart tissue damage related to aging, heart disease or heart attack
Heart disorder present at birth (congenital heart defect) Infection of heart tissue (myocarditis) A complication of heart surgery Underactive thyroid gland (hypothyroidism) Imbalance of electrolytes, mineral-related substances
necessary for conducting electrical impulses Obstructive sleep apnea, the repeated disruption of
breathing during sleep Medications, including some drugs for other heart
rhythm disorders, high blood pressure and psycho

Sinus bradycardia Manifestations
•Sinus bradycardia is most often asymptomatic. However, symptoms may include the following:
◦Syncope ◦Dizziness ◦Lightheadedness ◦Chest pain ◦Shortness of breath ◦Exercise intolerance

Sinus Bradycardia Treatment
Only Treated if symptomatic Some of the different medications used in the
treatment of sinus bradycardia include: •Atropine •AtroPen •Atropine-Care •Isopto Atropine •Sal-Tropine •Dioptic's Atropine Solution •Minim's Atropine Solution •Tropyn Z

Sinus Tachycardia
More than 100 bpm

Handy tip!!!
With very fast heart rates the P waves may be hidden in the preceding T wave, producing a ‘camel hump’ appearance.

characteristics
Rate is 101 to 180 bpm, Rhythm P-P interval regular R-R interval regular, Pwave positive (upright) in lead II, one precedes each QRS complex. P waves look alike. PR interval 0.12-0.20 seconds, QRS duration 0.10 sec or less

Common causes
Exercise Pain, anxiety Hypoxia, hypercarbia Acidaemia Sepsis, pyrexia Pulmonary embolism Hyperthyroidism

manifestations
Usually asymptomatic, if symptoms are present they may include the following:
•A racing heart rate or palpitations •The feeling of the heart pounding in the chest. •Dizziness in some cases •Actual syncope (fainting) •Consistently fast heart rate (above 100 BPM) even at rest,
although some nights it seems to slow to around 80 BPM •Periodic chest pain, sometimes sharp, others constraining and
chest "pressure" •Out of breath most times •Increased fatigue •Intolerance to exercise or any type of physical activity, even
walking up a few stairs •Severe anxiety

treatment
beta blockers calcium channel blockers antiarrhythmic drugs.